Question
1) An earnings restatement is a revision of one or more of a company's previous financial statements to correct an error. According to Investopedia, such
1) An earnings restatement is a revision of one or more of a company's previous financial statements to correct an error. According to Investopedia, such restatements can result from accounting mistakes, noncompliance, fraud, misrepresentation, or a simple clerical error. From those, only clerical error is a benign reason for a restatement; all others suggest either poor managerial quality or wrongdoing. As such, your friend says that investors should react negatively to earnings restatements.
You want to conduct an experiment to test your friends assertionmore specifically, the assertion that the return at time t on the stock of the company announcing the earnings restatement will be negative on average (across all such announcements). Please explain what you should doin terms of setting up your hypothesis, which data to collect, and how you would test your hypothesis. In particular, be specific about the exact statistical test to be implemented.
You can assume you have access to a large sample of earnings restatements, and to any data you deem relevant to your analysis.
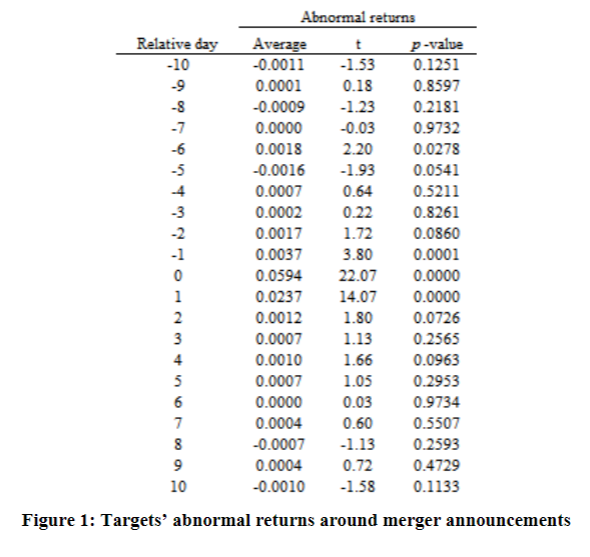
2) An event study of merger announcements tracks what happens to the targets returns around announcement dates. Merger announcements occur sometimes after the close of the market, so reactions to such announcements may take place in the next trading day. The pattern is shown in the figure below. Take the first row of the table, for example: it states that average abnormal returns (where abnormal return is measured as the targets stock return minus the market return) across targets for the 10th trading day preceding the merger announcement is 11 basis points, or 0.11%.
Discuss whether merger conveys good news, bad news or no news for the target. Define the null as the merger does not carry any news, and the alternative hypothesis as the merger conveys good news. Please write down the hypothesis and test it.
Then discuss whether markets are efficient in incorporating the information in the merger announcement.
Relative day -10 0.64 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Abnormal returns Average t p-value -0.0011 -1.53 0.1251 0.0001 0.18 0.8597 -0.0009 -1.23 0.2181 0.0000 -0.03 0.9732 0.0018 2.20 0.0278 -0.0016 -1.93 0.0541 0.0007 0.5211 0.0002 0.22 0.8261 0.0017 1.72 0.0860 0.0037 3.80 0.0001 0.0594 22.07 0.0000 0.0237 14.07 0.0000 0.0012 1.80 0.0726 0.0007 1.13 0.2565 0.0010 1.66 0.0963 0.0007 1.05 0.2953 0.0000 0.03 0.9734 0.0004 0.60 0.5507 -0.0007 -1.13 0.2593 0.0004 0.72 0.4729 -0.0010 -1.58 0.1133 Figure 1: Targets' abnormal returns around merger announcements Relative day -10 0.64 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Abnormal returns Average t p-value -0.0011 -1.53 0.1251 0.0001 0.18 0.8597 -0.0009 -1.23 0.2181 0.0000 -0.03 0.9732 0.0018 2.20 0.0278 -0.0016 -1.93 0.0541 0.0007 0.5211 0.0002 0.22 0.8261 0.0017 1.72 0.0860 0.0037 3.80 0.0001 0.0594 22.07 0.0000 0.0237 14.07 0.0000 0.0012 1.80 0.0726 0.0007 1.13 0.2565 0.0010 1.66 0.0963 0.0007 1.05 0.2953 0.0000 0.03 0.9734 0.0004 0.60 0.5507 -0.0007 -1.13 0.2593 0.0004 0.72 0.4729 -0.0010 -1.58 0.1133 Figure 1: Targets' abnormal returns around merger announcementsStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


