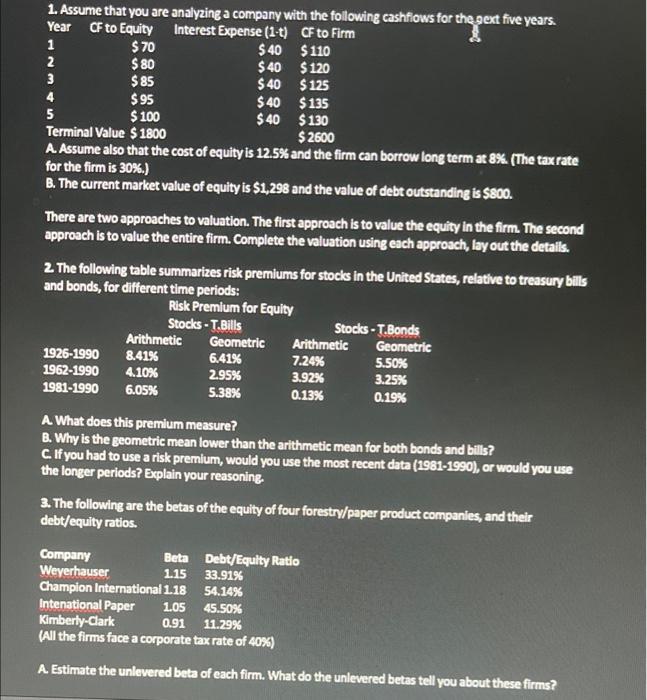
1. Assume that you are analyzing a company with the following cashfiows for the next five years. Year CF to Equity Interest Expense (1-t) CF to Firm 1 $ 70 $ 40 $110 2 $ 80 $ 40 $ 120 3 $85 $ 40 $125 4 $95 $ 40 $135 5 $ 100 $ 40 $ 130 Terminal Value $ 1800 $ 2600 A. Assume also that the cost of equity is 12.5% and the firm can borrow long term at 8% (The tax rate for the firm is 30%.) B. The current market value of equity is $1,298 and the value of debt outstanding is $800. There are two approaches to valuation. The first approach is to value the equity in the firm. The second approach is to value the entire firm. Complete the valuation using each approach, lay out the details. 2. The following table summarizes risk premiums for stocks in the United States, relative to treasury bills and bonds, for different time periods: Risk Premium for Equity Stocks - T. Bills Stocks - T.Bonds Arithmetic Geometric Arithmetic Geometric 1926-1990 8.41% 6.41% 7.24% 5.50% 1962-1990 4.10% 2.95% 3.92% 3.25% 1981-1990 6.05% 5.38% 0.13% 0.19% A What does this premium measure? B. Why is the geometric mean lower than the arithmetic mean for both bonds and bills? C. If you had to use a risk premium, would you use the most recent data (1981-1990), or would you use the longer periods? Explain your reasoning. 3. The following are the betas of the equity of four forestry/paper product companies, and their debt/equity ratios. Company Beta Debt/Equity Ratio Weyerhauser 1.15 33.91% Champion International 118 54.14% Intenational Paper 1.05 45.50% Kimberly-Clark 0.91 11.29% (All the firms face a corporate tax rate of 40%) A Estimate the unlevered beta of each firm. What do the unlevered betas tell you about these firms? B. Assume now that Kimberly Clark is planning to increase its debt/equity ratio to 30%. What will its new beta be? Cif you were valuing an initial public offering in the paper products area, what beta would you use in the valuation? (Assume that the firm going public plans to have a debt/equity ratio of 40%.) 4. The beta for Eastman Kodak is 1.10. The current six-month treasury bill rate is 3.25%, while the thirty- year bond rate is 6.25%. Estimate the cost of equity for Eastman Kodak, based upon the table in question 2. (a) using the treasury bill rate as your risk-free rate. (b) using the treasury bond rate as your risk-free rate. Which one of these estimates would you use in valuation? Why