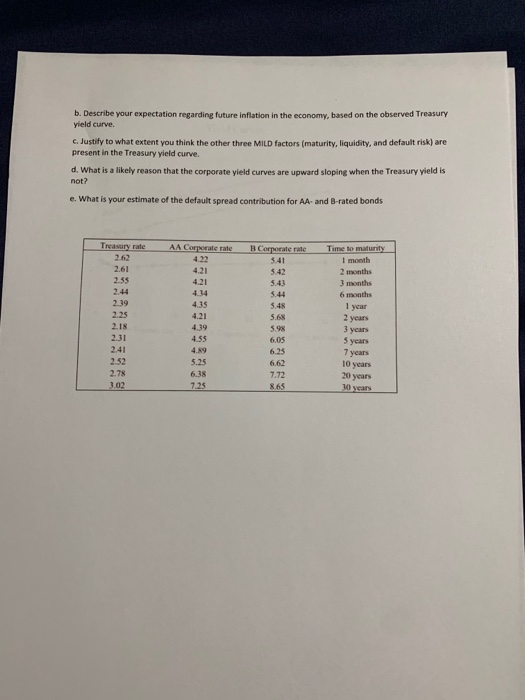
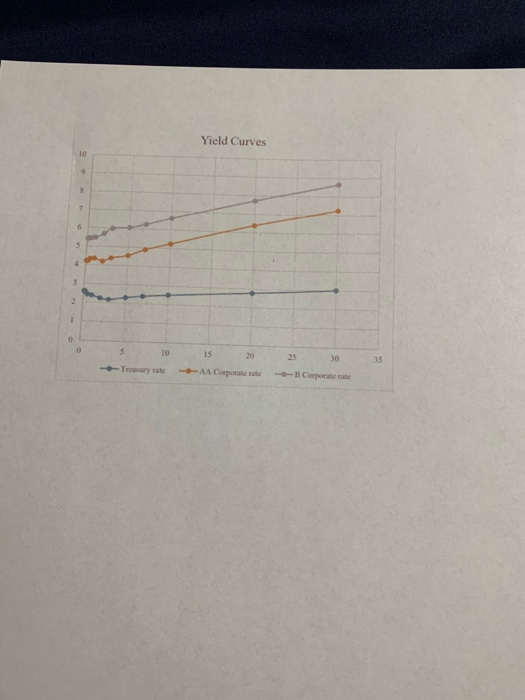
1. A $1,000 bond with a 6.5% semiannual coupon and 8 years to maturity is trading when interest rates have dropped to 5.4%. a. What is the present value of the bond? b. You believe that the relevant interest rate is going to decline to 5.1% in 6 months. If you are correct, what will the price of the bond be at that time? (Hint: two variables have changed.) c. If you were to buy the bond at the initial value (when rates were 5.4% in part A) and sell the bond six months later (when rates will be 5.1% in part B), what would be your holding period rate of return? 2. A $1,000 bond with a semiannual coupon of 4.3% and 14 years to maturity is currently trading at a price of $924 a. What is the bond's current yield? b. What is the band's YTM? c. If the bond is callable in 5 years with a $100 premium, what is the yield to call (VTC)? d. Given your answers to parts B and C, will the bond be called? Why or why not? 3. If the nominal rate of interest is 6.5% and the real rate of interest is believed to be 2%, what is the implied inflation rate, according to the approximate version of the Fisher equation? 4. Assume that a company has two outstanding semiannual bonds, both paying a coupon rate of 6%. However, one of the bonds has only 3 years remaining to maturity and the other has 25 years until maturity a. If the market rate of interest is 5%, what is the price of the 3-year bond? b. Again, assuming a market interest rate of 5%, what is the price of the 25-year bond? c. If the market rate of interest falls to 4%, which bond will experience the greater change in value? (Note: you do not have to provide the figures here, but you can double check that the results match your expectation.) d. Is it likely or possible that both bonds would have a coupon rate of 6%? Why or why not? 5. The table and graph below provide data on a hypothetical US Treasury yield curve along with hypothetical corporate yield curves for AA- and B-rated bonds. a. Describe the shape of the Treasury yield curve using appropriate terminology b. Describe your expectation regarding future inflation in the economy, based on the observed Treasury yield curve. c. Justify to what extent you think the other three MILD factors (maturity, liquidity, and default risk) are present in the Treasury yield curve d. What is a likely reason that the corporate yield curves are upward sloping when the Treasury yield is not? e. What is your estimate of the default spread contribution for AA- and B-rated bonds Treasury rate 2.61 2.55 Time to maturity 1 month 2 months 3 months 6 months 2.39 2.25 2.18 2.31 2.41 2.52 2.78 3.02 AA Corporate rate 4.22 4.21 4.21 4.34 4.35 4.21 4.39 4.55 4.89 5.25 6.38 7.25 B Corporate rate 5.41 5.42 5.43 5.44 5.48 5.68 5.98 6.05 6.25 6.62 7.72 8.65 1 year 2 years 3 years 5 years 7 years 10 years 20 years Yield Curves 10 9 6 5 2 0 5 10 15 20 30 35 --Treasury tale --AA Corporate -- Corporaterale