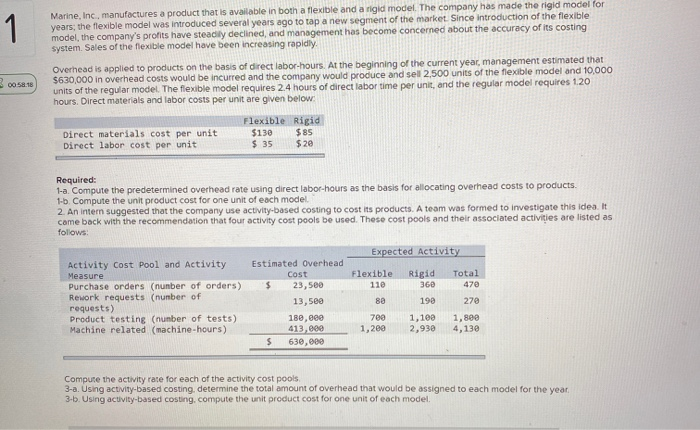
1 1 Marine, Inc., manufactures a product that is available in both a flexible and a rigid model. The company has made the rigid model for years, the flexible model was introduced several years ago to tap a new segment of the market. Since introduction of the flexible model, the company's profits have steadily declined, and management has become concerned about the accuracy of its costing system. Sales of the flexible model have been increasing rapidly. Overhead is applied to products on the basis of direct labor-hours. At the beginning of the current year, management estimated that $630,000 in overhead costs would be incurred and the company would produce and sel 2,500 units of the flexible model and 10,000 units of the regular model. The flexible model requires 2.4 hours of direct labor time per unit, and the regular model requires 120 hours. Direct materials and labor costs per unit are given below! 00 58.18 Direct materials cost per unit Direct labor cost per unit Flexible Rigid $130 $85 $ 35 $20 Required: 1-a. Compute the predetermined overhead rate using direct labor-hours as the basis for allocating overhead costs to products. 1-b. Compute the unit product cost for one unit of each model 2. An intern suggested that the company use activity-based costing to cost its products. A team was formed to investigate this idea. It came back with the recommendation that four activity cost pools be used. These cost pools and their associated activities are listed as follows: Expected Activity Flexible 110 Rigid 360 Total 470 Activity Cost Pool and Activity Measure Purchase orders (nunber of orders) Rework requests (number of requests) Product testing (nunber of tests) Machine related machine-hours) Estimated Overhead Cost $ 23,500 13,560 180,000 413,000 $ 630,000 80 190 270 700 1,200 1,100 2,930 1.800 4,130 Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools 3-a. Using activity-based costing, determine the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to each model for the year 3-6. Using activity-based costing, compute the unit product cost for one unit of each model. 1 1-b. Compute the unit product cost for one unit of each model. 2. An intern suggested that the company use activity-based costing to cost its products. A team was formed to investigate this idea. It came back with the recommendation that four activity cost pools be used. These cost pools and their associated activities are listed as follows: Expected Activity Flexible 110 Rigid 360 Total 470 S 0058-05 Activity Cost Pool and Activity Measure Purchase orders (number of orders) Rework requests (number of requests) Product testing (number of tests) Machine related (machine-hours) 80 190 Estimated Overhead Cost $ 23,500 13,500 180,000 413,000 $ 630,000 270 700 1,288 1,100 2,930 1,800 4,130 Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools. 3-a. Using activity-based costing, determine the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to each model for the year 3-6. Using activity-based costing, compute the unit product cost for one unit of each model. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req 1A Reg 1B Reg 2 Reg 3A Reg 30 Compute the predetermined overhead rate using direct labor-hours as the basis for allocating overhead costs to products. Predetermined overhead rate por DLH Re 11 Reg 18 > Product testing (number of tests) Machine related (machine-hours) 1,200 2,930 413,000 630,000 $ Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools. 3-a. Using activity-based costing, determine the total amount of overhead that would be assigne 3-b. Using activity-based costing, compute the unit product cost for one unit of each model. Complete this nuection by entering your answers in the tabs below. Reg 1B Req 1A Raq 1B Reg 2 Req 3A Req 3B Compute the unit product cost for one unit of each model. Unit Product Cost Flexible Rigid Purchase or 80 190 Rework requests (number of requests) Product testing (number of tests) Machine related (machine-hours) 13,500 180,000 413,000 630,000 700 1,200 1,100 2,930 $ Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools. 3-a. Using activity-based costing, determine the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to 3-b. Using activity-based costing, compute the unit product cost for one unit of each model. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Req 1A Req 1B Reg 2 Req 3A Reg 3B Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools. Activity Rate per order Activity Cost Pool Purchase orders Rework requests Product testing Machine-related per request per test per MH Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools. 3-a. Using activity-based costing, determine the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to each m 3-6. Using activity-based costing, compute the unit product cost for one unit of each model. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Reg 3B Reg 1A Reg 1B Reg 2 Req 3A Req 38 Using activity-based costing, determine the total amount of overhead that would be assigned to each model for the Total Amount of Overhead Flexible Rigid Prev 1 of 1 bento Next 413,00 requests Product testing number of Machine related machine-hours) $ 630,000 Compute the activity rate for each of the activity cost pools. 3-a. Using activity-based costing, determine the total amount of overhead that would be assig 3-6. Using activity-based costing, compute the unit product cost for one unit of each model. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Reg 1A Reg 1B Reg 2 Req 3A Req 3B Using activity-based costing, compute the unit product cost for one unit of each model. (Do not roun calculations and round your answers to 2 decimal places.) Unit Product Cost Flexible Rigid