1. Evaluate several options (loan denial, application grant, application deferral) available to the lender to determine the best option for this decision.
2. As a director of this institution, will you lend money or not? And with a rationale for this decision?

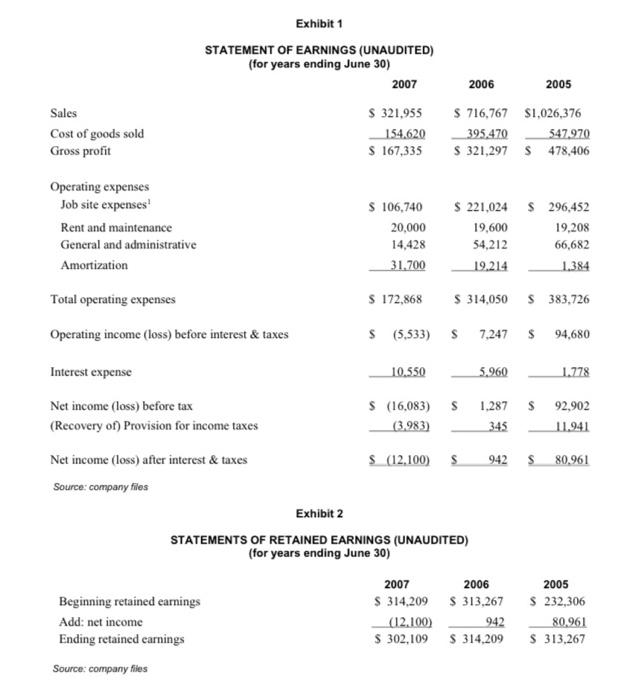
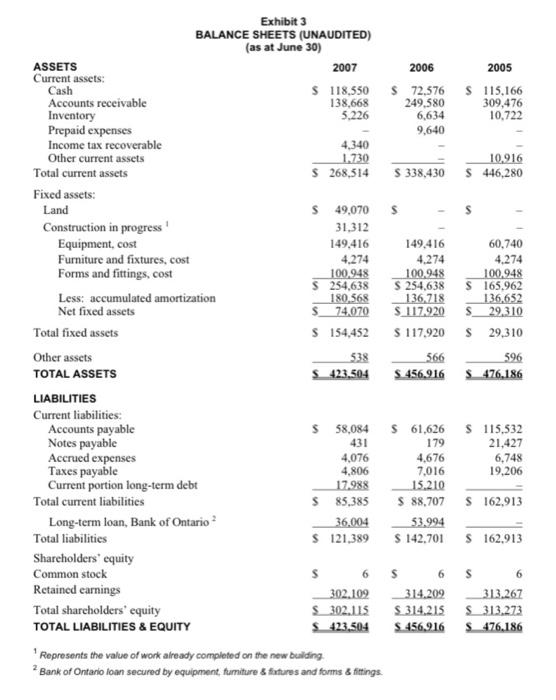
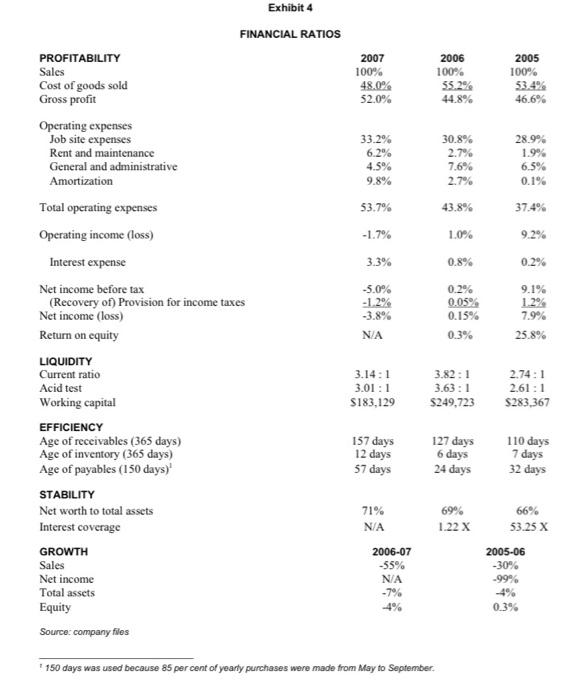
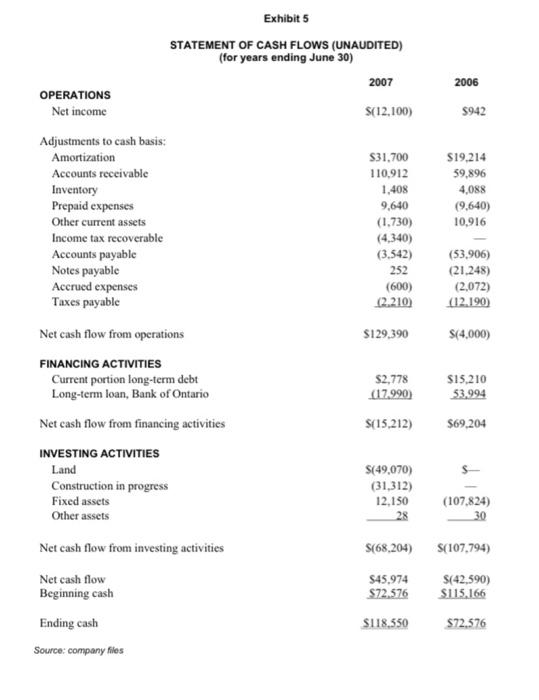
DRUTHERS FORMING LIMITED On July 30, 2007, Brad MacDougall, account manager at the Canadian Commercial Bank (CCB) in Barron., Ontario, reviewed his latest loan request. Garrett Sheppard, co-founder of Druthers Forming Limited (Druthers) and a long-time CCB customer, was requesting a $350.000 loan to construct a new building to house Druthers" existing operations. Construction was already well underway, with a completion date set for September 30, 2007. MacDougall noted that Druthers was currently operating without a line of credit, and he wondered whether the business could generate enough cash to cover all expenses, including the new loan payments, if approved. With his desk covered in financial and company data, MacDougall knew he must give Sheppard an answer by early next week if construction was to continue on schedule. COMPANY BACKGROUND Druthers Forming Limited was founded in 1987 by two brothers, Garrett and Norm Sheppard, and one other investor. When a third brother, Jack, joined in 1995 and replaced the other investor, Druthers became the Sheppards" second entirely-owned-and-operated firm. The other family business was Jack Sheppard Homes Lrd. (Sheppard Homes), a construction company that had been in business since 1964. Druthers, originally established to serve the needs of Sheppard Homes, specialized in the construction of poured concrete foundations for residential buildings, which was the first stage in building a home. In the late 1980 s, Jack Sheppard observed that demand for foundations far outstripped supply in the region, and long waits for foundation construction had become standard. Furthermore, one of the three fims that had been serving the existing market was winding down its operations and getting out of the foundation business. In an attempt to circumvent these obstacles, which were causing numerous lengthy delays in the construction of Sheppard Homes, the brothers started their own foundation company, Druthers Forming Limited. Whenever possible, Druthers also sold its services to other housing contractors who were anxious to have their foundations poured on schedule and to individuals building their own homes. The company's principal target market was Barron and areas within a 45-kilometre radius of Barron Township. During its early years, Druthers competed in a lucrative subset of the construction industry. Volume and market opportunities were very high due to the lack of competition in the area. However, by the late 1990 s, there were several firms that offered similar foundation services. The steady increase in competition since then had driven prices downward and reduced profit margins in recent years. (See Exhibits 1 to 5 for historical financial statements and selected company and industry ratios.) THE DRUTHERS AND SHEPPARD HOMES RELATIONSHIP Sheppard Homes built primarily single-family dwellings. Several other local construction firms served the multi-family residential sector, which included duplex, triplex and townhouse buildings. Druthers provided foundations for all of these different housing styles. Druthers" dependence on Sheppard Homes varied from year