Question: Let G be a context-free grammar on alphabet = a, +, and the} following production rules: (a) (5 points) Specify the parse tree and
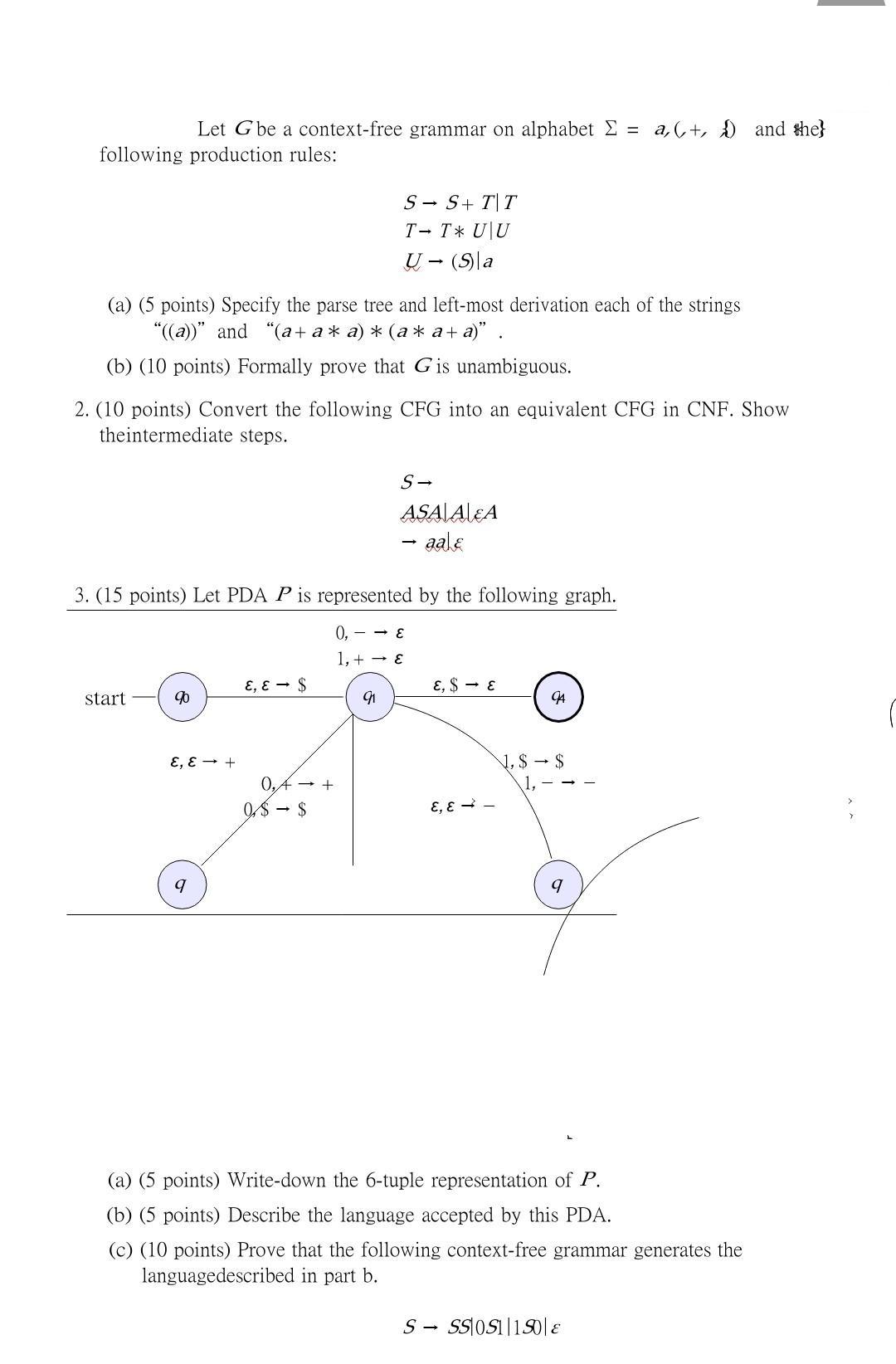
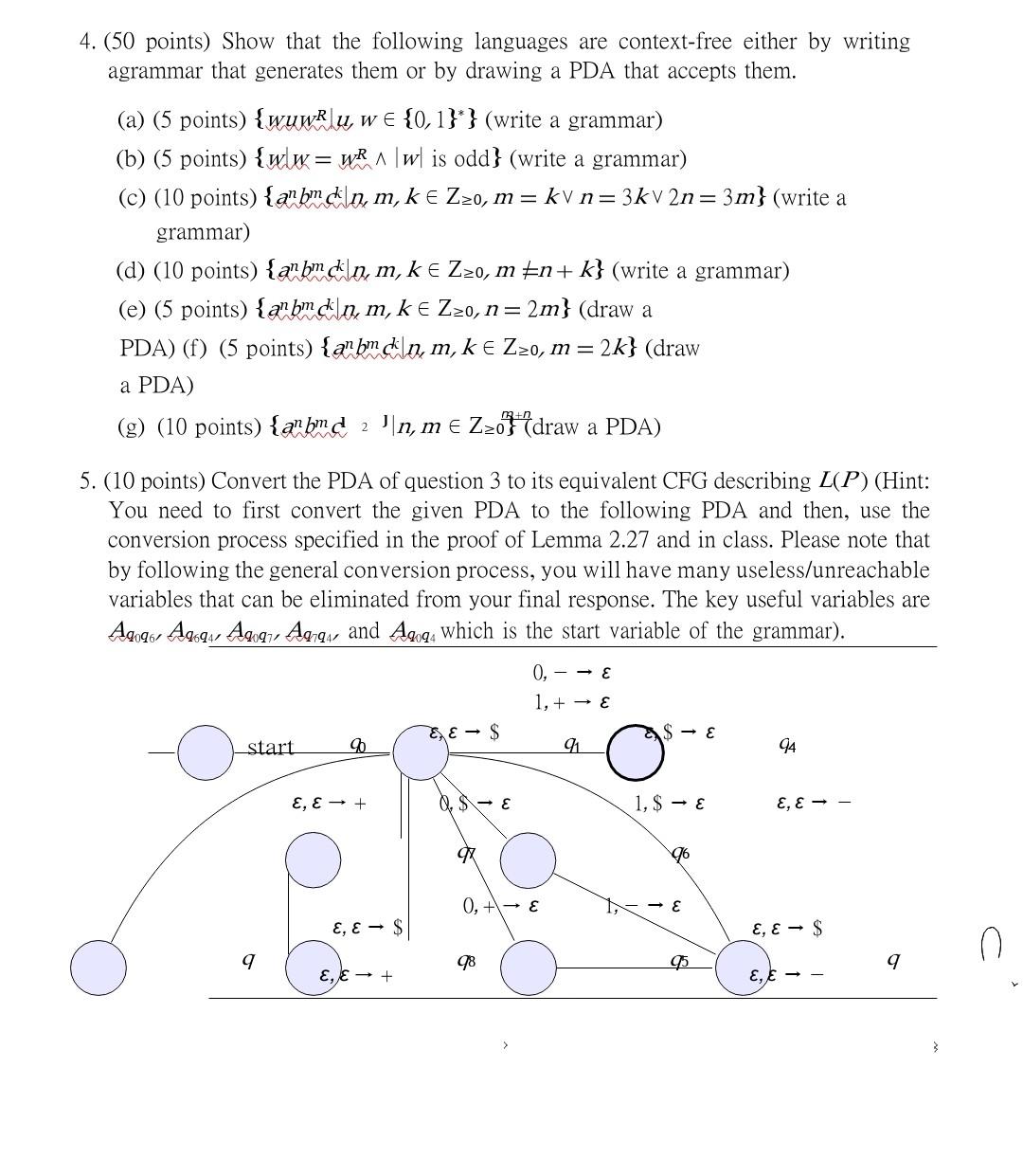
Let G be a context-free grammar on alphabet = a, +, and the} following production rules: (a) (5 points) Specify the parse tree and left-most derivation each of the strings "((a))" and "(a+a* a) * (a* a+a). (b) (10 points) Formally prove that G is unambiguous. 2. (10 points) Convert the following CFG into an equivalent CFG in CNF. Show theintermediate steps. start 3. (15 points) Let PDA P is represented by the following graph. 0,- E 1, + E 90 E, E + q SS+ TT T- T * U\U U (S) a E, E$ 0,4 + 0$- $ 91 S- ASA ALEA aale E, $ E E, E- 94 1,$- $ 1,- 9 (a) (5 points) Write-down the 6-tuple representation of P. (b) (5 points) Describe the language accepted by this PDA. (c) (10 points) Prove that the following context-free grammar generates the languagedescribed in part b. S SS 0S1|150| E 4. (50 points) Show that the following languages are context-free either by writing agrammar that generates them or by drawing a PDA that accepts them. (a) (5 points) {wuwu, w = {0, 1}} (write a grammar) (b) (5 points) {ww = wRA |w| is odd} (write a grammar) (c) (10 points) {n bm dn, m, k Zzo, m = kv n = 3kv 2n = 3m} (write a grammar) (d) (10 points) {anbm din, m, k = Zo, mn+ k} (write