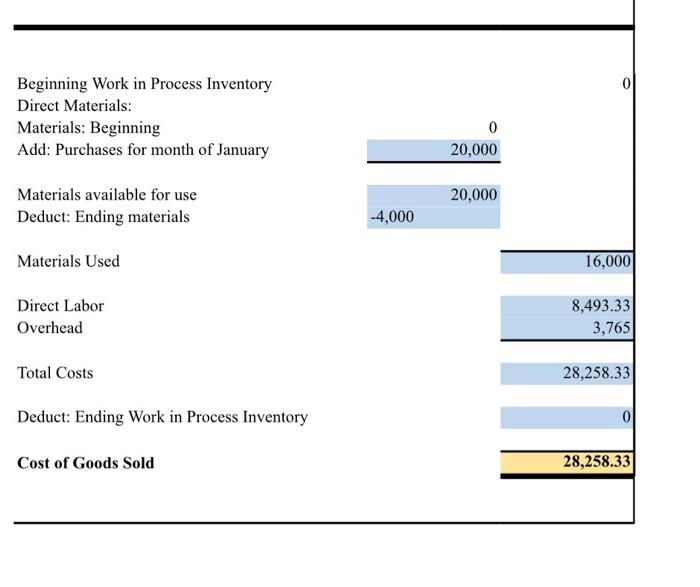
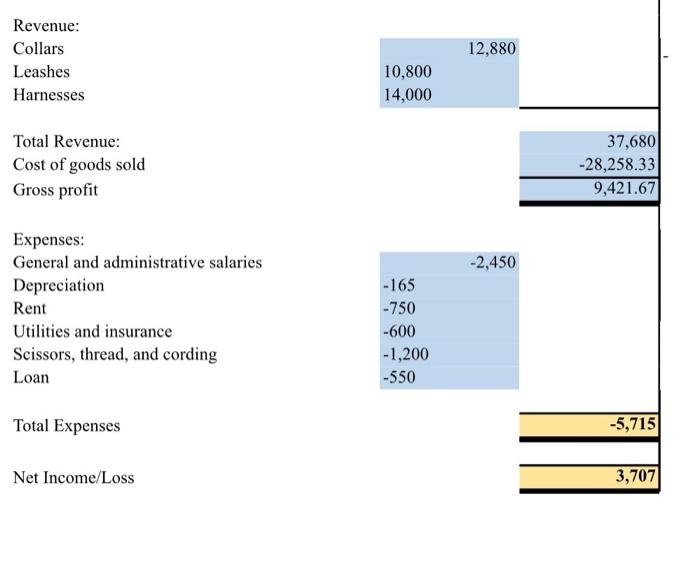
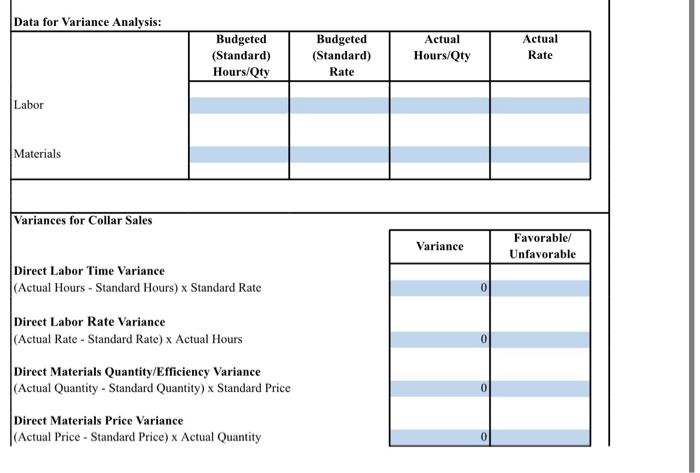
0 Beginning Work in Process Inventory Direct Materials: Materials: Beginning Add: Purchases for month of January 0 20,000 Materials available for use Deduct: Ending materials 20,000 -4,000 Materials Used 16,000 Direct Labor Overhead 8,493.33 3,765 Total Costs 28,258.33 Deduct: Ending Work in Process Inventory 0 Cost of Goods Sold 28,258.33 12,880 Revenue: Collars Leashes Harnesses 10,800 14,000 Total Revenue: Cost of goods sold Gross profit 37,680 -28,258.33 9,421.67 -2,450 Expenses: General and administrative salaries Depreciation Rent Utilities and insurance Scissors, thread, and cording Loan -165 -750 -600 -1,200 -550 Total Expenses -5,715 Net Income/Loss 3,707 Data for Variance Analysis: Budgeted (Standard) Hours/Qty Budgeted (Standard) Rate Actual Hours/Qty Actual Rate Labor Materials Variances for Collar Sales Variance Favorable/ Unfavorable Direct Labor Time Variance (Actual Hours - Standard Hours) x Standard Rate 0 Direct Labor Rate Variance (Actual Rate - Standard Rate) x Actual Hours Direct Materials Quantity/Efficiency Variance (Actual Quantity - Standard Quantity) x Standard Price Direct Materials Price Variance (Actual Price - Standard Price) Actual Quantity For your statement of cost of goods sold, use the following data regarding the actual costs incurred by the business over the past month: Materials purchased: S20,000 Consumed 80% of the purchased materials Direct labor: 88,493.33 Overhead costs: $3,765 Note: Assume that the beginning materials and ending work in process are zero for the month. Use the following revenue and cost information for the income statement. Note that the revenue you use will depend on the pricing level options you chose in Milestone Two. Also, assume that after accounting for weekends and other holidays, there were 20 business days in the first month of operation. For example, if you chose a sales price of S20 per collar, the actual number of collars sold in the month was 33 per day or 33 x 20 = 660 per month Price Established Sales Number of lems Sold per Day Collars $30 33 2x 52X 23 Leashes 28 $26 23 $30 18 Harnesses 525 530 22 535 The other costs incurred by the business include: General and administrative salaries Receptionist: S1.950 o Owner salary: $500 Depreciation: 165 Rent: $750 Utilities and insurance: 5600 Scissors, thread, and cording: $1,200 Loan repayment: $550 Variance At the end of the month, you find that the labor and materials spent on manufacturing collars was different from what you estimated: The collar maker had to work ninc hours a day instead of cight due to an increased demand for collars. . Because of the increased demand, the hourly rate you paid your employee for making the collars increased to $16.50. An increase in the cost of raw material led the direct material cost per collar to increase to SIO. . However, you more collars than you , number of collars sold in the month was 33 per day or 33 x 20 = 660 per month Number of Items Sold per Day 33 28 23 Established Sales Price Collars $20 $24 $28 Leashes $22 $26 $30 Harnesses $25 $30 $35 28 23 18 25 20 The other costs incurred by the business include: General and administrative salaries Receptionist: $1,950 Owner salary: $500 Depreciation: $165 Rent: $750 Utilities and insurance: $600 Scissors, thread, and cording: $1,200 Loan repayment: $550 Variance At the end of the month, you find that the labor and materials spent on manufacturing collars was different from what you estimated: The collar maker had to work nine hours a day instead of eight due to an increased demand for collars. Because of the increased demand, the hourly rate you paid your employee for making the collars increased to $16.50. An increase in the cost of raw material led the direct material cost per collar to increase to $10. . However, you also made and sold 60 more collars than you expected to sell in the month. You now need to determine the variance in the materials and labor cost from what you estimated in Milestone Two based on the market research data