Question
1. Consider the following scenario: Two parties want to perform a key exchange using the Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange algorithm. They agree on a prime number
1.
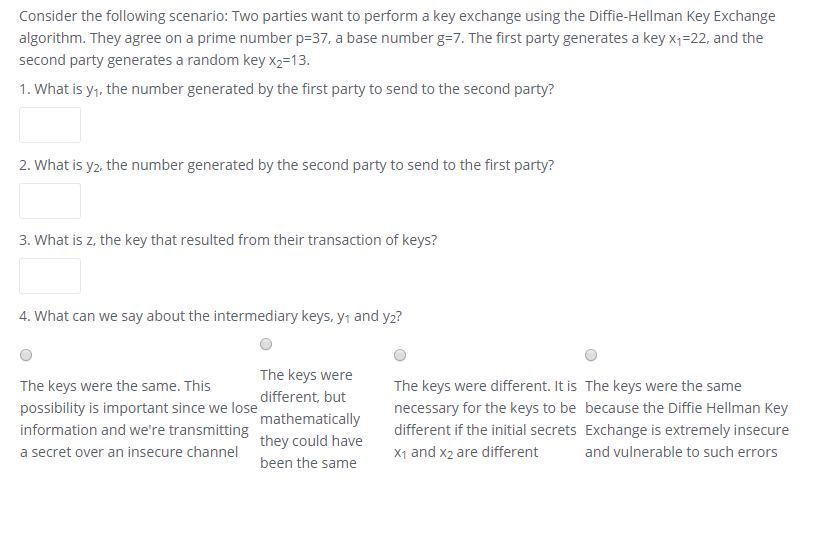
Consider the following scenario: Two parties want to perform a key exchange using the Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange algorithm. They agree on a prime number p=37, a base number g=7. The first party generates a key x1=22, and the second party generates a random key x2=13.
1. What is y1, the number generated by the first party to send to the second party?
Answer
2. What is y2, the number generated by the second party to send to the first party?
Answer
3. What is z, the key that resulted from their transaction of keys?
Answer
4. What can we say about the intermediary keys, y1 and y2?
|
The keys were the same. This possibility is important since we lose information and we're transmitting a secret over an insecure channel |
The keys were different, but mathematically they could have been the same |
The keys were different. It is necessary for the keys to be different if the initial secrets x1 and x2 are different |
The keys were the same because the Diffie Hellman Key Exchange is extremely insecure and vulnerable to such errors |
2.
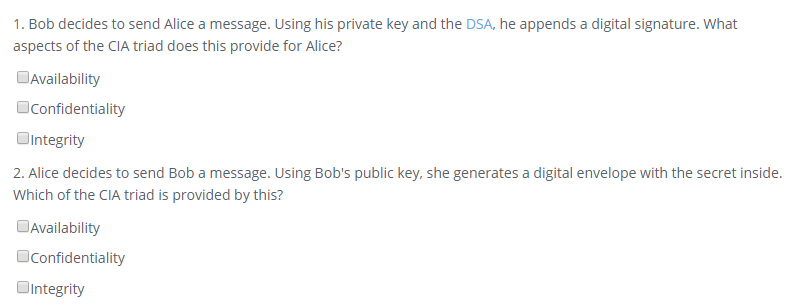
Bob decides to send Alice a message. Using his private key and the DSA, he appends a digital signature. What aspects of the CIA triad does this provide for Alice?
Availability
Confidentiality
Integrity
Alice decides to send Bob a message. Using Bob's public key, she generates a digital envelope with the secret inside. Which of the CIA triad is provided by this?
Availability
Confidentiality
Integrity
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