a grammar) (e) (5 points) {n bmcn, m, k = Zzo, n=2m} (draw a PDA) (f) (5 points) {m dn, m, k Zzo, m = 2k} (draw a PDA) (g) (10 points) {anbmd 2n, me Zzo (draw a PDA) 5. (10 points) Convert the PDA of question 3 to its equivalent CFG describing L(P) (Hint: You need to first convert the given PDA to the following PDA and then, use the conversion process specified in the proof of Lemma 2.27 and in class. Please note that by following the general conversion process, you will have many useless/unreachable variables that can be eliminated from your final response. The key useful variables are A9096 A9694, A9097, A4, and A4 which is the start variable of the grammar). start 9 % E, E + E, ES E, E+ EE $ $- E 97 0,- E 1, + E 0, + E 98 91 SE 1, $ E 96 94 E, E- E, E$ E, E- 9 0 Let G be a context-free grammar on alphabet = a, +, and the} following production rules: (a) (5 points) Specify the parse tree and left-most derivation each of the strings "((a))" and "(a+a* a) * (a* a+a). (b) (10 points) Formally prove that G is unambiguous. 2. (10 points) Convert the following CFG into an equivalent CFG in CNF. Show theintermediate steps. start 3. (15 points) Let PDA P is represented by the following graph. 