Question
1. A bank borrows $100,000 from the Fed, leaving a $100,000 Treasury bond on deposit with the Fed to serve as collateral for the loan.
1. A bank borrows $100,000 from the Fed, leaving a $100,000 Treasury bond on deposit with the Fed to serve as collateral for the loan. The discount rate that applies to the loan is 4 percent, and the Fed is currently mandating a reserve ratio of 10 percent. How much of the $100,000 borrowed by the bank must be kept as required reserves? (Hint: what has happened to the amount of checkable deposits?)
2. Suppose that the reserve requirement for checking deposits is 10 percent and that banks do not hold any excess reserves.
If the Fed sells $1 million of government bonds, what is the effect on the economy’s level of Excess Reserves?
(b) What is the effect on the economy’s money supply?
Now suppose the Fed lowers the reserve requirement to 5%, but banks choose to hold another 5% of deposits as Excess Reserves.
(c) What is the effect on the monetary multiplier?
What is the effect on the economy’s money supply?
3. The Fed conducts a $10 million open-market purchase of government bonds. If the required reserve ratio is 10 percent, what is the largest possible increase in the money supply that could result? Explain.
What is the smallest possible increase? Explain.
4. Suppose that inflation is 2 percent, the federal funds rate is 4 percent, and real GDP falls 2 percent below potential GDP. According to the Taylor rule, in what direction and by how much should the Fed change the real Federal Funds rate
5. Answer each of the following questions referring to the diagram below.
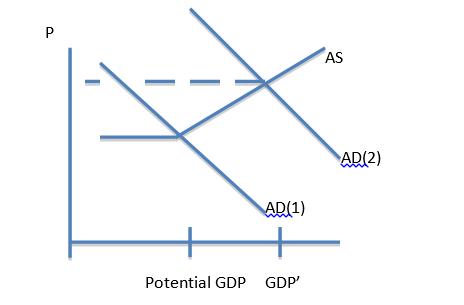
(a) Suppose the economy begins at GDP = Potential GDP. And that the government engages in a public works program of $100 billion, which increases AD from AD(1) to AD (2), as shown above. If the economy’s MPC = .8, by how much will the AD curve shift to the right? That is, what is the horizontal distance between AD(1) and AD(2
(b) The fiscal stimulus has produced a rise in the price level, since GDP = GDP’ is now above its potential, i.e., we have an inflationary gap. To move GDP down to its long-run potential level, the Fed most likely would decrease reserves by selling government securities in the market place so as to lower the federal funds rate and, by the monetary multiplier, the nation’s money supply. Explain why this action would decrease the level of aggregate demand.
(c) Assuming the Fed is successful, Indicate in the diagram above the new AD line that would follow the Fed’s actions. Why did you draw it as you did?
(d) Is this an example of “pushing-” or “pulling on a string”? Does it reflect the Fed’s experience of the past five years? If so, why? If not, why not?
P AD(1) Potential GDP GDP' AS AD(2)
Step by Step Solution
3.45 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
1 The required reserves for the bank in this situation would be 10000 This is calculated by taking the 100000 borrowed from the Fed multiplied by the reserve ratio of 10 which gives a result of 10000 ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


