
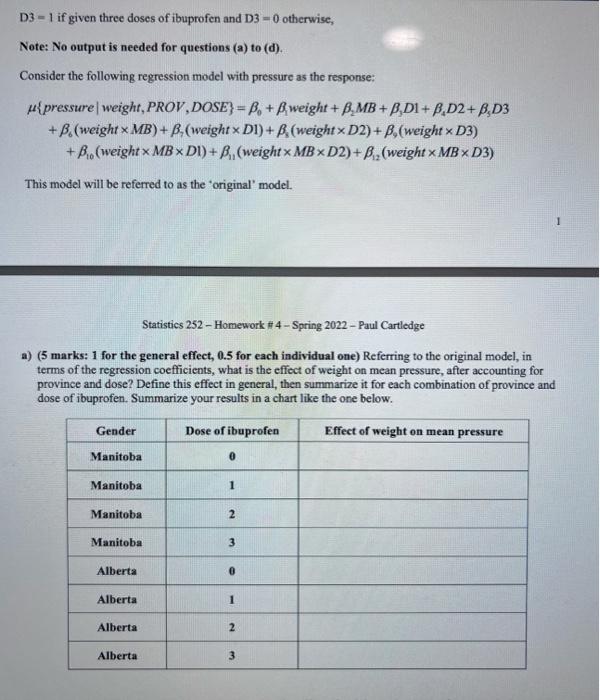
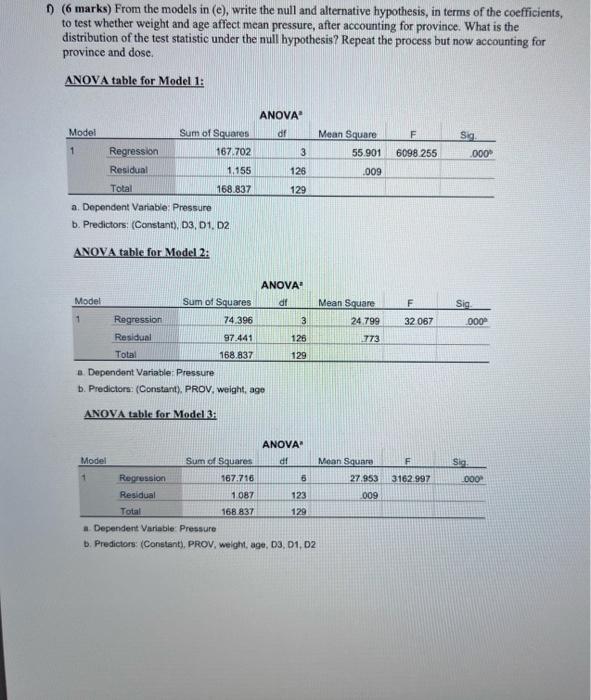
1) (29 marks total) Persistent patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a medical condition that affects many very low-birth weight infants. Infants with PDA have an increased risk of serious ailment such as severe heart failure. The Apgar score is used to assess the health of an infant one minute after birth. The one-minute Apgar score measures how well the newbom tolerated the birthing process. A score of seven to 10 is normal and indicates the newborn is in good condition. Any score less than seven indicates that the baby needs assistance such as helping the infant breathe. Airway pressure is a measure of respiratory status, usually measured seven days after birth. Some researchers determined that early ibuprofen administration might prevent PDA in preterm neonates. A sample of 130 such infants was randomly divided into 4 groups. 32 were treated with one dose of ibuprofen, 33 with two doses, 33 with three doses, and 32 with a saline solution. The following is the description of variables under study. Variable Description of Variables Province Dose Birthplace of infant (Manitoba OR Alberta), Dose of ibuprofen (an integer from 0 to 3), Birth weight (in pounds), Weight Age Gestational age (in weeks), Score One-minute Apgar score, Pressure Airway pressure (in cm HO) seven days after birth. Define variables PROV and DOSE using the following indicator variables: MB = 1 for an infant from Manitoba and MB=0 for an infant from Alberta, D1 = 1 if given one dose of ibuprofen and D1 = 0 otherwise, D2= 1 if given two doses of ibuprofen and D2 = 0 otherwise, D3= 1 if given three doses of ibuprofen and D3 = 0 otherwise, Note: No output is needed for questions (a) to (d). Consider the following regression model with pressure as the response: upressure weight, PROV, DOSE} = B + Bweight + B.MB+ B,DI+ B,D2 + B,D3 + B.(weight x MB) + B, (weight x D1) + B, (weight xD2) + B, (weight xD3) +B(weightx MBXx D1) + B, (weight x MBxD2) + B, (weightx MBxD3) This model will be referred to as the 'original' model. D3-1 if given three doses of ibuprofen and D3-0 otherwise, Note: No output is needed for questions (a) to (d). Consider the following regression model with pressure as the response: upressure weight, PROV, DOSE} = B+Bweight + BMB + B,D1+ B,D2+ B,D3 + B. (weightx MB) + B,(weight x D1) + B, (weight x D2) + B,(weight x D3) +B (weightx MB x D1) + B, (weightx MBxD2) + B (weight x MB x D3) This model will be referred to as the 'original' model. Statistics 252-Homework #4 - Spring 2022-Paul Cartledge a) (5 marks: 1 for the general effect, 0.5 for each individual one) Referring to the original model, in terms of the regression coefficients, what is the effect of weight on mean pressure, after accounting for province and dose? Define this effect in general, then summarize it for each combination of province and dose of ibuprofen. Summarize your results in a chart like the one below. Gender Dose of ibuprofen Effect of weight on mean pressure Manitoba 0 Manitoba 1 Manitoba 2 Manitoba 3 Alberta 0 Alberta 1 Alberta 2 Alberta 3 Dose of ibuprofen 0 1 2 Gender Effect of weight on mean pressure Manitoba Manitoba Manitoba Manitoba 3 Alberta 0 Alberta 1 Alberta 2 Alberta b) (2 marks) Modify the original model to test that the effect of weight on the mean of pressure is the same for Manitobans and Albertans with the same dose of ibuprofen; otherwise, the effect of weight on the mean of pressure is possibly different for Manitobans and Albertans without having the same dose of ibuprofen. Just state the hypotheses in terms of constraints. You do not have to rewrite the model. c) (3 marks) Referring