Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1: Data Table 1 A 2 One-time equipment costs B Upgrade Replace $ 3,000,000 $ 4,500,000 3 Variable manufacturing cost per desk $ 145
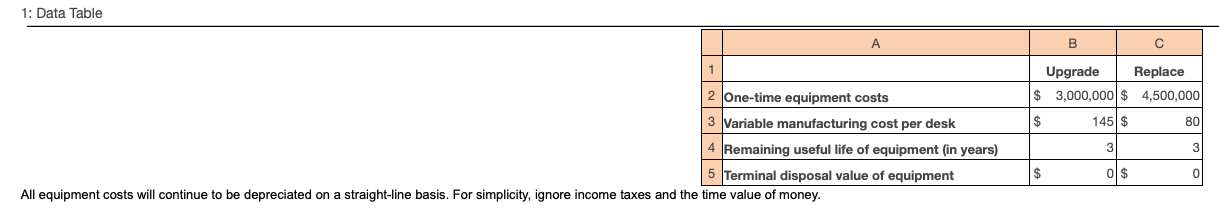

1: Data Table 1 A 2 One-time equipment costs B Upgrade Replace $ 3,000,000 $ 4,500,000 3 Variable manufacturing cost per desk $ 145 $ 80 4 Remaining useful life of equipment (in years) 3 3 5 Terminal disposal value of equipment $ 0 $ 0 All equipment costs will continue to be depreciated on a straight-line basis. For simplicity, ignore income taxes and the time value of money. Requirement 3. Assume that the capital expenditures to replace and upgrade the production equipment are as given in the original exercise, but that the production and sales quantity is not known. For what production and sales quantity would TechAide (a) upgrade the equipment or (b) replace the equipment First determine the equation you will use to calculate the quantity TechAide would use to base its decisions. Then select the amounts that will be used in the equation. (Round to the nearest whole number when solving for y.) Upgrade (9) (11) < or > < or > Based on the equation above, TechAide will upgrade when y (13)- Replace (10) (12) and will replace when y (14). Requirement 4. Assume that all data are as given in the original exercise. Dan Doria is TechAide's manager, and his bonus is based on operating income. Because he is likely to relocate after about a year, his current bonus is his primary concern. Which alternative would Doria choose? Explain. Begin by calculating the operating income under each alternative. (If an input field is not used in the table, leave the input field empty; do not enter a zero. Round all amounts to the nearest whole number.) (15) Revenues Cash operating costs Depreciation Loss on disposal of old equipment Total costs Operating income Upgrade Replace Doria would choose to (16) because it results in a higher net income over a (17). The TechAide Company produces and sells 7,200 modular computer desks per year at a selling price of $400 each. Its current production equipment, purchased for $1,650,000 and with a 5-year useful life, is only 2 years old. It has a terminal disposal value of $0 and is depreciated on a straight-line basis. The equipment has a current disposal price of $550,000. However, the emergence of a new molding technology has led TechAide to consider either upgrading or replacing the production equipment. The following table presents data for the two alternatives: 1(Click to view the data for the two alternatives.) Read the requirements. Requirement 1. Should TechAide upgrade its production line or replace it? Show your calculations. Determine the total relevant costs over 3 years. (If an input field is not used in the table, leave the input field empty; do not enter a zero. Use parentheses or a minus sign for numbers to be subtracted.) (1) (2) (3) Total relevant costs Over 3 years Upgrade Replace Difference Based on the analysis above, TechAide should (4). the equipment. Requirement 2. Now suppose the one-time equipment cost to replace the production equipment is somewhat negotiable. All other data are as given previously. What is the maximum one-time equipment cost that TechAide would be willing to pay to replace rather than upgrade the old equipment? First, determine the equation you will use to calculate the maximum one-time equipment cost, which is denoted as X. Then, select the correct components of the equation and solve for X. (5) Replace (7) s Upgrade (6) (8) The maximum one-time equipment cost that TechAide will be willing to pay to replace the old equipment rather than upgrade it is
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


