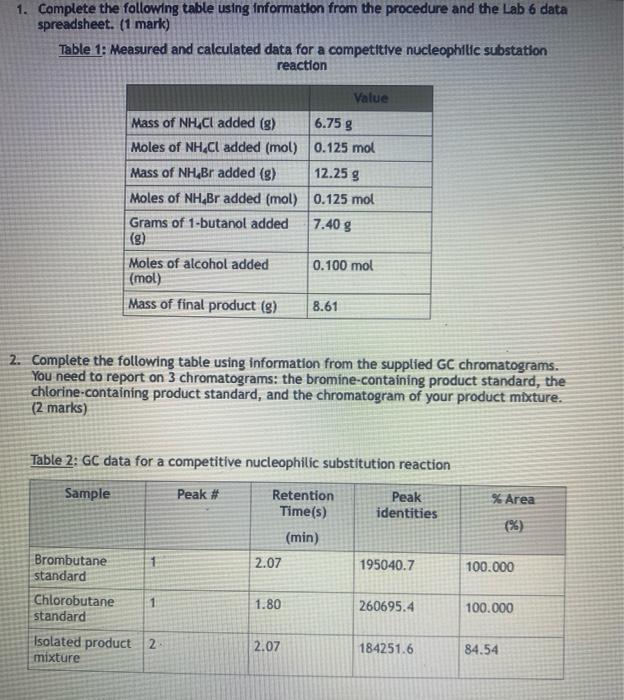
1. Complete the following table using information from the procedure and the Lab 6 data spreadsheet. (1 mark) Table 1: Measured and calculated data for a competltive nucleophilic substation reaction 2. Complete the following table using information from the supplied GC chromatograms. You need to report on 3 chromatograms: the bromine-containing product standard, the chlorine-containing product standard, and the chromatogram of your product mixture. (2 marks) Table 2: GC data for a competitive nucleophilic substitution reaction 3. Assume that the peak areas are proportional to the number of moles of compound present in the sample. Using the formula below to calculate the theoretical yleld based upon the observed mole ratio. Express the % areas as decimals; MW= molecular weight. (1 mark) Theo. yleld =( moles limiting reagent )[(% area C4H9Cl)(MW (atsa) )+(% area C4H9Br) ( MW CaA9Br )] 4. Calculate the overall percent yield of the combined product. (1 mark) 5. Provide three reasons that could explain the low product yleld. ( 3 marks) 6. Explain why the reaction mixture is acidified at the beginning of the experiment. (1 mark) 7. Which is the better nucleophile, chloride ion or bromide ion? Why? You may want to consult an authoritative outside resource to answer this question; if so, include a reference in CSE format. ( 2 marks) 8. Based on your product analysis, determine if this reaction proceeded through an SN1 or S 22 mechanism. (2 marks) 9. Predict the results if 2-butanol were used as the alcohol in place of 1-butanol or tert: butanol. ( 2 marks) 1. Complete the following table using information from the procedure and the Lab 6 data spreadsheet. (1 mark) Table 1: Measured and calculated data for a competltive nucleophilic substation reaction 2. Complete the following table using information from the supplied GC chromatograms. You need to report on 3 chromatograms: the bromine-containing product standard, the chlorine-containing product standard, and the chromatogram of your product mixture. (2 marks) Table 2: GC data for a competitive nucleophilic substitution reaction 3. Assume that the peak areas are proportional to the number of moles of compound present in the sample. Using the formula below to calculate the theoretical yleld based upon the observed mole ratio. Express the % areas as decimals; MW= molecular weight. (1 mark) Theo. yleld =( moles limiting reagent )[(% area C4H9Cl)(MW (atsa) )+(% area C4H9Br) ( MW CaA9Br )] 4. Calculate the overall percent yield of the combined product. (1 mark) 5. Provide three reasons that could explain the low product yleld. ( 3 marks) 6. Explain why the reaction mixture is acidified at the beginning of the experiment. (1 mark) 7. Which is the better nucleophile, chloride ion or bromide ion? Why? You may want to consult an authoritative outside resource to answer this question; if so, include a reference in CSE format. ( 2 marks) 8. Based on your product analysis, determine if this reaction proceeded through an SN1 or S 22 mechanism. (2 marks) 9. Predict the results if 2-butanol were used as the alcohol in place of 1-butanol or tert: butanol. ( 2 marks)