Question
1. Consider the dataset shown in the table below. Note that x1 through x9 are integer-valued counts sorted in ascending order (i.e., x1 corresponds to
1. Consider the dataset shown in the table below.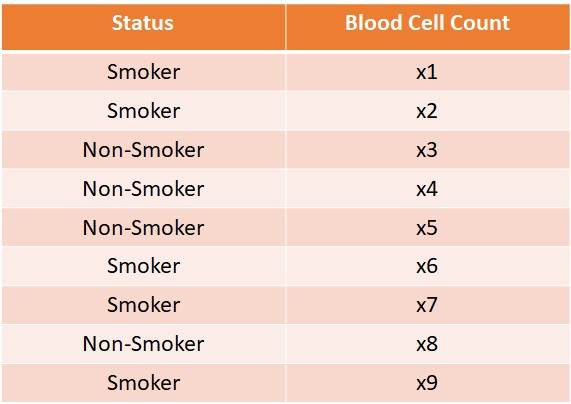
Note that x1 through x9 are integer-valued counts sorted in ascending order (i.e., x1 corresponds to the lowest cell count while x9 has the highest cell count). Suppose we apply the following methods (equal interval width, equal frequency, and entropy-based) to discretize the blood cell count attribute into 3 bins. The bins obtained are listed below:
- Equal Width: - Bin 1: x1, x2 - Bin 2: x3, x4, x5, x6, x7, x8 - Bin 3: x9 - Equal Frequency: - Bin 1: x1, x2, x3 - Bin 2: x4, x5, x6 - Bin 3: x7, x8, x9 - Entropy-based discretization with smoking status as class attribute: - Bin 1: x1, x2 - Bin 2: x3, x4, x5 - Bin 3: x6, x7, x8, x9
Explain the effect of applying each transformation below on the discretization methods listed above. Specifically, state whether the elements assigned to the bins can change to a different bin if you apply discretization on the transformed attribute values.
(a) Centering the attribute: xxmxxm
(b) Standardizing the attribute: xxmsxxms
(c) Applying logarithmic transform: xlog(x)xlog(x)
where x corresponds to one of the original blood count values (x1 to x9), m denotes the mean (average) value of the 9 numbers, and s denotes the standard deviation of the 9 numbers. Note: you do not need to know the exact values of x1 to x9 in order to answer this question.
Solution:
(a) Centering the attribute
i. Equal-width: ii. Equal frequency: iii. Entropy-based:
(b) Standardizing the attribute
i. Equal-width: ii. Equal frequency: iii. Entropy-based:
(c) Applying log transform:
i. Equal-width: ii. Equal frequency: iii. Entropy-based:
Note: You do not have to list the elements assigned to each bin after the transformation and discretization. You only need to answer whether it is possible for some of the elements to change their bin membership after the transformation and discretization. For example, suppose x3 was originally assigned to bin #2 using the equal width method. After applying the transformation, its value is converted to x3'. After applying equal width discretization on the transformed values, suppose x3' was assigned to bin #1. In this case, your answer for the equal-width method should be "Yes it is affected by the transformation because ...". However, if x3' remains in bin #2 after it was discretized, then your answer should be "No it is not affected by the transformation because ..."
Status Smoker Smoker Non-Smoker Non-Smoker Non-Smoker Smoker Smoker Non-Smoker Smoker Blood Cell Count X1 x2 X3 X4 x5 x6 x7 x8 x9 Status Smoker Smoker Non-Smoker Non-Smoker Non-Smoker Smoker Smoker Non-Smoker Smoker Blood Cell Count X1 x2 X3 X4 x5 x6 x7 x8 x9Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


