Question
1. A meta-analysis is a non-linear correlation. a variation on Cronbach's alpha. a type of t test. an analysis that integrates data from several different
1.
A meta-analysis is
a non-linear correlation.
a variation on Cronbach's alpha.
a type of t test.
an analysis that integrates data from several different studies.
2.
What are the steps of a meta-analysis?
Analyze results; analyze the analysis of those results; analyze the analysis of the results analysis; and so on.
Form a question; gather relevant studies; extract data and assess bias; integrate the results; interpret the findings; report the result.
Shock; release; depression; distress; panic; guilt; hostility; renewed hope; finally, acceptance.
You put your left foot in; you put your left foot out; you put your left foot in and you shake it all about.
3.
With meta-analysis, any one study included in the analysis can result in each of the followingexcept
underestimating the true effect due to sampling error.
overestimating the true effect due to sampling error.
distorting the results of the remainder of the studies included in the meta-analysis.
providing a biased estimate of the true effect due to the use of convenience sampling.
4.
To integrate across studies with a meta-analysis, it is essential that results be
fixed effectso as not to have to assume different populations.
on the same scaleeither using the same measure or all expressed in standardized terms.
consistentonly analyze studies that show exactly the same pattern of results.
unclearonly analyze studies in which the results didn't reach significance, because those with significant results will all have the same weight.
5.
When integrating results in a meta-analysis
all studies are weighted equally.
the researcher weighs some studies more based on personal preference.
smaller studies are given more weight.
larger studies are given more weight.
6.
In ESCI, the diamond ratio indicates
the degree of homogeneity in effect sizes; bigger means more homogeneity.
the degree of heterogeneity in effect sizes, bigger means more heterogeneity.
the overall effect size.
the CI of the overall effect size.
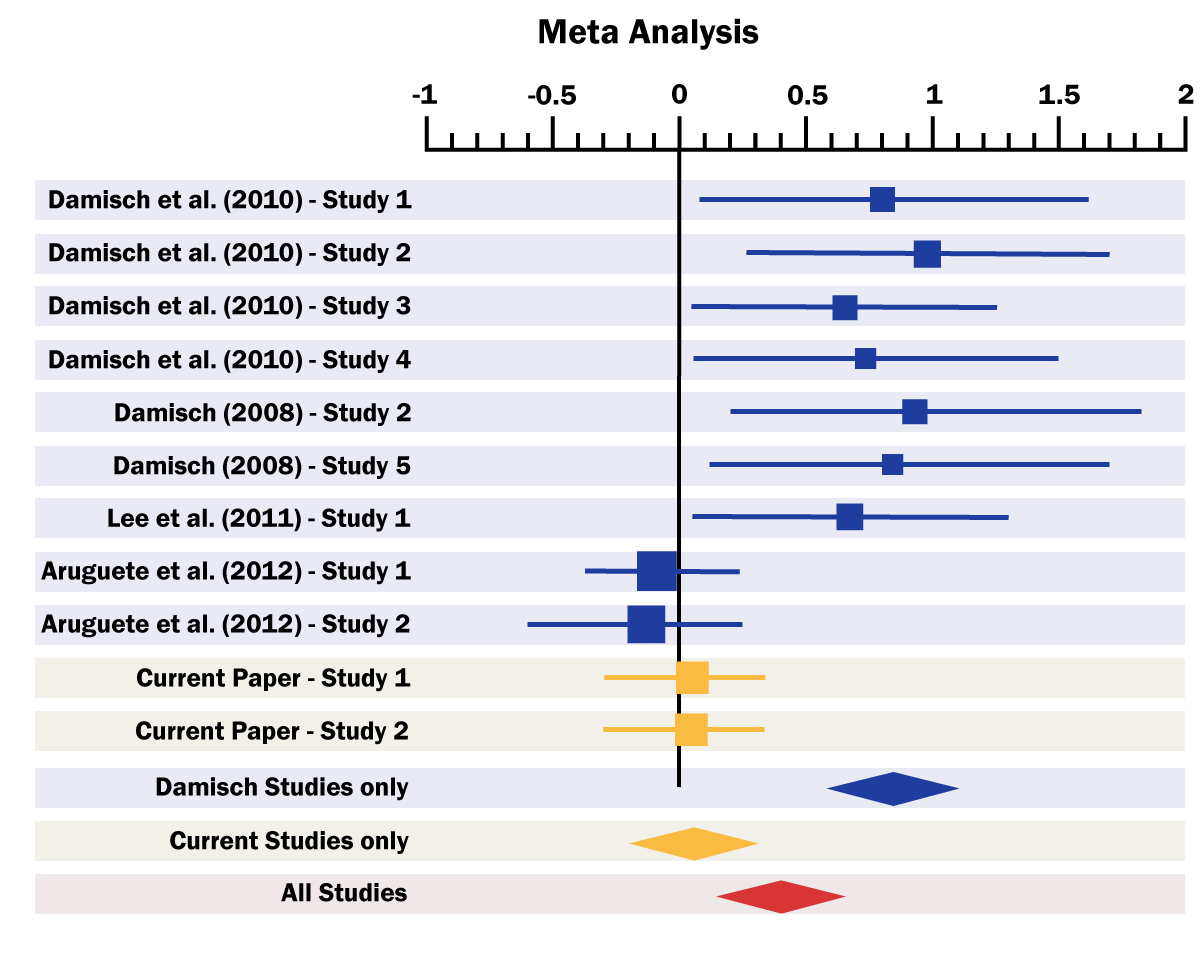
7.
What is the name for this type of figure?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


