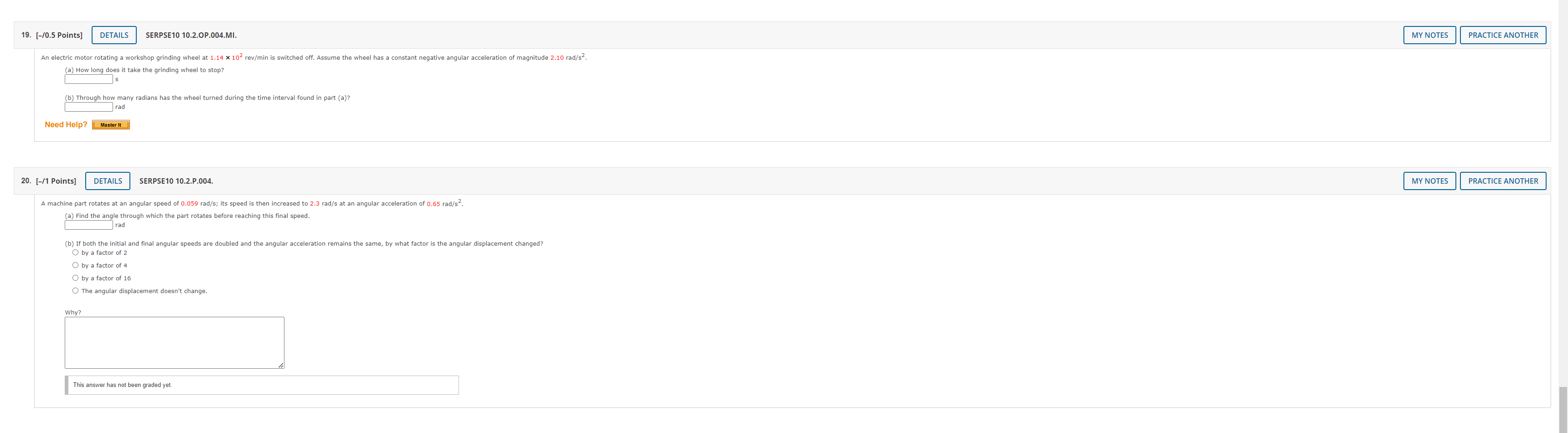
Question: 7. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.4.OP.014.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A 4.00-kg block is set into motion up an inclined plane with an initial speed
![7. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.4.OP.014.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6671a669af71c_2016671a66990c28.jpg)
![8. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 9.3.OP.007. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A ball](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/6671a66c9030e_2046671a66c71569.jpg)
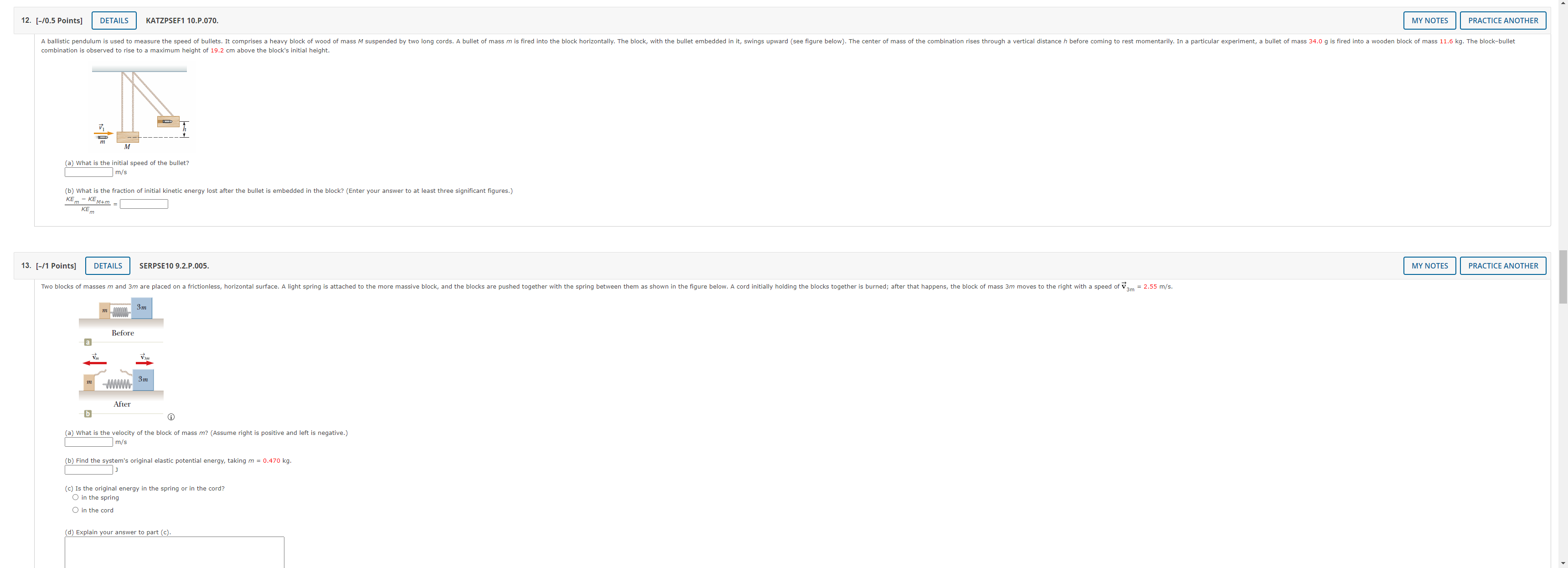
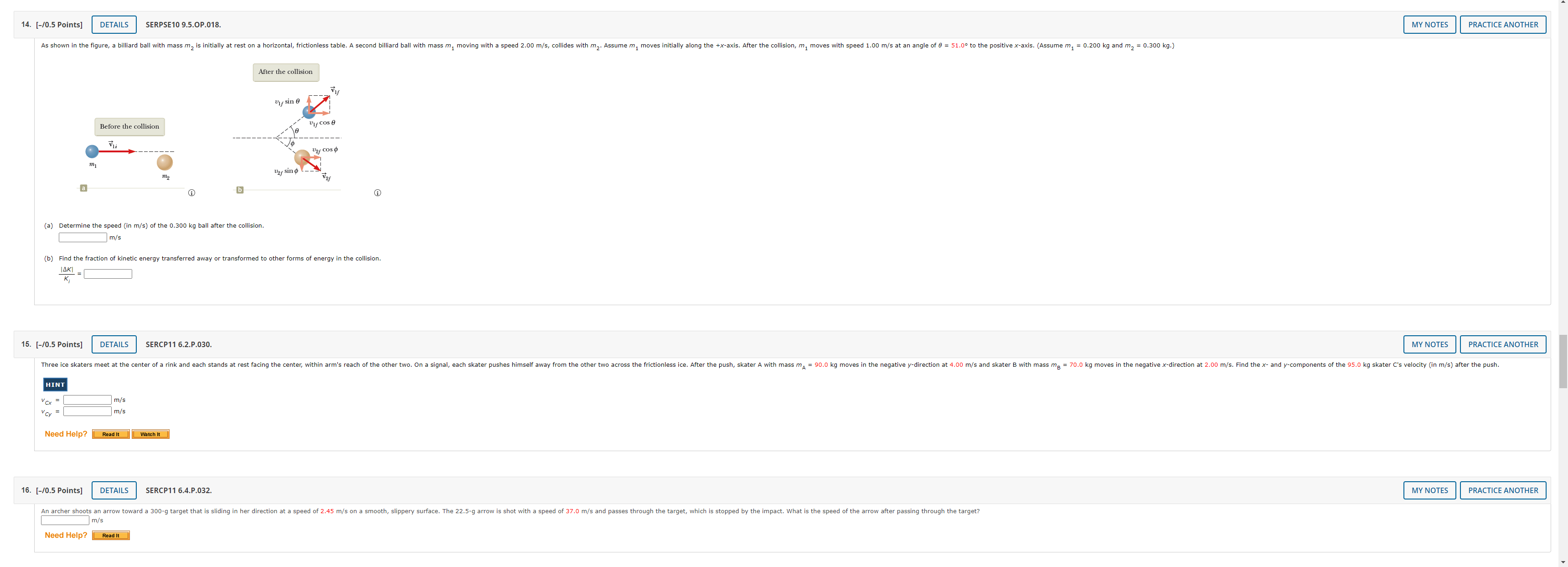
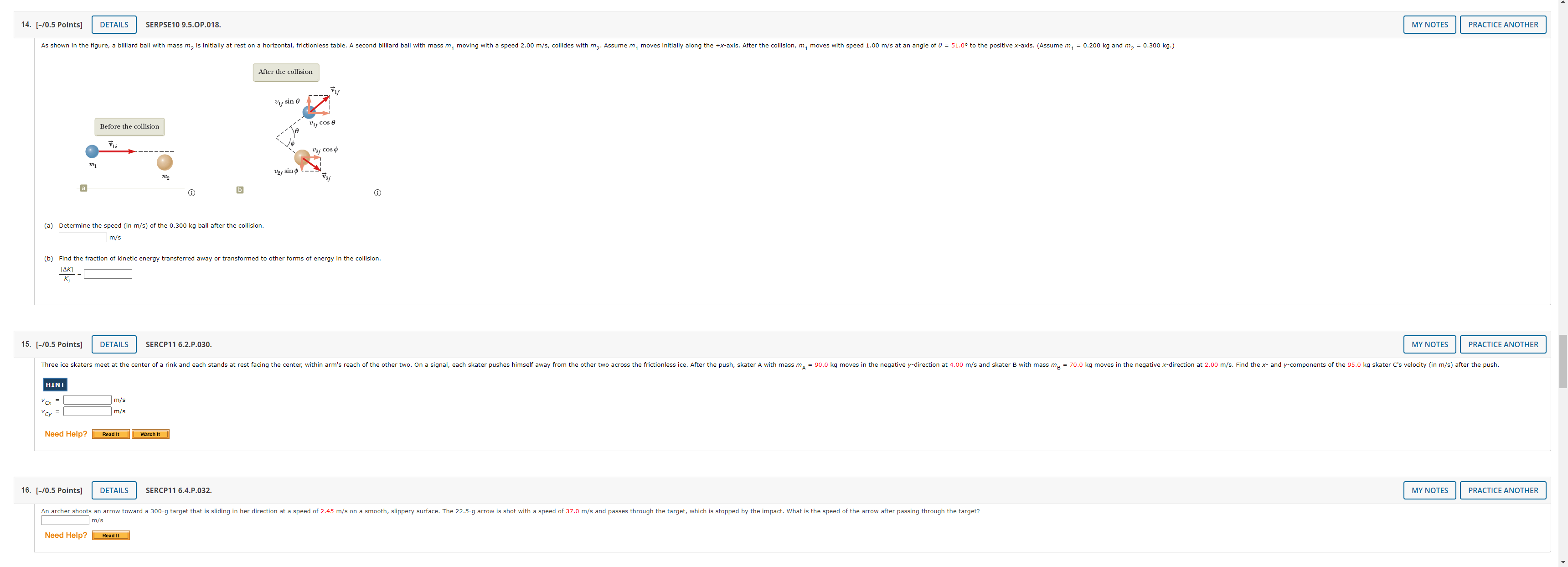
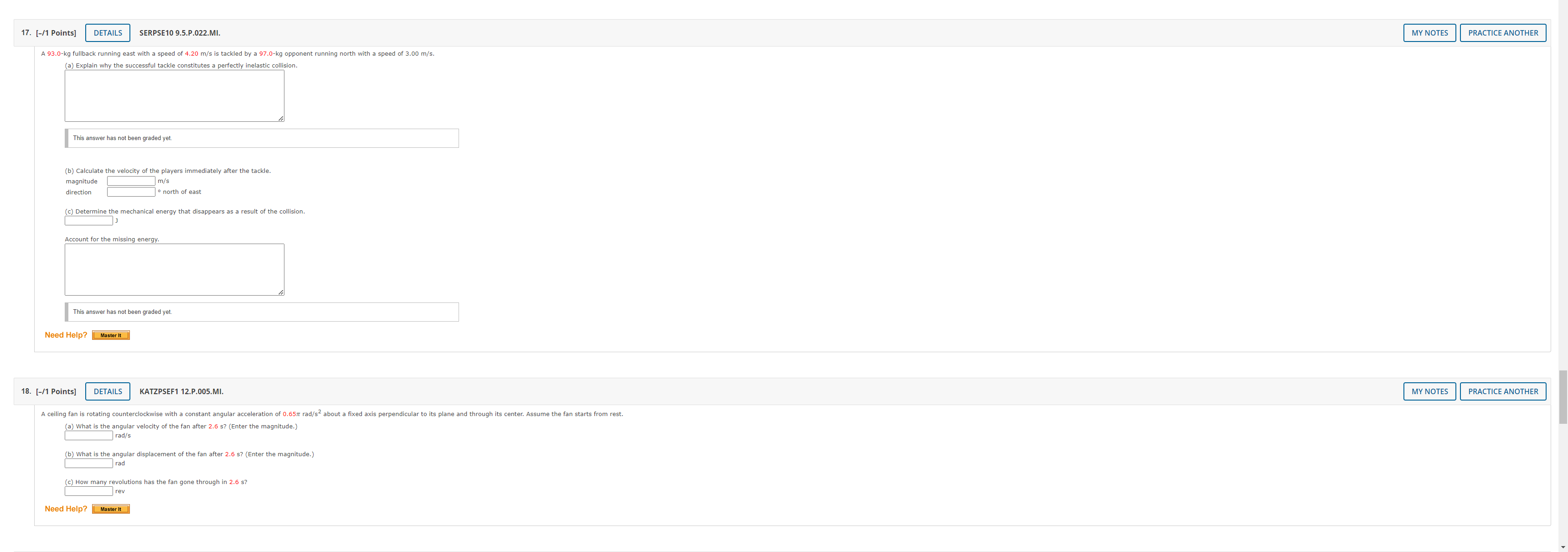
7. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 8.4.OP.014.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A 4.00-kg block is set into motion up an inclined plane with an initial speed of v; = 8.60 m horizontal. (a) For this motion, determine the change in the block's kinetic energy. b) For this motion, determine the change in potential energy of the block-Earth system. (c) Determine the friction force exerted on the block (assumed to be constant). N (d) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction? Need Help? Master It 8. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 9.3.OP.007. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A ball falls from height of 18.5 m, hits the floor, and rebounds vertically upward to height of 15.5 m. Assume that mball = 0.365 kg. (a) What is the impulse (in kg . m/s) delivered to the ball by the floor? magnitude kg . m/s direction -Select-.. v (b) If the ball is in contact with the floor for 0.0400 seconds, what is the average force (in N) the floor exerts on the ball? magnitude direction -Select-- 9. [-/0.5 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 9.3.P.009.