to the original model, write the null and alternative hypothesis, in terms of the coefficients, to test whether the effect of weight is the same for all doses of ibuprofen for Albertans. What is the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis? d) (3 marks) Referring to the original model, write the null and alternative hypothesis, in terms of the coefficients, to test whether weight has any effect on mean pressure. What is the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis? (10 marks) Consider the following three models: Model 1: {pressure | DOSE} = B+BD1+ B.D2+ B,D3 Model 2: {pressure weight, age, PROV} = B+Bweight+Page + BMB, upressure DOSE, weight, age, PROV} = B+BDI+BD2+ B,D3 Model 3: + Bweight + Bage+B MB Carry out the most appropriate test to determine if weight, age, or province affect mean pressure, after accounting for dose. f) (6 marks) From the models in (e), write the null and alternative hypothesis, in terms of the coefficients, to test whether weight and age affect mean pressure, after accounting for province. What is the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis? Repeat the process but now accounting for province and dose. ANOVA table for Model 1: ANOVA Model df Mean Square F Sig 1 Regression 3 6098.255 55.901 .009 Residual Total a. Dependent Variable: Pressure b. Predictors: (Constant), D3, D1, D2 ANOVA table for Model 2: Model Sum of Squares Mean Square 1 74.396 24.799 Regression Residual Total 97.441 773 168.837 a Dependent Variable: Pressure b. Predictors: (Constant), PROV, weight, age ANOVA table for Model 3: Model Sum of Squares Regression 167.716 Residual 1.087 123 Total 168.837 129 a. Dependent Variable Pressure b. Predictors: (Constant), PROV, weight, age, D3, D1, D2 Sum of Squares 167.702 1.155 168.837 126 129 ANOVA df 3 126 129 ANOVA df 6 Mean Square 27.953 009 F 32 067 F 3162.997 .000 Sig 000 Sig 000 1) (29 marks total) Persistent patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a medical condition that affects many very low-birth weight infants. Infants with PDA have an increased risk of serious ailment such as severe heart failure. The Apgar score is used to assess the health of an infant one minute after birth. The one-minute Apgar score measures how well the newbom tolerated the birthing process. A score of seven to 10 is normal and indicates the newborn is in good condition. Any score less than seven indicates that the baby needs assistance such as helping the infant breathe. Airway pressure is a measure of respiratory status, usually measured seven days after birth. Some researchers determined that early ibuprofen administration might prevent PDA in preterm neonates. A sample of 130 such infants was randomly divided into 4 groups. 32 were treated with one dose of ibuprofen, 33 with two doses, 33 with three doses, and 32 with a saline solution. The following is the description of variables under study. Variable Description of Variables Province Dose Birthplace of infant (Manitoba OR Alberta), Dose of ibuprofen (an integer from 0 to 3), Birth weight (in pounds), Weight Age Gestational age (in weeks), Score One-minute Apgar score, Pressure Airway pressure (in cm HO) seven days after birth. Define variables PROV and DOSE using the following indicator variables: MB = 1 for an infant from Manitoba and MB=0 for an infant from Alberta, D1 = 1 if given one dose of ibuprofen and D1 = 0 otherwise, D2= 1 if given two doses of ibuprofen and D2 = 0 otherwise, D3= 1 if given three doses of ibuprofen and D3 = 0 otherwise, Note: No output is needed for questions (a) to (d). Consider the following regression model with pressure as the response: upressure weight, PROV, DOSE} = B + Bweight + B.MB+ B,DI+ B,D2 + B,D3 + B.