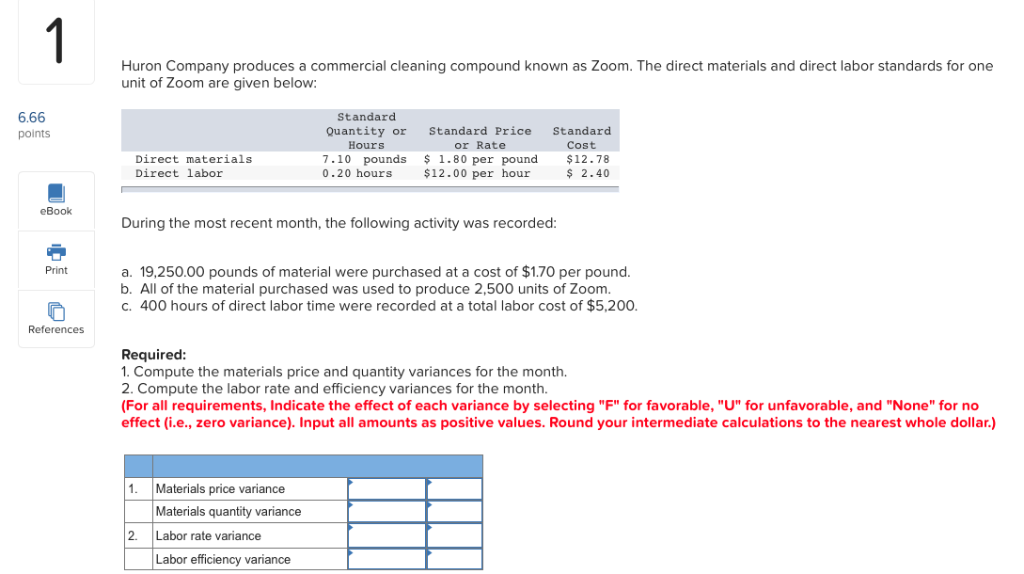
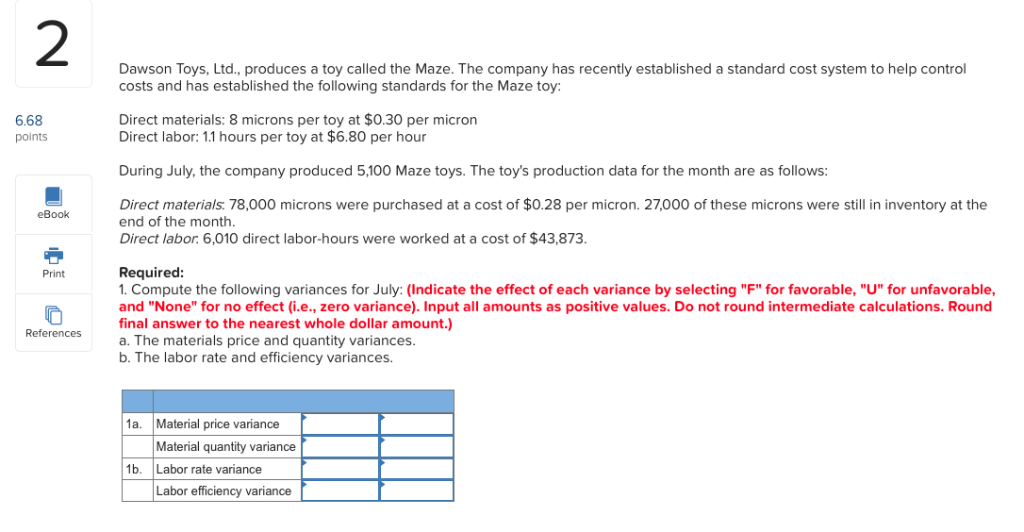

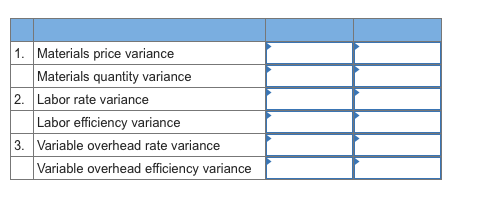
1 Huron Company produces a commercial cleaning compound known as Zoom. The direct materials and direct labor standards for one unit of Zoom are given below: 6.66 Standard Quantity or Standard Standard Price points Hours unds 7.10 $ 1.80 per pound Direct materials $12.78 $ 2.40 Direct labor 0.20 hours $12.00 per hour eBook During the most recent month, the following activity was recorded: 19,250.00 pounds of material were purchased at a cost of $1.70 per pound. b. All of the material purchased was used to produce 2,500 units of Zoo c. 400 hours of direct labor time were recorded at a total labor cost of $5,200. Print References Required 1. Compute the materials price and quantity variances for the month. 2. Compute the labor rate and efficiency variances for the month (For all requirements, Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Round your intermediate calculations to the nearest whole dollar.) Materials price variance 1 Materials quantity variance Labor rate variance 2 Labor efficiency variance 2 Dawson Toys, Ltd., produces a toy called the Maze. The company has recently established a standard cost system to help control costs and has established the following standards for the Maze toy: Direct materials: 8 microns per toy at $0.30 per micron Direct labor: 1.1 hours per toy at $6.80 per hour 6.68 points During July, the company produced 5,100 Maze toys. The toy's production data for the month are as follows: Direct materials: 78,000 microns were purchased at a cost of $0.28 per micron. 27,000 of these microns were still in inventory at the end of the month. Direct labor. 6,010 direct labor-hours were worked at a cost of $43,873. eBook Required: 1. Compute the following variances for July: (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round final answer to the nearest whole dollar amount.) a. The materials price and quantity variances. b. The labor rate and efficiency variances. Print References Material price variance 1a Material quantity variance Labor rate variance Labor efficiency variance 1b 3 Marvel Parts, Inc., manufactures auto accessories. One of the company's products is a set of seat covers that can be adjusted to fit evstem in nearly any small Car. The company has a standard cost system in dse tsproducts. Accordig to the standards that have been for all of its cCording to set for the seat covers, the factory should work 1,000 hours each month to produce 2,000 sets of covers. The standard costs associated with this level of production are: 6.66 Per Set points Total of Direct materials 41,400 $ 8,000 $20.70 4.00 Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead (based on direct labor-hours) 3,400 1.70 eBook $26.40 During August, the factory worked only 1,050 direct labor-hours and produced 2,400 sets of covers. The following actual costs were recorded during the month: Print Per Set References of Covers Total $ 48,000 $10,080 $ 5,040 Direct materials (7,500 yards) Direct labor $20.00 4.20 Variable manufacturing overhead 2.10 $26.30 At standard, each set of covers should require 3.0 yards of material. All of the materials purchased during the month were used in production. Required: 1. Compute the materials price and quantity variances for August. 2. Compute the labor rate and efficiency variances for August. 3. Compute the variable overhead rate and efficiency variances for August. (Indicate the effect of each variance by selecting "F" for favorable, "U" for unfavorable, and "None" for no effect (i.e., zero variance). Input all amounts as positive values.) 1. Materials price variance Materials quantity variance 2. Labor rate variance Labor efficiency variance 3. Variable overhead rate variance Variable overhead efficiency variance










