Consider a set of samples {x1, x2,...,xN} that are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) according to a Gaussian distribution p(xi) = G (x;; ,
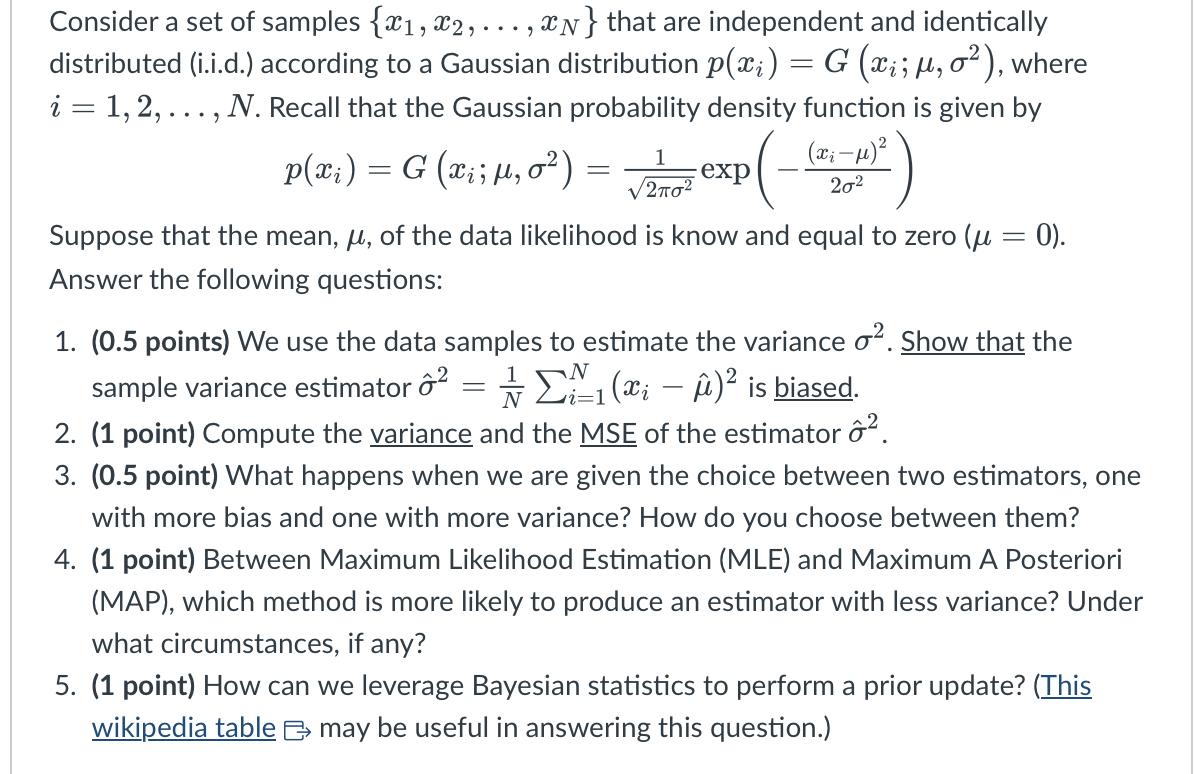
Consider a set of samples {x1, x2,...,xN} that are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) according to a Gaussian distribution p(xi) = G (x;; , o), where i = 1, 2,..., N. Recall that the Gaussian probability density function is given by P(xi) = G (x;; , 0) = = exp(- xi 1 2O2 (x-1)2 202 Suppose that the mean, , of the data likelihood is know and equal to zero ( = 0). Answer the following questions: 1. (0.5 points) We use the data samples to estimate the variance o. Show that the 1 sample variance estimator o = 1 (xi - ) is biased. N 2. (1 point) Compute the variance and the MSE of the estimator . 3. (0.5 point) What happens when we are given the choice between two estimators, one with more bias and one with more variance? How do you choose between them? 4. (1 point) Between Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) and Maximum A Posteriori (MAP), which method is more likely to produce an estimator with less variance? Under what circumstances, if any? 5. (1 point) How can we leverage Bayesian statistics to perform a prior update? (This wikipedia table may be useful in answering this question.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
100% Satisfaction Guaranteed-or Get a Refund!
Step: 2Unlock detailed examples and clear explanations to master concepts

Step: 3Unlock to practice, ask and learn with real-world examples

See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
-
 Access 30 Million+ textbook solutions.
Access 30 Million+ textbook solutions.
-
 Ask unlimited questions from AI Tutors.
Ask unlimited questions from AI Tutors.
-
 Order free textbooks.
Order free textbooks.
-
 100% Satisfaction Guaranteed-or Get a Refund!
100% Satisfaction Guaranteed-or Get a Refund!
Claim Your Hoodie Now!

Study Smart with AI Flashcards
Access a vast library of flashcards, create your own, and experience a game-changing transformation in how you learn and retain knowledge
Explore Flashcards