Question: ( 1 5 points ) Consider the following Markov Decision Process. Unlike most MDP models where actions have many potential outcomes of varying probability, assume
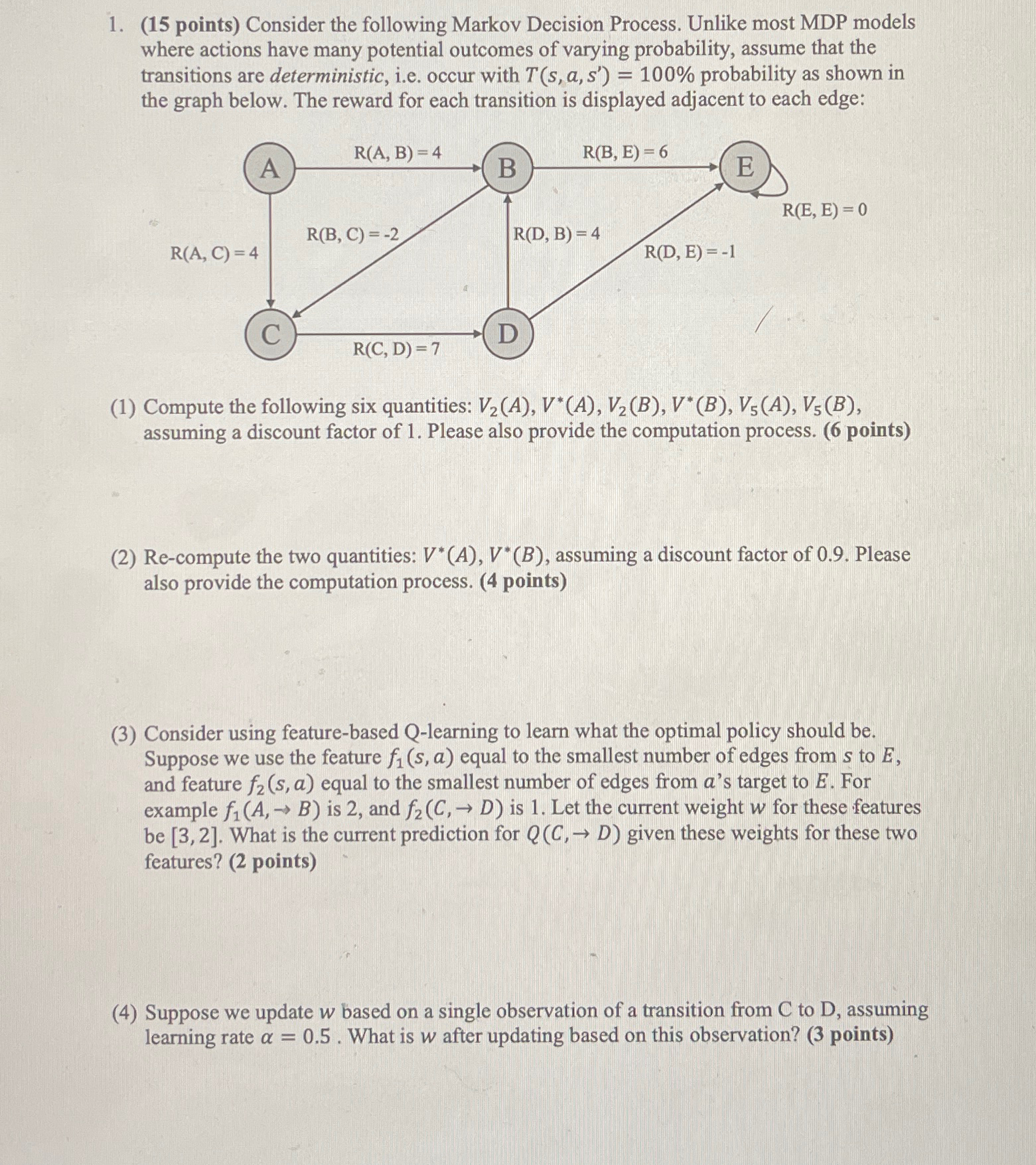
points Consider the following Markov Decision Process. Unlike most MDP models where actions have many potential outcomes of varying probability, assume that the transitions are deterministic, ie occur with probability as shown in the graph below. The reward for each transition is displayed adjacent to each edge:
Compute the following six quantities: assuming a discount factor of Please also provide the computation process. points
Recompute the two quantities: assuming a discount factor of Please also provide the computation process. points
Consider using featurebased Qlearning to learn what the optimal policy should be Suppose we use the feature equal to the smallest number of edges from to and feature equal to the smallest number of edges from s target to For example is and is Let the current weight for these features be What is the current prediction for given these weights for these two features? points
Suppose we update based on a single observation of a transition from C to D assuming learning rate What is after updating based on this observation? points
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


