Question: 1. A 2 B 5 10. 3 J = D 2345 4 E 11 Consider the MDP corresponding to the above graph, where the
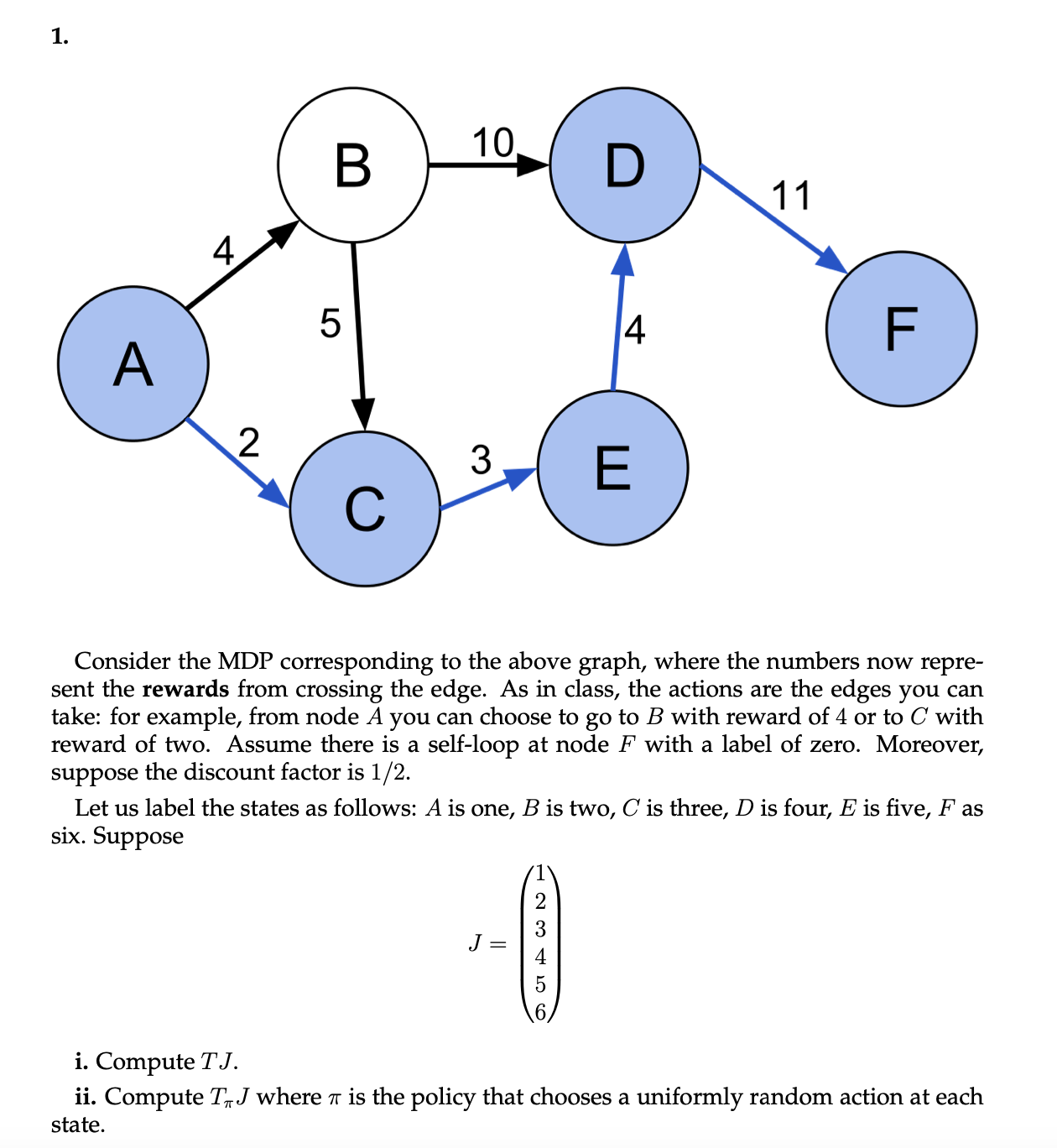
1. A 2 B 5 10. 3 J = D 2345 4 E 11 Consider the MDP corresponding to the above graph, where the numbers now repre- sent the rewards from crossing the edge. As in class, the actions are the edges you can take: for example, from node A you can choose to go to B with reward of 4 or to C with reward of two. Assume there is a self-loop at node F with a label of zero. Moreover, suppose the discount factor is 1/2. Let us label the states as follows: A is one, B is two, C is three, D is four, E is five, F as six. Suppose F i. Compute TJ. ii. Compute TJ where is the policy that chooses a uniformly random action at each state. 1. A 2 B 5 10. 3 J = D 2345 4 E 11 Consider the MDP corresponding to the above graph, where the numbers now repre- sent the rewards from crossing the edge. As in class, the actions are the edges you can take: for example, from node A you can choose to go to B with reward of 4 or to C with reward of two. Assume there is a self-loop at node F with a label of zero. Moreover, suppose the discount factor is 1/2. Let us label the states as follows: A is one, B is two, C is three, D is four, E is five, F as six. Suppose F i. Compute TJ. ii. Compute TJ where is the policy that chooses a uniformly random action at each state.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To compute TJ and Tpi J for the given Markov Decision Process MDP lets first understand the terminology TJ indicates the application of the Bellman op... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


