Question: 1 I understand d . that this is an open book non-supervised quiz. ded . that I am allowed access to my course material and


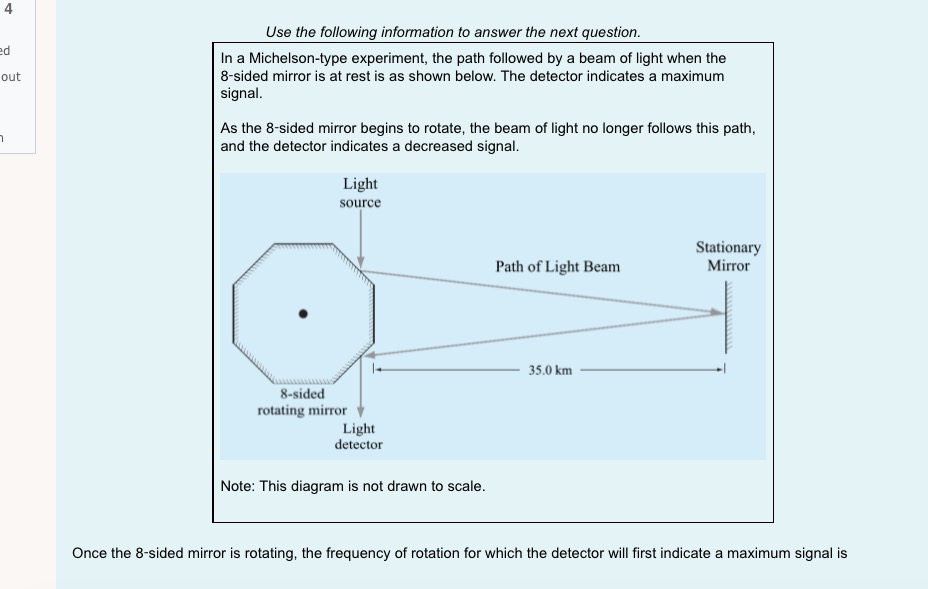

