Question
1. Given Angies budget and profit goals, suggest which metrics Angie should use to assess the success of her new venture. Prices and costs are
1. Given Angies budget and profit goals, suggest which metrics Angie should use to assess the success of her new venture. Prices and costs are per tray, so use trays as the basic unit when determining per-unit amounts
2. Analyze and compare Angies overall actual results with her expected results to determine why her accountant is concerned.
3. Angies accountant recommended that your team drill down further into the sales mix and cost figures to determine how the different product types are affecting profits. Look for any sales-mix issues and suggest potential solutions.
4. Offer suggestions for how Angie should determine a price quote (per tray) for the special-order customer.
5. Offer suggestions to improve Angies operations and to help her decide whether to continue the business and, if so, how to grow it. Consider potential alternative products, services, and marketing options
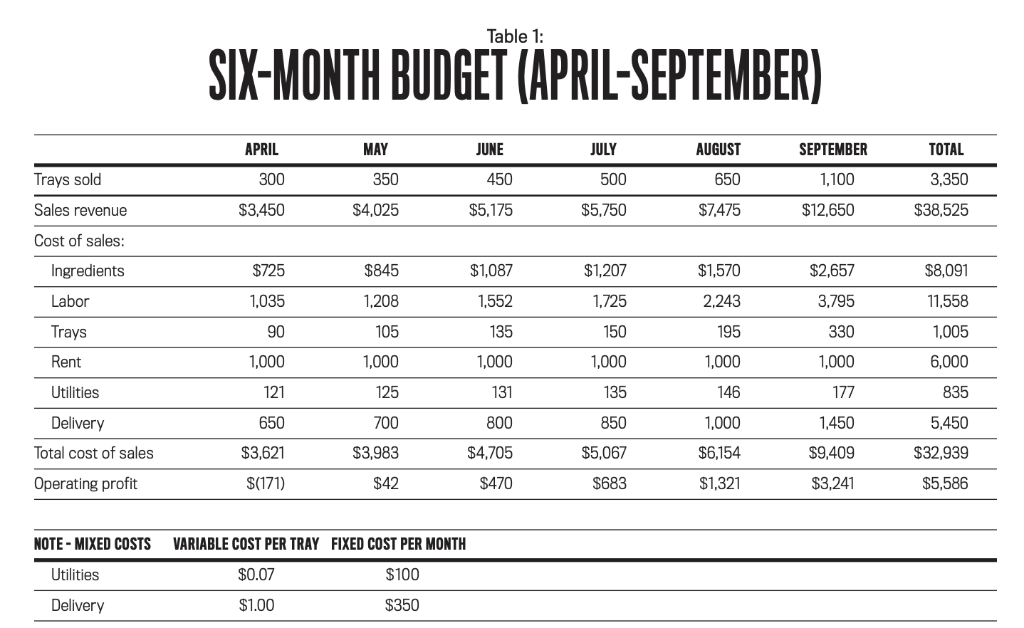
Starting her business: When looking to start a business around her empanadas, Angie first considered a large-scale rollout of pre-packaged empanadas for grocery stores and big-box retailers but quickly realized that option was premature. She then decided to explore the possibility of a smaller-scale rollout, selling empanadas to local restaurants. Over the next few days, Angie did some basic research and found that there were about 800 restaurants in the local metropolitan area. Because empanadas are common throughout Latin America, she narrowed the prime target market to some form of Latin American food. She found approximately 100 restaurants that could be classified as Latin American, with the majority identifiable as Mexican restaurants. Of these, she identified 21 as national or regional chains such as Taco Bell and Chipotle Mexican Grill. Angie identified a local chain of seven restaurants as unsuited for the product. This left 72 restaurants that she labeled prime target customers. Digging further, Angie made a second list of non-Latino restaurants and bars that might be interested in her empanadas. Excluding national chains and types of cuisine that were obviously a poor fit, she pared down the list to 130 in total. At the same time, she was perfecting her recipes and estimating costs. She identified a few fully equipped kitchens she could rent for between $700 and $2,000 a month, depending on size, equipment, and location. She also estimated the cost of other items, including ingredients, labor, trays, utilities, and delivery. Then she classified each cost as fixed, variable, or mixed based on the advice of her accountant. After some additional market testing and interactions with potential clients, Angie prepared a six-month budget (see Table 1). Angies Empanadas opened on April 1. The business is located in a metropolitan area with a total population of about 400,000. The area houses a university with approximately 20,000 students, several private colleges, and a technical college. Both the university and the technical college offer restaurant administration degrees. The primary local industries are agriculture and light manufacturing. Angie signed a one-year lease on a kitchen near the university that would provide sufficient capacity and a ready labor supply to help her reach her short-term profit goal of $4,000 per month by the end of the first year. She feels the business needs to make at least that much profit to be worth her time. Otherwise, she will pursue her talent for photography. Angie does much of the preparation and assembly of the empanadas herself, but she hires additional labor as needed, mostly students, to help make and deliver the product. The preparation and assembly is done by hand, and the dough needs to be made daily. This means labor is a relatively large part of the products cost. Because the ingredients are organic, they also are relatively costly. Angie relies on quality and excellent taste to differentiate her products, but shes also trying to keep the price low to gain a foothold in the market. She purchases the trays locally, and they are recyclable but not reusable, meaning she must use new trays for every batch.