to year. In recent times, anywhere from 30 per cent to 70 per cent of Druthers' sales came from Sheppard Homes. The largest fluctuation in the building business was the health of the cconomy. When the economy was in a downturn, multi-unit homes tended to become more popular, increasing Druthers' sales to other construction firms. Conversely, when the economy boomed, so did demand for single-family homes, and business between Druthers and Sheppard Homes increased. The operation of Sheppard Homes was the main business focus for all three brothers. This company generated the most income, and its prosperity was closely tied to that of Druthers. When Sheppard Homes was busy, Druthers had a steady demand for foundations, along with any outside work the company might have time for. Page 3 FINANCIAL ANALYSIS AND CREDIT EVALUATION-FIN331, BANK 331 Garrett Sheppard joined Sheppard Homes in 1982 , immediately affer graduating with an honors business administration degree from the Richard lvey School of Business at The University of Western Ontario. As well as helping to operate both companies, Garrett was active in the community and had served as president of the local Homebuilders' Association for several years. Norm Sheppard had supplied the architectural expertise for both companies since 1987. Most buyers appreciated the opportunity to sit down with Norm to design their own homes, a service that was not always available from other companies in the Barron area. A cousin of the Sheppards, Eric, was also involved with the family businesses as a finish carpenter for Sheppard Homes, although he was not a Druthers co-owner. The Sheppards" youngest brother, Jack, completed the Druthers' management team. After joining the family businesses in the early 1990 s, Jack aceepted the role of site manager for both firms. The skill sets of the brothers were extremely complementary, and both companies were highly regarded in the local construction industry. INDUSTRY AND ECONOMY Druthers* sales were influenced by three main factors: the economy, which drove housing starts; the competition; and, often most significantly, other builders" reluctance to use Druthers" services because of its affiliation with Sheppard Homes - a competing building firm within the home construction industry. Housing starts were cyclical and fluctuated directly with the economy. Some firms were experiencing a downtum, which they believed was a result of recent forecasts of a looming economic slowdown in the Ontario housing market. However, Druthers was somewhat insulated from such economic swings because it served both the single home and multi-fesidential markets. Nevertheless, the effects of increasing competition in the market were becoming apparent from the financial statements. Most supplicrs offered Druthers 30-to-60-day credit terms, and Druthers did the same for construction companies that they supplied with foundations. Relationships and a firm's reputation were important factors in the construction industry. Most benilders were very loyal and used the same foundation company repeatedly. They looked for a competitive price. reliable prompt service and a quality product. Over the years. Druthers had built a solid reputation and had developed a loyal customer base. Despite the reputable business the brothers had built, Druthers often had difficulty attracting new customers because other builders were reluctant to use the services of a company that was affiliated with a competing building firm. Growth into the commercial construction segment was also