
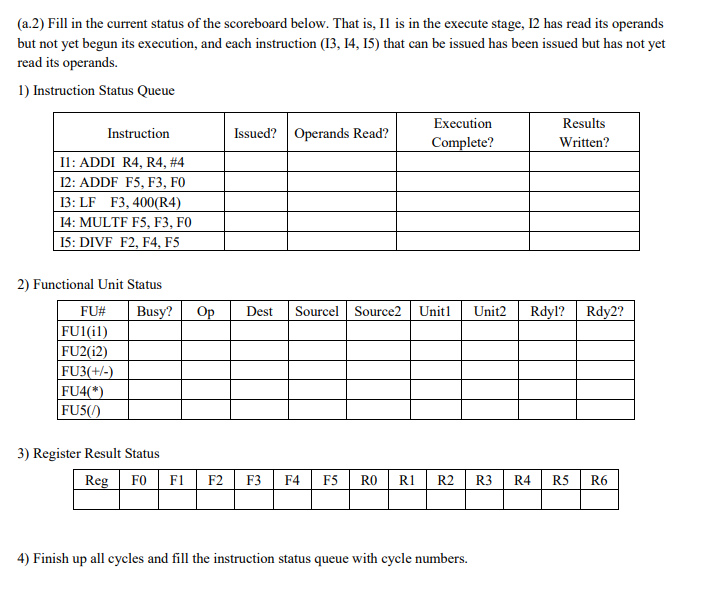
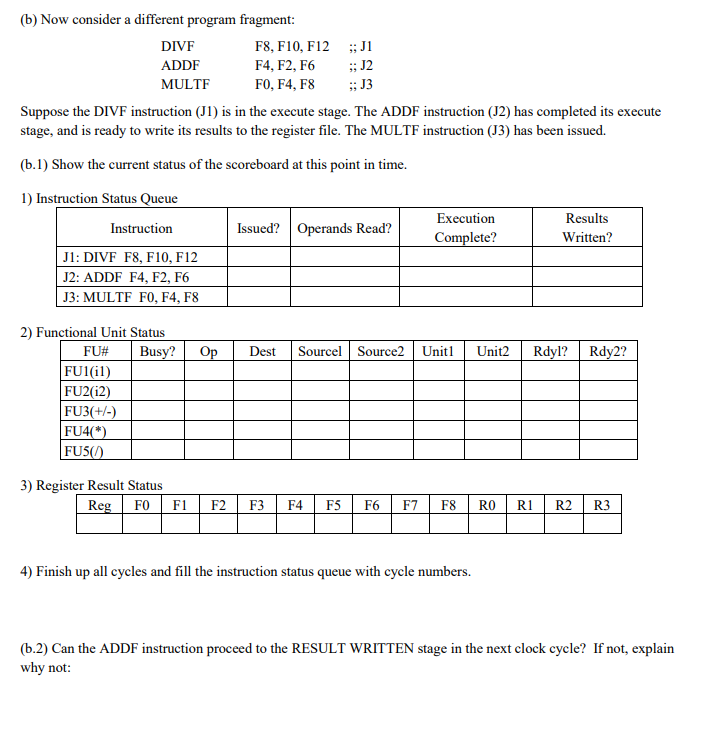
1. (20 pts) Suppose we are using scoreboarding to dynamically schedule code. We have five functional units: 2 ALU's for integer operations including loads and stores for both integer as well as floating point values), 1 floating point addition and subtraction unit, 1 FP multiplication unit, and 1 FP division unit. The execution stage latencies for the various functional units are shown below. Consider the following program: Function units cycles instructions instruction type instruction no. 11 12 FUI (ALU integer) FU2 (ALU integer) FU3 (FP add/subtract) FU4 (FP multiplication) FU5 (FP division) 13 ADDI R4, R4, #4 ADDF F5, F3, FO LF F3, 400(R4) MULTF F5, F3, FO DIVF F2, F4, F5 Integer Float Integer Float Float 15 | Suppose that the first instruction (11) is currently in the execute stage. The second instruction (12) has issued but its operands have not yet been read. Assume that at the start of this code fragment, no functional unit is computing values targeted for FO and F3 (so 12's operands are ready). (a.1) For each of the remaining instructions (13, 14, 15), determine whether the instruction can be issued. If it cannot be issued, explain why not. Can 13, "LF F3, 400(R4)", be issued? YES_NO__ If not, why not? NO Can 14, "MULTF F5, F3, FO", be issued? YES If not, why not? NO Can 15, "DIVF F2, F4, F5", be issued? YES If not, why not? (a.2) Fill in the current status of the scoreboard below. That is, Il is in the execute stage, 12 has read its operands but not yet begun its execution, and each instruction (13, 14, 15) that can be issued has been issued but has not yet read its operands. 1) Instruction Status Queue Instruction Issued? Operands Read? Execution Complete? Results Written? 11: ADDI R4, R4, #4 12: ADDF F5, F3, FO 13: LF F3, 400(R4) 14: MULTF F5, F3, FO 15: DIVF F2, F4, F5 2) Functional Unit Status Busy? Op Dest Sourcel Source2 Unit1 Unit2 Rdyl? Rdy2? FU# FU1(il) FU2(12) FU3(+/-) FU4(*) FU5(0) 3) Register Result Status Reg F0 F1 F2 F3 F4F5 RO R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 4) Finish up all cycles and fill the instruction status queue with cycle numbers. (b) Now consider a different program fragment: DIVF F8, F10, F12 ADDF F4, F2, F6 MULTF FO, F4, F8 ; J1 ;; J2 ;; J3 Suppose the DIVF instruction (11) is in the execute stage. The ADDF instruction (J2) has completed its execute stage, and is ready to write its results to the register file. The MULTF instruction (33) has been issued. (5.1) Show the current status of the scoreboard at this point in time. 1) Instruction Status Queue Instruction Issued? Operands Read? Execution Complete? Results Written? J1: DIVF F8, F10, F12 J2: ADDF F4, F2, F6 J3: MULTF FO, F4, F8 Op Dest Sourcel Source2 Unit1 Unit2 Rdyl? Rdy2? 