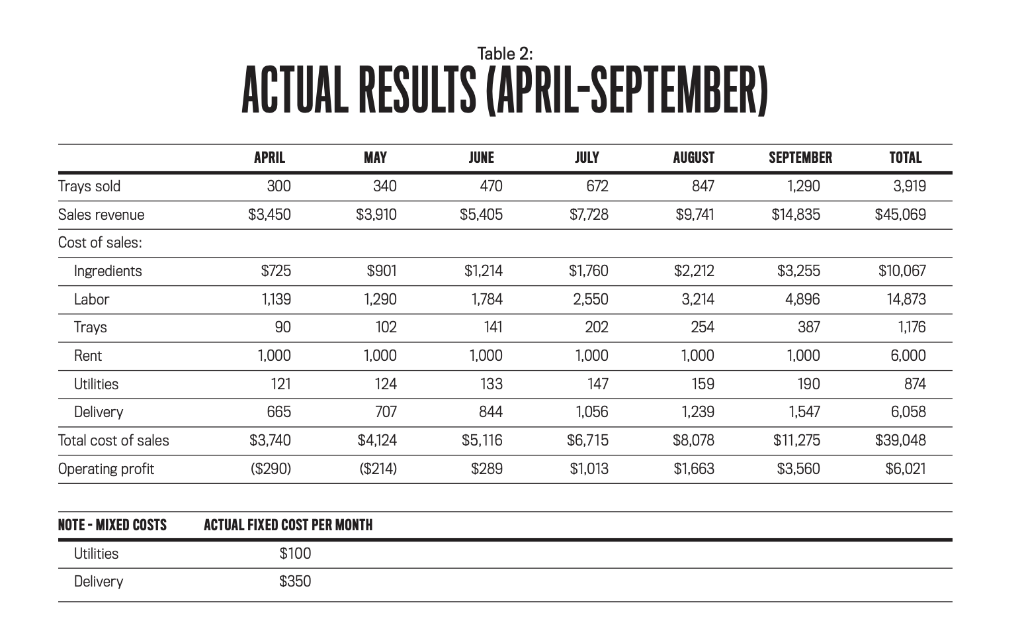
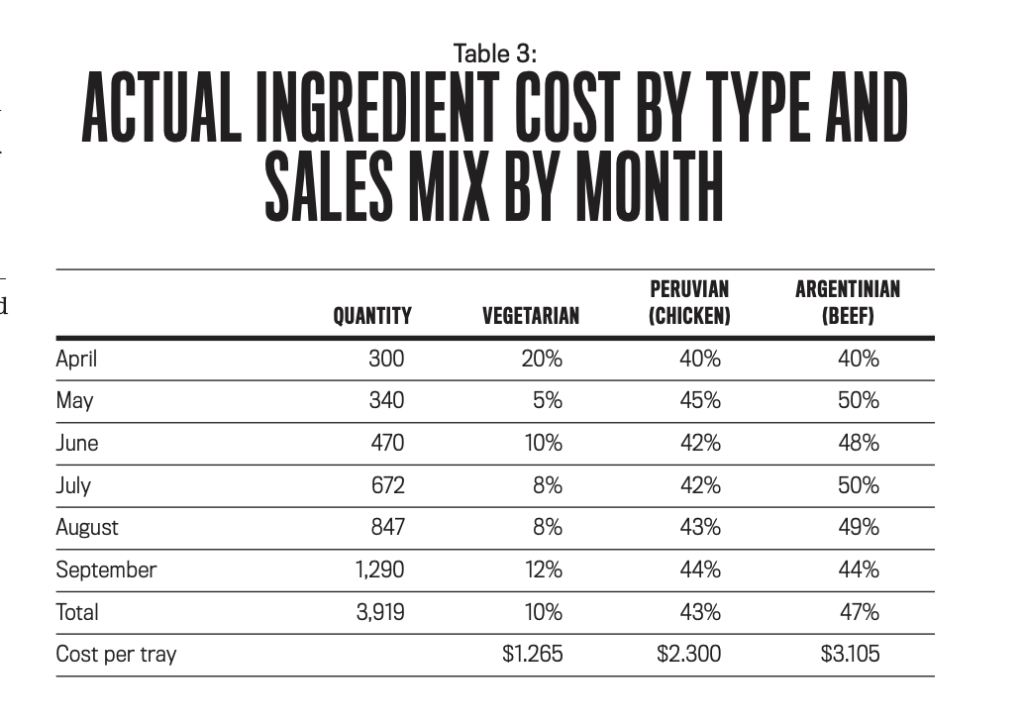
6 month budget review: In early October, Angie compared the actual results for the first six months after the launch of her business to her original budget (see Table 2). She had expected to grow her business slowly, so she was excited when she realized that she had sold 569 more trays than budgeted and her profit exceeded the budgeted semiannual profit by $435. She was also delighted by her monthly sales figures, which had exceeded expectations each of the last four months. Based on her early success, Angie is thinking of expanding her operation to a larger space and investing in kitchen equipment as well as other assets, such as delivery trucks. But her part-time accountant isnt as excited. He did some additional analysis across the three types of empanadas and found that the overall cost per tray for each type differs significantly (see Table 3), yet they are all priced the same. He doubts that she could reach her goal of $4,000 a month in profit by the end of the first year without making some price changes.
Special Orders: Angie recently received an inquiry from one of her customers, a local organic restaurant and catering company, asking for special pricing for large-event orders. Angie previously provided the customer with an order of 50 trays of empanadas in September. The catering company picked up the trays at Angies kitchen, saving delivery costs, and said it would continue to do so. The customer would standardize its order at 40% vegetarian empanadas, 40% Peruvian, and 20% Argentinian, but it would also require a more expensive tray ($0.75 per unit vs. the current cost of $0.30) that can double as a serving dish. This customer would also provide extended lead times for the orders. Angie doesnt expect that the additional orders would impact her other customers. She sees this as a good opportunity but is unsure what price to quote this customer so that both sides would benefit. Angie recognized that she needs some professional help and hired your consulting team to advise her on financial planning and analysis to evaluate the first six months of operations. She also wants advice on how to reach her profit goals.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


