Question
1. Birdie Golf, Inc. has been in acquisition talks with Hybrid Golf Company for the past months. After several rounds of negotiations, the offer under
1. Birdie Golf, Inc. has been in acquisition talks with Hybrid Golf Company for the past months. After several rounds of negotiations, the offer under discussion is a cash offer of $352 million for Hybrid Golf. Both companies have niche markets in golf club industry, and the companies believe a merger will result in significant synergies due to economies of scale in manufacturing and marketing, as well as significant savings in general and administrative expenses. Bryce Bichon, the financial officer of Birdie, has been instrumental in the acquisition negotiations. Bryce has prepared the following pro forma financial statements for Hybrid Golf assuming the merger takes place. The financial statements include all synergistic benefits from the acquisition.
Note: all figures are in $M
Projected Income Statement:
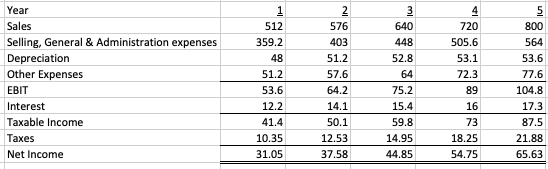
Projected Balance Sheet:
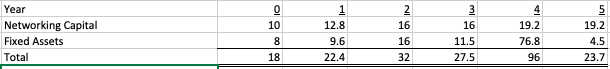
Sources of Financing:
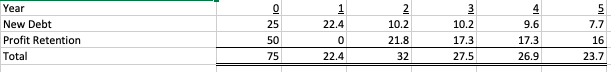
The management of Birdie Golf feels that the capital structure at Hybrid Golf is not optimal. If the acquisition takes place, Hybrid Golf will immediately increase its leverage by changing its debt-to-equity ratio to 1:1.
Currently:
- Hybrid Golf has 5.2 million common shares outstanding each trading at $55.
- The firm has a 0.2 million coupon bonds each trading at 71.5. These are 5.19% 10-year $1000 par bonds issued 2.25 years ago and pays interest semi-annually.
- Hybrids cost of debt is expected to increase by 20% due to change in capital structure. The risk-free rate is 4 percent, and the market risk premium is 7%. The current equity beta for Hybrid Golf stock is 1.30.
- Corporate Tax Rate is 25%
Answer the following using the information above:
a. Determine the existing WACC and new WACC of Hybrid after changing the capital structure.
b. Derive the free cash flows of Hybrid Corp. for each of the years 1 to 5.
c. Determine the maximum price per share that Birdie should be willing to pay to acquire Hybrid?
Year Sales Selling, General & Administration expenses Depreciation Other Expenses EBIT Interest Taxable income Taxes Net Income 512 359.2 48 51.2 53.6 12.2 41.4 10.35 31.05 2 576 403 51.2 57.6 64.2 14.1 50.1 12.53 37.58 640 448 52.8 64 75.2 15.4 59.8 14.95 44.85 720 505.6 53.1 72.3 89 16 73 18.25 54.75 800 564 53.6 77.6 104.8 17.3 87.5 21.88 65.63 12.8 19.2 Year Networking Capital Fixed Assets Total 9.6 76.8 19.2 4.5 23.7 22.4 27.5 Year New Debt Profit Retention Total 27.5 Year Sales Selling, General & Administration expenses Depreciation Other Expenses EBIT Interest Taxable income Taxes Net Income 512 359.2 48 51.2 53.6 12.2 41.4 10.35 31.05 2 576 403 51.2 57.6 64.2 14.1 50.1 12.53 37.58 640 448 52.8 64 75.2 15.4 59.8 14.95 44.85 720 505.6 53.1 72.3 89 16 73 18.25 54.75 800 564 53.6 77.6 104.8 17.3 87.5 21.88 65.63 12.8 19.2 Year Networking Capital Fixed Assets Total 9.6 76.8 19.2 4.5 23.7 22.4 27.5 Year New Debt Profit Retention Total 27.5Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