not feasible because most commercial builders used concrete block foundations, which were slightly cheaper than the poured concrete foundations supplied by Druthers. Contrary to popular belief, Druthers' business was not overly seasonal since work continued throughout the winter whenever there was demand. Druthers controlled its labour costs during slack periods by laying off workers - a common industry practice. FINANCIAL PROJECTIONS MacDougall turned his attention towards the information Garren Sheppard had provided regarding the company's future operations. The majority of the 5,500-square-foot building had already been rented out by Druthers to the Barron Best Club (approximately 4,000 square feet). Druthers and Sheppard Hoenes would share the remainder of the space upon completion of the building's construction. The property allowed for the building of additional room if needed in the future. Once moved into the building, Druthers would save $20,000 annually that it was currently paying for rented premises. Annual rental income carned on the new property would total 560,000 . Sheppard estimated that Druthers would pay a total of $18,000 in property taxes for fiscal 2008 and $18.500 for fiscal 2009, and additional maintenance expenses of $7,000 annually would be incurred for upkecp of the new building. If a new loan were approved, annual principal payments would be $30,000 for each of fiscal 2008 and fiscal 2009 , and annual interest expense on the new loan would be approximately 520,300 for the first two years until the principle owing was lowered. Upon completion, set for September 30, 2007, the building, valued at $350,000, would be depreciated on a straight-line basis over 20 years. In addition to these new loan payments, the total current portion on the existing long-term debt for fiscal 2008 would be $21,276 and $14,728 for fiscal 2009. Although market information was limited, Garrett Sheppard believed that Druthers held about 35 per cent of the concrete foundation construction market in Barron and the surrounding area. Despite the prevailing economic and business conditions, he felt Druthers' sales would increase 10 per cent in fiscal 2008 and 15 per cent in fiscal 2009. Some of this increase resulted from a downward trend in the price of concrete purchased from ready-mix companies, a cost savings that had not yet been passed on to customers. Therefore, Druthers' cost of goods sold was projected to decrease slightly to 47.5 per cent of sales as the company rebounded during the next few years. Sheppard also explained that about 85 per cent of Druthers' accounts receivable were due from Sheppard Homes; therefore, the age of receivables could be reduced quickly by transferring money "from one pocket to the other" if liquidity became a problem. For this reason. Sheppard was not concerned about the firm's lengthening days of accounts receivable. Additionally, he predicted that for the next two years, jobsite expenses would remain at the same dollar amount as that of 2007 . Income taxes would be approximately 20 per cent. Other items on the statement of earmings would remain roughly the same percentage of sales as was experienced in 2007. THE DECISION Although Garrett Sheppard anticipated growth in Druthers" future, the company had shown some disappointing results in the past two years, and MacDougall was concerned about extending financing at such a low point in the business's operations. Construction plans were already underway, however, and MacDougall knew that the brothers were relying on the CCB to finance the building as of September 30 . 