2) Functional Unit Status FU# Busy? FU1(il) FU2(12) FU3(+/-) FU4(*) FU5/) 3) Register Result Status RegFO F1 F2 F3 F4F5F6F7F8 RO R1 R2 R3 4) Finish up all cycles and fill the instruction status queue with cycle numbers. (1.2) Can the ADDF instruction proceed to the RESULT WRITTEN stage in the next clock cycle? If not, explain why not: 1. (20 pts) Suppose we are using scoreboarding to dynamically schedule code. We have five functional units: 2 ALU's for integer operations including loads and stores for both integer as well as floating point values), 1 floating point addition and subtraction unit, 1 FP multiplication unit, and 1 FP division unit. The execution stage latencies for the various functional units are shown below. Consider the following program: Function units cycles instructions instruction type instruction no. 11 12 FUI (ALU integer) FU2 (ALU integer) FU3 (FP add/subtract) FU4 (FP multiplication) FU5 (FP division) 13 ADDI R4, R4, #4 ADDF F5, F3, FO LF F3, 400(R4) MULTF F5, F3, FO DIVF F2, F4, F5 Integer Float Integer Float Float 15 | Suppose that the first instruction (11) is currently in the execute stage. The second instruction (12) has issued but its operands have not yet been read. Assume that at the start of this code fragment, no functional unit is computing values targeted for FO and F3 (so 12's operands are ready). (a.1) For each of the remaining instructions (13, 14, 15), determine whether the instruction can be issued. If it cannot be issued, explain why not. Can 13, "LF F3, 400(R4)", be issued? YES_NO__ If not, why not? NO Can 14, "MULTF F5, F3, FO", be issued? YES If not, why not? NO Can 15, "DIVF F2, F4, F5", be issued? YES If not, why not? (a.2) Fill in the current status of the scoreboard below. That is, Il is in the execute stage, 12 has read its operands but not yet begun its execution, and each instruction (13, 14, 15) that can be issued has been issued but has not yet read its operands. 1) Instruction Status Queue Instruction Issued? Operands Read? Execution Complete? Results Written? 11: ADDI R4, R4, #4 12: ADDF F5, F3, FO 13: LF F3, 400(R4) 14: MULTF F5, F3, FO 15: DIVF F2, F4, F5 2) Functional Unit Status Busy? Op Dest Sourcel Source2 Unit1 Unit2 Rdyl? Rdy2? FU# FU1(il) FU2(12) FU3(+/-) FU4(*) FU5(0) 3) Register Result Status Reg F0 F1 F2 F3 F4F5 RO R1 R2 R3 R4 R5 R6 4) Finish up all cycles and fill the instruction status queue with cycle numbers. (b) Now consider a different program fragment: DIVF F8, F10, F12 ADDF F4, F2, F6 MULTF FO, F4, F8 ; J1 ;; J2 ;; J3 Suppose the DIVF instruction (11) is in the execute stage. The ADDF instruction (J2) has completed its execute stage, and is ready to write its results to the register file. The MULTF instruction (33) has been issued. (5.1) Show the current status of the scoreboard at this point in time. 1) Instruction Status Queue Instruction Issued? Operands Read? Execution Complete? Results Written? J1: DIVF F8, F10, F12 J2: ADDF F4, F2, F6 J3: MULTF FO, F4, F8 Op Dest Sourcel Source2 Unit1 Unit2 Rdyl? Rdy2? 2) Functional Unit Status FU# Busy? FU1(il) FU2(12) FU3(+/-) FU4(*) FU5/) 3) Register Result Status RegFO F1 F2 F3 F4F5F6F7F8 RO R1 R2 R3 4) Finish up all cycles and fill the instruction status queue with cycle numbers. (1.2) Can the ADDF instruction proceed to the RESULT WRITTEN stage in the next clock cycle? If not, explain why not