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER The front 1.20 m of a 1,600-kg car is designed as a "crumple zone" that collapses to absorb the shock of a collision. (a) If a car traveling 23.0 m/s stops uniformly in 1.20 m, how long does the collision last? S (b) what is the magnitude of the average force on the car? c) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the car? Express the acceleration as a multiple of the acceleration of gravity. g10. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 9.2.P.004. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A 59.0-kg boy and his 43.0-kg sister, both wearing roller blades, face each other at rest. The girl pushes the boy hard, sen the west. Ignore friction. (a) Describe the subsequent motion of the girl. O She will move east, directly away from her brother with a speed 5.24 m/s. She will move west, in the same r brother, with a speed 2.80 m/s. She will move east, directly away from her brother with a speed 3.84 m/s. She will move east, directly away from her er with a speed 1.4 m/s b) How much potential energy in the girl's body is converted into mechanical energy of the boy-girl system? c) Is the momentum of the boy-girl system conserved in the pushing-apart process? O Yes NO (d) If so, explain how that is possib This answer has not been graded yet. (e) If so, explain how that is possible considering there is n conserved.") This answer has not been graded yet. 11. [-/0.5 Points] DETAILS KATZPSEF1 10.P.066. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A parcel moving in a horizontal direction with speed vo = 13 m/s breaks into two fragments of weights 1.1 N and 1.8 N, respectively. The speed of the larger piece remains horizontal immediately after the separation and increases to V1. = 27 m/s. Find the necessary speed and direction of the smaller piece immediately after the separation. (Assume the initial direction of the parcel is positive. Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) m/s12. [-/0.5 Points] DETAILS KATZPSEF1 10.P.070. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A ballistic pendulum is used to measure the speed of bullets. It comprises a heavy block of wood of mass M suspended by two long cords. A bullet of mass m is fired into the block horizontally. The block, with the bullet embedded in it, swings upward (see figure below). The center of mass of the combination rises through a vertical distance h before coming to rest momentarily. In a particular experiment, a bullet of mass 34.0 g is fired into a wooden block of mass 11.6 kg. The block-bullet combination is observed to rise to a maximum height of 19.2 cm above the block's initial height. (a) What is the initial speed of the bullet? m/s (b) what is the fraction of initial kinetic energy lost after the bullet is embedded in the block? (Enter your answer to at least three significant figures.) KE m - KEM+m = KE 13. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 9.2.P.005. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER Two blocks of masses m and 3m are placed on a frictionless, horizontal surface. A light spring is attached to the mo h the spring between them as shown in the figure below. A cord initially holding the blocks together is burned; after that happens, the block of mass 3m moves to the right with a speed of V 3m = 2.55 m/s. 3m Before 3m WWWW After a) What is the velocity of the block of mass m? (Assume right is positive and left is negative.) m/s (b) Find the system's original elastic potential energy, taking m = 0.470 kg. c) Is the original energy in the spring or in the cord? O in the spring O in the cord d) Explain your answer to part (c).14. [-/0.5 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 9.5.OP.018. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER As shown in the figure, a billiard ball with mass my is initially at rest on a horizontal, frictionless table. A second billiard ball with mass m, moving with a speed 2.00 m/s, collides with my. Assume m, moves initially along the +x-axis. After the collision, m, moves with speed 1.00 m/s at an angle of 8 = 51.0 to the positive x-axis. (Assume m, = 0.200 kg and m2 = 0.300 kg.) After the collision Uf sin e Before the collision Uif Cos e Vli 2/ COS by sind_ _ b i (a) Determine the speed (in m/s) of the 0.300 kg ball after the collision. m/ (b) Find the fraction of kinetic energy transferred away or transformed to other forms of energy in the collision. 14KI 15. [-/0.5 Points] DETAILS SERCP11 6.2.P.030. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER Three ice skaters meet at the center of a rink and each stands at rest facing the center, within arm's reach of the other two. On a signal, each skater pushes himself away from the other two across the frictionless ice. After the push, skater A with mass ma = 90.0 kg moves in the negative y-direction at 4.00 m/s and skater B with mass mg = 70.0 kg moves in the negative x-dir ection at 2.00 m/s. Find the x- and y-components of the 95.0 kg skater C's velocity (in m/s) after the push. HINT m/s m/s Need Help? Read It Watch It 16. [-/0.5 Points] DETAILS SERCP11 6.4.P.032 MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER An archer shoots an arrow toward a 300-g target that is sliding in her direction at a speed of 2.45 m/s on a smooth, slippery surface. The 22.5-g arrow is shot with a speed of 37.0 m/s and passes through the target, which is stopped by the impact. What is the speed of the arrow after passing through the target? m/s Need Help? Read It17. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 9.5.P.022.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A 93.0-kg fullback running east with a speed of 4.20 m/s is tackled by a 97.0-kg opponent running north with a speed of 3.00 m/s. (a) Explain why the successful tackle constitutes a perfectly inelastic collision. This answer has not been graded yet. b) Calculate the