2007. Furthermore, without a short-term source of financing, MacDougall wondered whether Druthers could generate sufficient cash to cover its debt payments over the next few years. Before he could respond to Sheppard's request, MacDougall had to answer several questions in a very short period of time. Exhibit 1 STATEMENT OF EARNINGS (UNAUDITED) (for years ending June 30 ) Operating expenses Job site expenses 1 Rent and maintenance General and administrative Amortization Total operating expenses \begin{tabular}{rrrrr} $106,740 & $221,024 & $ & 296,452 \\ 20,000 & & 19,600 & & 19,208 \\ 14,428 & & 54,212 & & 66,682 \\ 31,700 & & 19,214 & & 1,384 \\ \cline { 4 - 6 }$172,868 & $314,050 & $ & 383,726 \end{tabular} Operating income (loss) before interest \& taxes Interest expense \begin{tabular}{rrrrr} $(5,533) & $ & 7,247 & $ & 94,680 \\ 10.550 & & 5,960 & & 1.778 \\ \hdashline \end{tabular} Net income (loss) before tax (Recovery of) Provision for income taxes Net income (loss) after interest & taxes $(12,100)$942$80.961 Source: company files Exhibit 2 STATEMENTS OF RETAINED EARNINGS (UNAUDITED) (for years ending June 30 ) Beginning retained earnings Source: company fies Exhibit 3 BALANCE SHEETS (UNAUDITED) (as at June 30) ASSETS Current assets: CashAccountsreceivableInventoryPrepaidexpensesIncometaxrecoverableOthercurrentassets$118,550138,6685,2264,340$268,514$249,5806,6349,640$338,43072,576309,47610,722$446,280$115,166 Fixed assets: Land Construction in progress 1 Equipment, cost Furniture and fixtures, cost Forms and fittings, cost Less: accumulated amortization Net fixed assets Total fixed assets Other assets TOTAL ASSETS LIABILITIES Current liabilities: 1 Represents the value of work already completed on the new bulding. 2 Bank of Ontanio loan secured by equipment, fumiture s fitures and forms s fittings. Exhibit 4 FINANCIAL RATIOS PROFITABILITY Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit 2007100%48.0%52.0%2006100%55.2%44.8%2005100%53.4%46.6% Operating expenses Job site expenses Rent and maintenance General and administrative Amortization 33.2%6.2%4.5%9.8%30.8%2.7%7.6%2.7%28.9%1.9%6.5%0.1% Total operating expenses Operating income (loss) Interest expense 53.7%1.7%3.3%5.0%1.2%3.8%N/A43.8%1.0%0.8%0.2%0.05%0.15%0.3%37.4%9.2%0.2%9.1%1.2%7.9%25.8% LIQUIDITY Current ratio Acid test Working capital 3.14:13.01:1$183,1293.82:13.63:1$249,7232.74:12.61:1$283,367 EFFICIENCY Age of receivables (365 days) Age of inventory ( 365 days) Age of payables (150 days) 1 157days12days57days127days6days24days110days7days32days STABILITY Net worth to total assets Interest coverage 71%N/A69%1.22X66%53.25X GROWTH Sales Net income Total assets Equity 20060755%N/A7%4%20050630%99%4%0.3% Source: company files 150 days was used because 85 per cent of yearly purchases were made from May to September. Exhibit 5 STATEMENT OF CASH FLOWS (UNAUDITED) (for years ending June 30 ) OPERATIONS Net income S(12,100)$942 Adjustments to cash basis: FINANCING ACTIVITIES Current portion long-term debt Long-term loan, Bank of Ontario \begin{tabular}{rr} 52,778 & 515,210 \\ (17,990) & 53,994 \\ \hline \end{tabular} Net cash flow from financing activities $(15,212)$69,204 INVESTING ACTIVITIES Land Construction in progress Fixed assets. Other assets S(49,070)(31,312)12,15028$(107,824)30 Net cash flow from investing activities $(68,204)$(107,794) Net cash flow Beginning cash \begin{tabular}{rr} $45,974 & $(42,590) \\ $72,576 & $115,166 \\ \hline \end{tabular} Ending cash 5118.550572.576 Source: company files