Question
Using Figure 9.2, suppose P0 is $10 and P1 $11. Suppose a new firm with the same LRAC curve as the incumbent tries to break
Using Figure 9.2, suppose P0 is $10 and P1 $11. Suppose a new firm with the same LRAC curve as the incumbent tries to break into the market by selling 4,000 units of output. (Taylor & Greenlaw, 2014, p. 223).
Estimate from the graph what the new firm?s average cost of producing output would be.
If the incumbent continues to produce 6,000 units, how much output would be supplied to the market by the two firms?
Estimate what would happen to the market price as a result of the supply of both the incumbent firm and the new entrant.
Approximately how much profit would each firm earn? 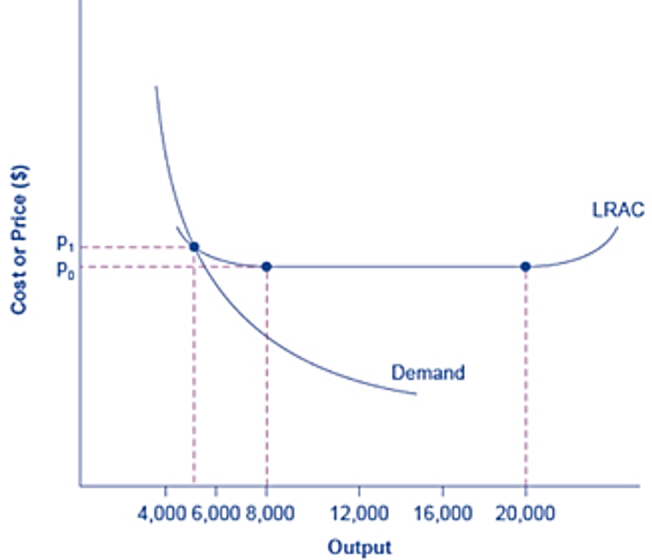
Figure 9.2 Economies of Scale and Natural Monopoly In this market, the demand curve intersects the long.run average cost (LRAC) curve at its downward-sloping part. A natural monopoly occurs when the quantity demanded is less than the minimum quantity it takes to be at the bottom of the long-run average cost curve.
Cost or Price ($) P Po 4,000 6,000 8,000 Demand 12,000 16,000 20,000 Output LRAC
Step by Step Solution
3.38 Rating (142 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
From the given figure it can be seen that the points P 0 and P 1 corresponds to the LRAC curves according to the output given on the horizontal axis For example output level 5000 units corresponds to ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