velocity of the players immediately after the tackle. magnitude m/s direction . north of east (c) Determine the mechanical energy that disappears as a result of the collision. Account for the missing energy. This answer has not been graded yet. Need Help? Master It 18. [-/1 Points] DETAILS KATZPSEF1 12.P.005.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A ceiling fan is rotating counterclockwise with a constant angular acceleration of 0.651 rad/s2 about a fixed axis perpendi d through its center. Assume the fan starts from rest. (a) What is the angular velocity of the fan after 2.6 s? (Enter the magnitude.) rad/s b) What is the angular displacem nt of the fan after 2.6 s? (Enter the magnitude.) rad c) How many revolutions has the fan gone through in 2.6 s? rev Need Help? Master It19. [-/0.5 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 10.2.OP.004.MI. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER An electric motor rotating a workshop grinding wheel at 1.14 x 102 rev/min is switched off. Assume the wheel has a constant negative angular acceleration of magnitude 2.10 rad/s2 (a) How long does it take the grinding wheel to stop? b) Through how many radians has the wheel turned during the time interval found in part (a)? Need Help? Master It 20. [-/1 Points] DETAILS SERPSE10 10.2.P.004. MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER A machine part rotates at an angular speed of 0.059 rad/s; its speed is then increased to 2.3 rad/s at an angular acceleration of 0.65 rad/s2. (a) Find the angle through which the part rotates before reaching this final speed. rad (b) If both the initial and final angular speeds are doubled and the angular acceleration remains the same, by what factor is the angular displacement changed? O by a factor of 2 O by a factor of 4 by a factor of 16 O The angular displacement doesn't change. Why? This answer has not been graded yet
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