(weight x MB) + B, (weight x D1) + B, (weight xD2) + B, (weight xD3) +B(weightx MBXx D1) + B, (weight x MBxD2) + B, (weightx MBxD3) This model will be referred to as the 'original' model. D3-1 if given three doses of ibuprofen and D3-0 otherwise, Note: No output is needed for questions (a) to (d). Consider the following regression model with pressure as the response: upressure weight, PROV, DOSE} = B+Bweight + BMB + B,D1+ B,D2+ B,D3 + B. (weightx MB) + B,(weight x D1) + B, (weight x D2) + B,(weight x D3) +B (weightx MB x D1) + B, (weightx MBxD2) + B (weight x MB x D3) This model will be referred to as the 'original' model. Statistics 252-Homework #4 - Spring 2022-Paul Cartledge a) (5 marks: 1 for the general effect, 0.5 for each individual one) Referring to the original model, in terms of the regression coefficients, what is the effect of weight on mean pressure, after accounting for province and dose? Define this effect in general, then summarize it for each combination of province and dose of ibuprofen. Summarize your results in a chart like the one below. Gender Dose of ibuprofen Effect of weight on mean pressure Manitoba 0 Manitoba 1 Manitoba 2 Manitoba 3 Alberta 0 Alberta 1 Alberta 2 Alberta 3 Dose of ibuprofen 0 1 2 Gender Effect of weight on mean pressure Manitoba Manitoba Manitoba Manitoba 3 Alberta 0 Alberta 1 Alberta 2 Alberta b) (2 marks) Modify the original model to test that the effect of weight on the mean of pressure is the same for Manitobans and Albertans with the same dose of ibuprofen; otherwise, the effect of weight on the mean of pressure is possibly different for Manitobans and Albertans without having the same dose of ibuprofen. Just state the hypotheses in terms of constraints. You do not have to rewrite the model. c) (3 marks) Referring to the original model, write the null and alternative hypothesis, in terms of the coefficients, to test whether the effect of weight is the same for all doses of ibuprofen for Albertans. What is the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis? d) (3 marks) Referring to the original model, write the null and alternative hypothesis, in terms of the coefficients, to test whether weight has any effect on mean pressure. What is the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis? (10 marks) Consider the following three models: Model 1: {pressure | DOSE} = B+BD1+ B.D2+ B,D3 Model 2: {pressure weight, age, PROV} = B+Bweight+Page + BMB, upressure DOSE, weight, age, PROV} = B+BDI+BD2+ B,D3 Model 3: + Bweight + Bage+B MB Carry out the most appropriate test to determine if weight, age, or province affect mean pressure, after accounting for dose. f) (6 marks) From the models in (e), write the null and alternative hypothesis, in terms of the coefficients, to test whether weight and age affect mean pressure, after accounting for province. What is the distribution of the test statistic under the null hypothesis? Repeat the process but now accounting for province and dose. ANOVA table for Model 1: ANOVA Model df Mean Square F Sig 1 Regression 3 6098.255 55.901 .009 Residual Total a. Dependent Variable: Pressure b. Predictors: (Constant), D3, D1, D2 ANOVA table for Model 2: Model Sum of Squares Mean Square 1 74.396 24.799 Regression Residual Total 97.441 773 168.837 a Dependent Variable: Pressure b. Predictors: (Constant), PROV, weight, age ANOVA table for Model 3: Model Sum of Squares Regression 167.716 Residual 1.087 123 Total 168.837 129 a. Dependent Variable Pressure b. Predictors: (Constant), PROV, weight, age, D3, D1, D2 Sum of Squares 167.702 1.155 168.837 126 129 ANOVA df 3 126 129 ANOVA df 6 Mean Square 27.953 009 F 32 067 F 3162.997 .000 Sig 000 Sig 000










