Question: 1. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.3.P.007.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A crate of mass 9.8 kg is pulled up a rough incline with an initial
![1. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.3.P.007.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6676ccb3794aa_6836676ccb35bf39.jpg)
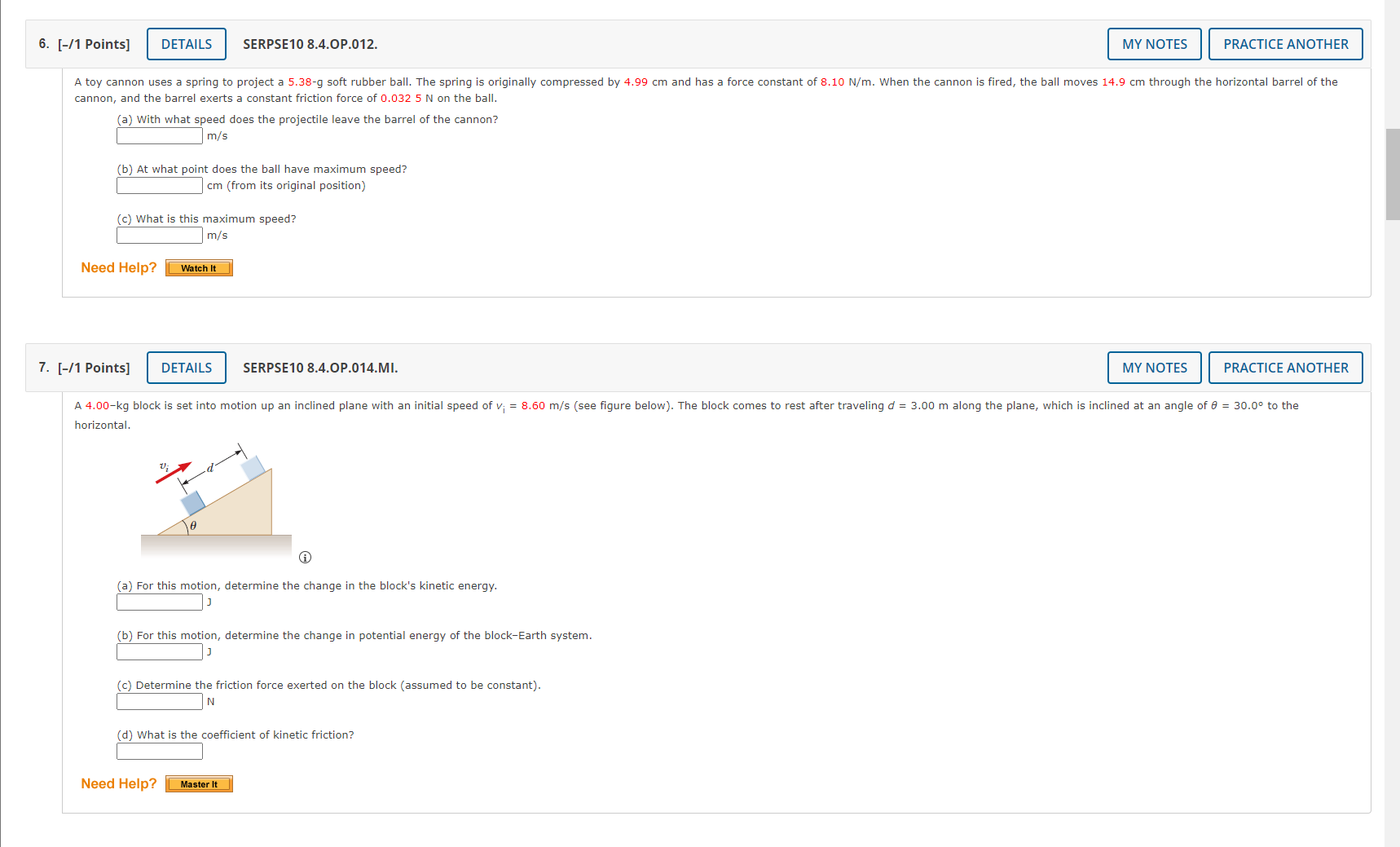
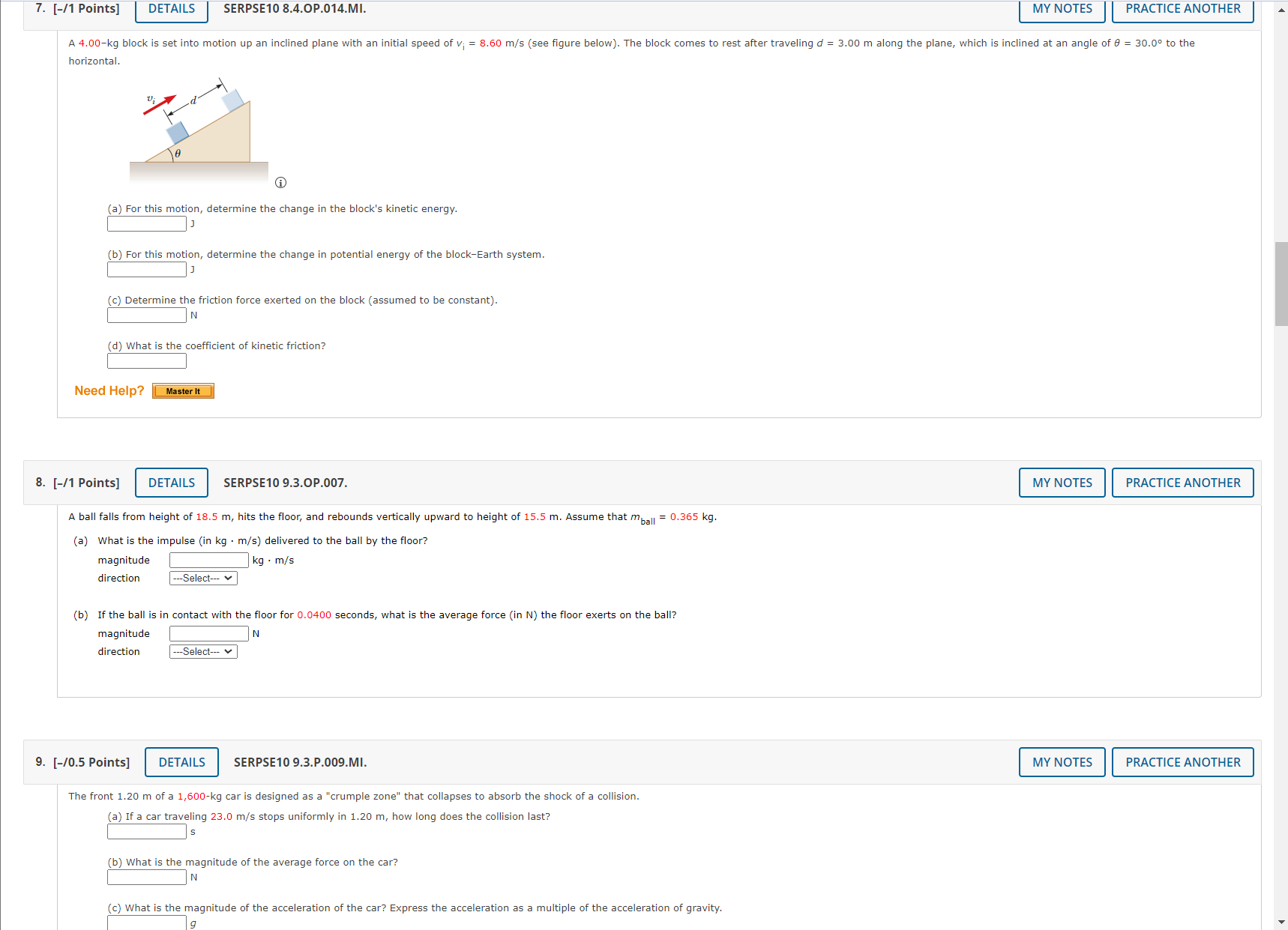
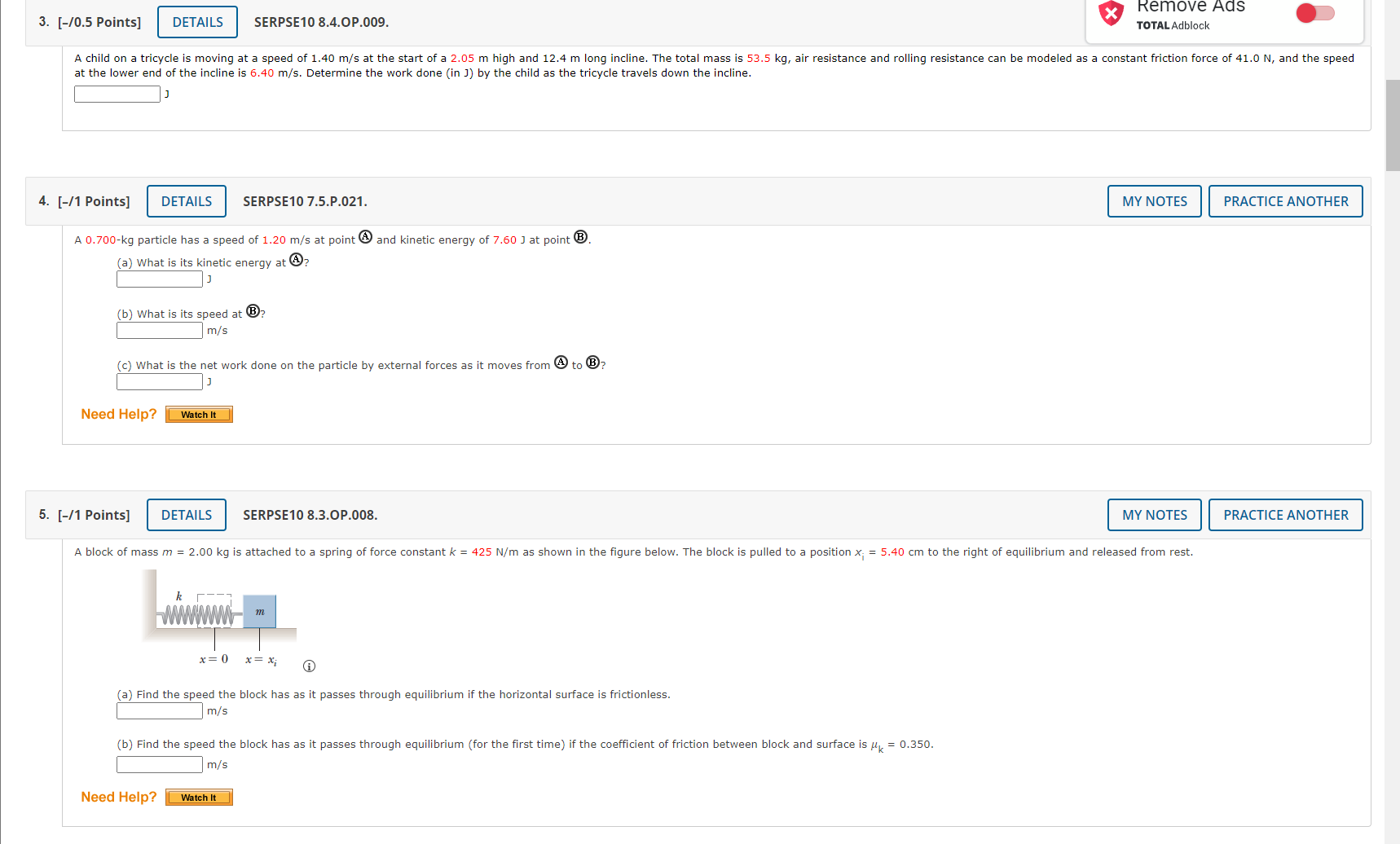
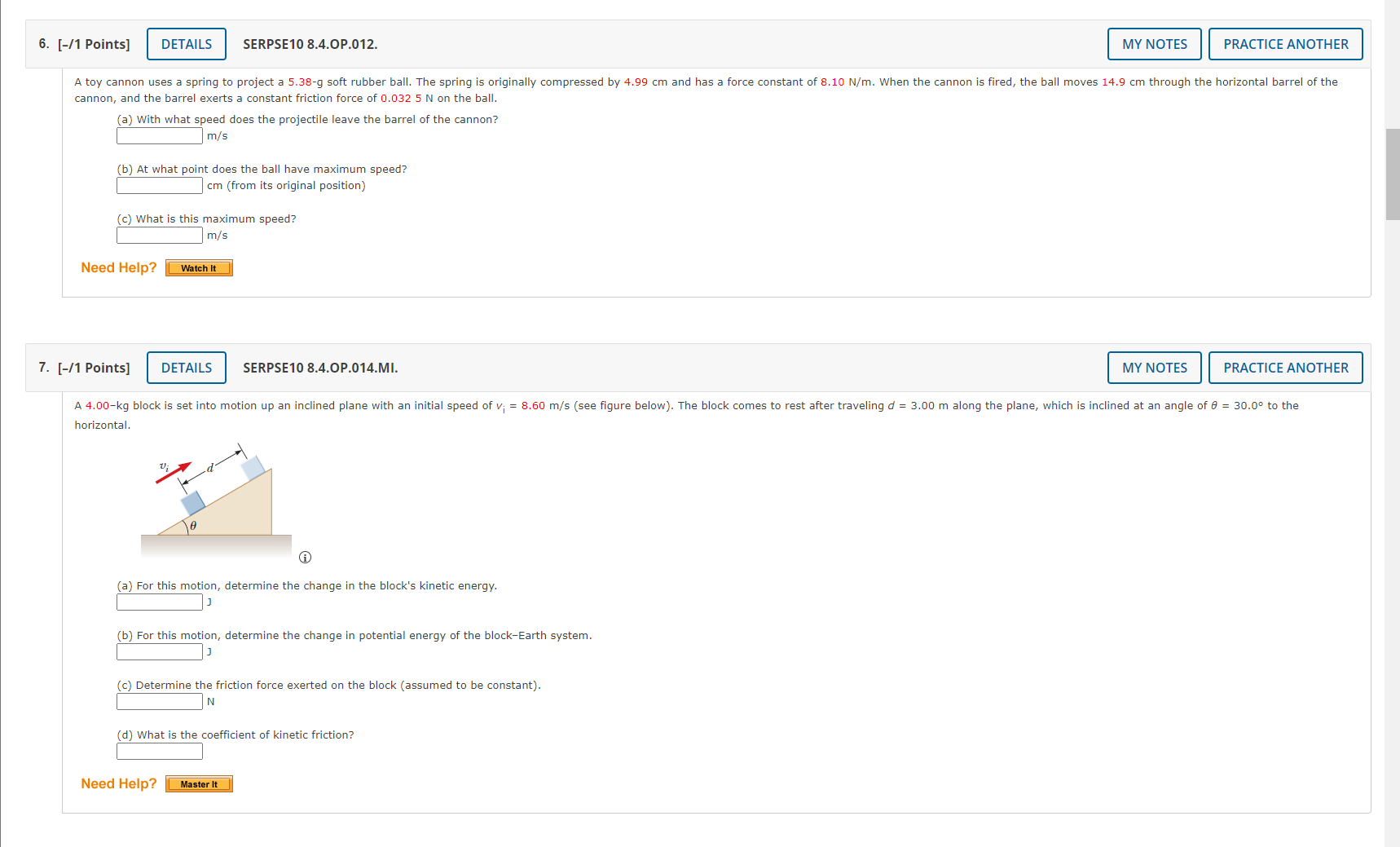
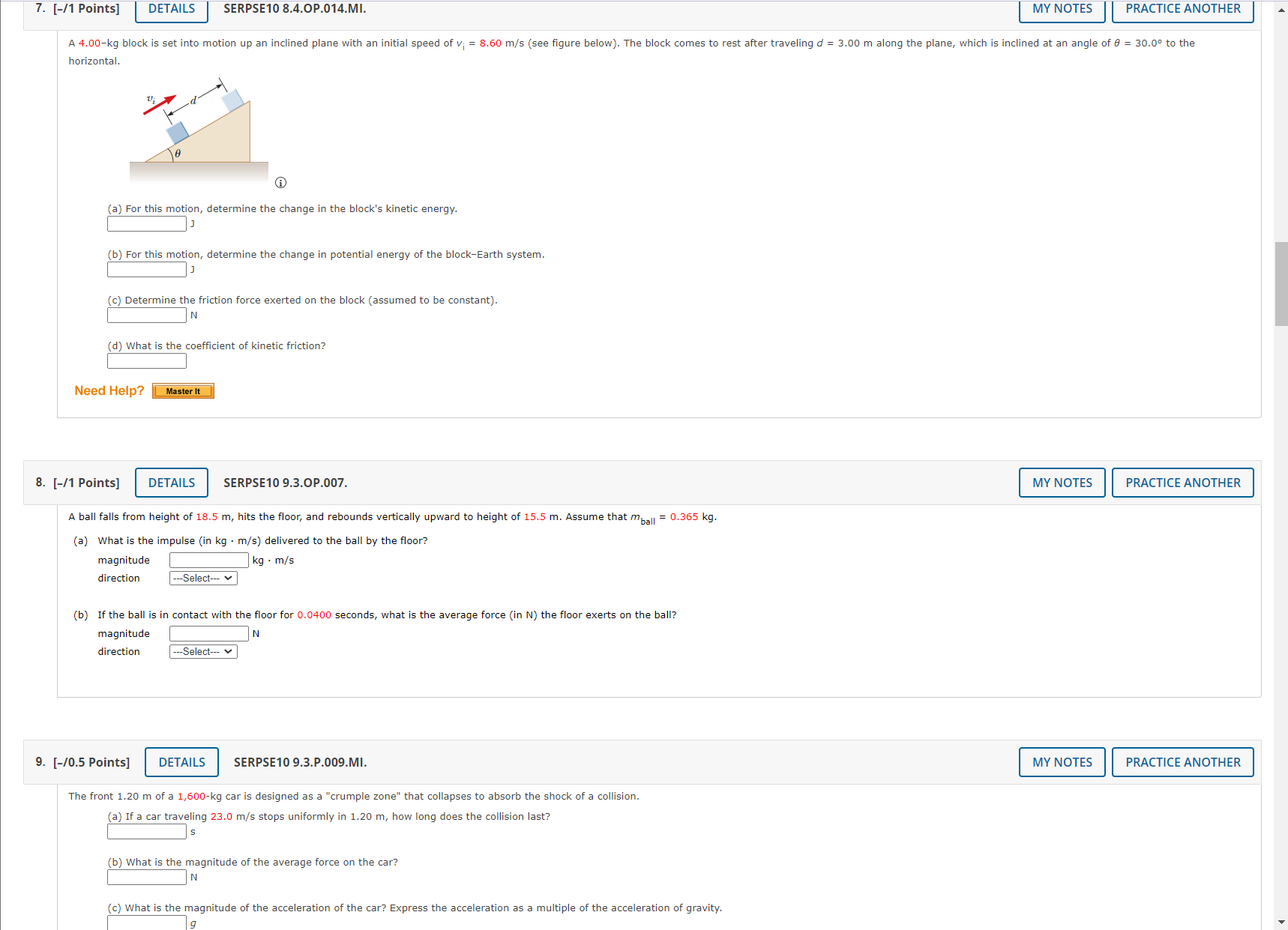
1. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.3.P.007.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A crate of mass 9.8 kg is pulled up a rough incline with an initial speed of 1.52 m/s. The pulling force is 102 N parallel to the incline, which makes an angle of 20.50 with the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.400, and the crate is pulled 5.02 m. (a) How much work is done by the gravitational force on the crate? (b) Determine the increase in internal energy of the crate-incline system owing to friction. (c) How much work is done by the 102-N force on the crate? (d) What is the change in kinetic energy of the crate? (e) What is the speed of the crate after being pulled 5.02 m? m/s Need Help? Master It Submit Answer 2. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.2.P.003. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A block of mass m = 5.10 kg is released from rest from point @ and slides on the frictionless track shown in the figure below. (Let h; = 5.50 m.) m 2 C na 3.20 m 2.00 m (a) Determine the block's speed at points B and C. VB= m/s V= m/s (b) Determine the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point @ to point @. Need Help? Watch ItRemove Ads 3. [-/0.5 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.4.OP.009. X TOTAL Adblock A child on a tricycle is moving at a speed of 1.40 m/s at the start of a 2.05 m high and 12.4 m long incline. The total mass is 53.5 kg, air resistance and rolling resistance can be modeled as a constant friction force of 41.0 N, and the speed at the lower end of the incline is 6.40 m/s. Determine the work done (in J) by the child as the tricycle travels down the incline. 4. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 7.5.P.021. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A 0.700-kg particle has a speed of 1.20 m/s at point @ and kinetic energy of 7.60 j at point B. (a) What is its kinetic energy at A? (b) What is its speed at B? m/s (c) What is the net work done on the particle by external forces as it moves from @ to B? Need Help? Watch It 5. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.3.OP.008. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A block of mass m = 2.00 kg is attached to a spring of force constant k = 425 N/m as shown in the figure below. The block is pulled to a position x; = 5.40 cm to the right of equilibrium and released from rest. m *=0 *=X; (a) Find the speed the block has as it passes through equilibrium if the horizontal surface is frictionless. m/s (b) Find the speed the block has as it passes through equilibrium (for the first time) if the coefficient of friction between block and surface is Uk = 0.350. m/s Need Help? Watch It6. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.4.OP.012. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A toy cannon uses a spring to project a 5.38-g soft rubber ball. The spring is originally compressed by 4.99 cm and has a force constant of 8.10 N/m. When the cannon is fired, the ball moves 14.9 cm through the horizontal barrel of the cannon, and the barrel exerts a constant friction force of 0.032 5 N on the ball. (a) With what speed does the projectile leave the barrel of the cannon? m/s (b) At what point does the ball have maximum speed? cm (from its original position) (c) What is this maximum speed? m/s Need Help? Watch It 7. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.4.OP.014.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A 4.00-kg block is set into motion up an inclined plane with an initial speed of v; = 8.60 m/s (see figure below). The block comes to rest after traveling d = 3.00 m along the plane, which is inclined at an angle of 0 = 30.0 to the horizontal. e (a) For this motion, determine the change in the block's kinetic energy. (b) For this motion, determine the change in potential energy of the block-Earth system. (c) Determine the friction force exerted on the block (assumed to be constant). IN (d) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction? Need Help? Master It7. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.4.OP.014.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A 4.00-kg block is set into motion up an inclined plane with an initial speed of v; = 8.60 m/s (see figure below). The block comes to rest after traveling d = 3.00 m along the plane, which is inclined at an angle of 0 = 30.0 to the horizontal. (a) For this motion, determine the change in the block's kinetic energy. (b) For this motion, determine the change in potential energy of the block-Earth system. (c) Determine the friction force exerted on the block (assumed to be constant). 'd) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction? Need Help? Master It 8. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 9.3.OP.007. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A ball falls from height of 18.5 m, hits the floor, and rebounds vertically upward to height of 15.5 m. Assume that mball = 0.365 kg. (a) What is the impulse (in kg . m/s) delivered to the ball by the floor? magnitude kg . m/s direction ---Select--- (b) If the ball is in contact with the floor for 0.0400 seconds, what is the average force (in N) the floor exerts on the ball? magnitude direction ---Select--- v 9. [-/0.5 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 9.3.P.009.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER The front 1.20 m of a 1,600-kg car is designed as a "crumple zone" that collapses to absorb the shock of a collision. (a) If a car traveling 23.0 m/s stops uniformly in 1.20 m, how long does the collision last? (b) What is the magnitude of the average force on the car? (c) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the car? Express the acceleration as a multiple of the acceleration of gravity.10. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 9.2.P.004. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A 59.0-kg boy and his 43.0-kg sister, both wearing roller blades, face each other at rest. The girl pushes the boy hard, sending him backward with a velocity 2.80 m/s toward the west. Ignore friction. (a) Describe the subsequent motion of the girl. O She will move east, directly away from her brother with a speed 5.24 m/s. O She will move west, in the same direction as her brother, with a speed 2.80 m/s. She will move east, directly away from her brother with a speed 3.84 m/s. O She will move east, directly away from her brother with a speed 1.4 m/s. (b) How much potential energy in the girl's body is converted into mechanical energy of the boy-girl system? (c) Is the momentum of the boy-girl system conserved in the pushing-apart process? O Yes O No (d) If so, explain how that is possible considering there are large forces acting. (If momentum is not conserved, enter "Momentum is not conserved.") This answer has not been graded yet. (e) If so, explain how that is possible considering there is no motion beforehand and plenty of motion afterward. (If momentum is not conserved, enter "Momentum is not conserved.") This answer has not been graded yet
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