0,- E 1, + E 90 E, E + q SS+ TT T- T* UU U (S) a E, E$ 0,4 + 0$ - $ 91 S- ASA ALEA aale E, $ E E, E- 94 1,$- $ 1,- 9 (a) (5 points) Write-down the 6-tuple representation of P. (b) (5 points) Describe the language accepted by this PDA. (c) (10 points) Prove that the following context-free grammar generates the languagedescribed in part b. S SS0S1|150| E 4. (50 points) Show that the following languages are context-free either by writing agrammar that generates them or by drawing a PDA that accepts them. (a) (5 points) {wuwu, w = {0, 1}} (write a grammar) (b) (5 points) {ww = wRA |w| is odd} (write a grammar) (c) (10 points) {@nbm dn, m, k = Zzo, m = kv n = 3kv 2n= 3m} (write a grammar) (d) (10 points) {anbm d , m, k = Z0, mn+ k} (write a grammar) (e) (5 points) {n bmd , m, k = Zzo, n = 2m} (draw a PDA) (f) (5 points) {amdn, m, k = Zo, m = 2k} (draw a PDA) (g) (10 points) {anbmd 2n, me Zzo (draw a PDA) 5. (10 points) Convert the PDA of question 3 to its equivalent CFG describing L(P) (Hint: You need to first convert the given PDA to the following PDA and then, use the conversion process specified in the proof of Lemma 2.27 and in class. Please note that by following the general conversion process, you will have many useless/unreachable variables that can be eliminated from your final response. The key useful variables are A9096 A9694, A9097, A9, and A4 which is the start variable of the grammar). start 9 % E, E + E, ES E, E+ EE $ $- E 97 0,- E 1, + E 0, + E 98 91 SE 1, $ E 96 94 E, E- E, E$ E, E- 9 0
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


