Question
1) Calculate the standard enthalpy of hydrogenation of liquid benzene from its standard enthalpy of combustion (-3268 kJ/mol) and the standard enthalpy of combustion of
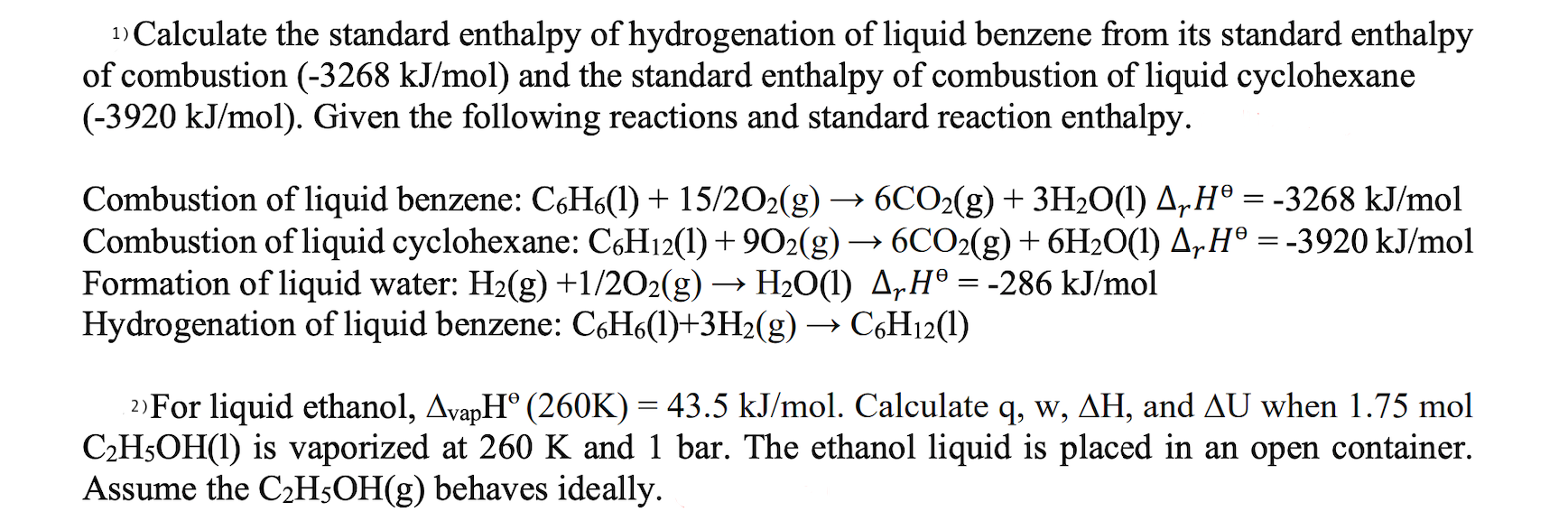
1) Calculate the standard enthalpy of hydrogenation of liquid benzene from its standard enthalpy of combustion (-3268 kJ/mol) and the standard enthalpy of combustion of liquid cyclohexane (-3920 kJ/mol). Given the following reactions and standard reaction enthalpy.
Combustion of liquid benzene: C6H6(l) + 15/2O2(g) 6CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) = -3268 kJ/mol
Combustion of liquid cyclohexane: C6H12(l) + 9O2(g) 6CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) = -3920 kJ/mol
Formation of liquid water: H2(g) +1/2O2(g) H2O(l) = -286 kJ/mol
Hydrogenation of liquid benzene: C6H6(l)+3H2(g) C6H12(l)
2) For liquid ethanol, vapH (260K) = 43.5 kJ/mol. Calculate q, w, H, and U when 1.75 mol C2H5OH(l) is vaporized at 260 K and 1 bar. The ethanol liquid is placed in an open container. Assume the C2H5OH(g) behaves ideally.
1) Calculate the standard enthalpy of hydrogenation of liquid benzene from its standard enthalpy of combustion (3268kJ/mol) and the standard enthalpy of combustion of liquid cyclohexane (3920kJ/mol). Given the following reactions and standard reaction enthalpy. Combustion of liquid benzene: C6H6(l)+15/2O2(g)6CO2(g)+3H2O(l)rH=3268kJ/mol Combustion of liquid cyclohexane: C6H12(l)+9O2(g)6CO2(g)+6H2O(l)rH=3920kJ/mol Formation of liquid water: H2(g)+1/2O2(g)H2O(l)rH=286kJ/mol Hydrogenation of liquid benzene: C6H6(l)+3H2(g)C6H12(l) 2) For liquid ethanol, vapHe(260K)=43.5kJ/mol. Calculate q,w,H, and U when 1.75mol C2H5OH(l) is vaporized at 260K and 1 bar. The ethanol liquid is placed in an open container. Assume the C2H5OH(g) behaves ideally
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