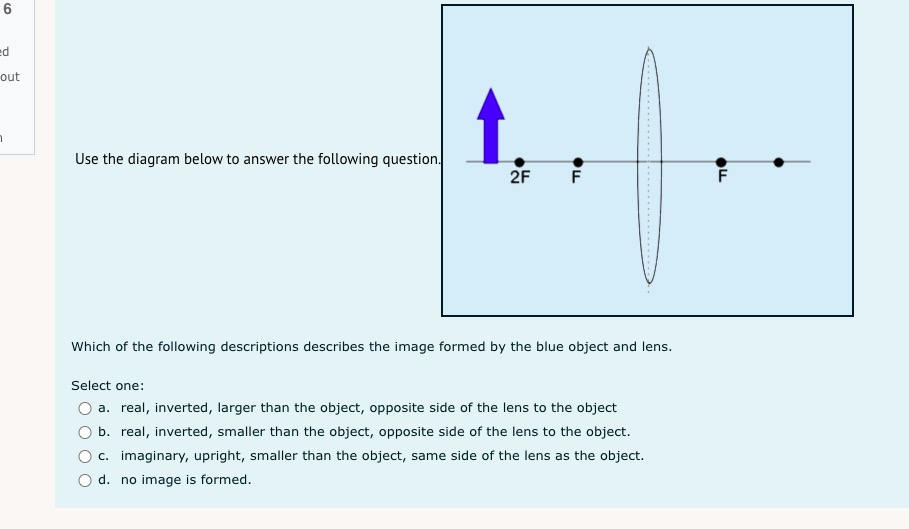

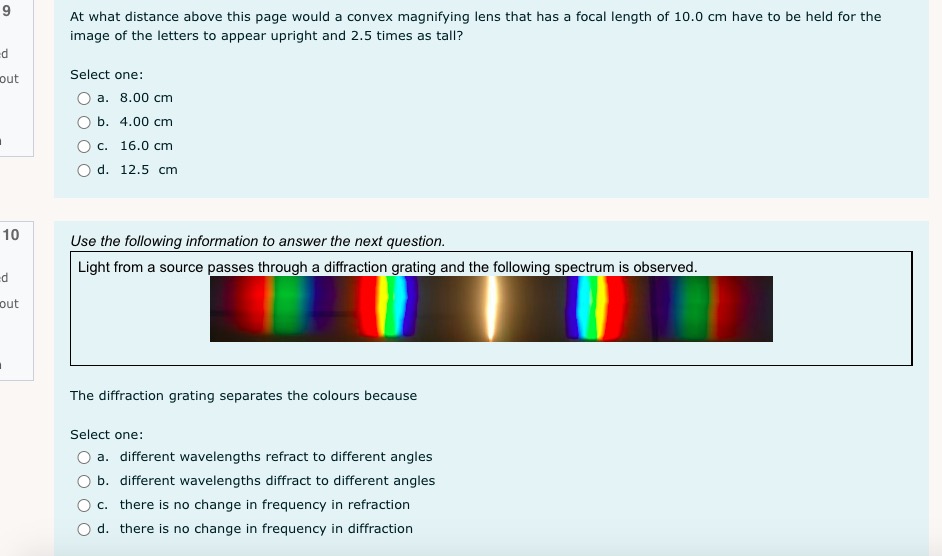
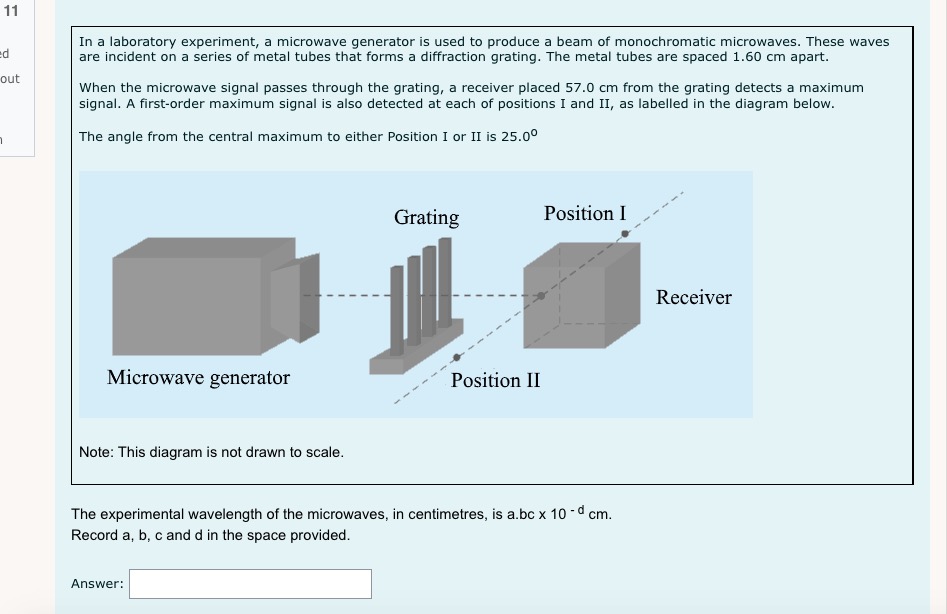
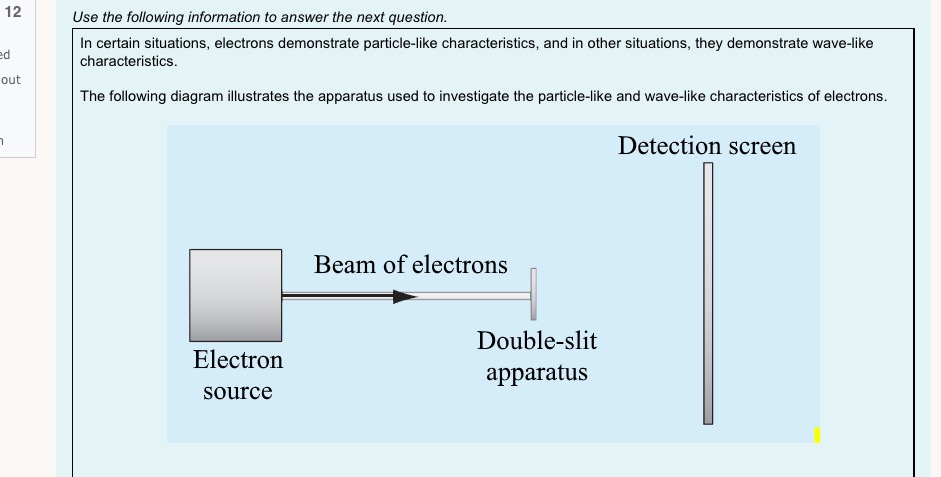
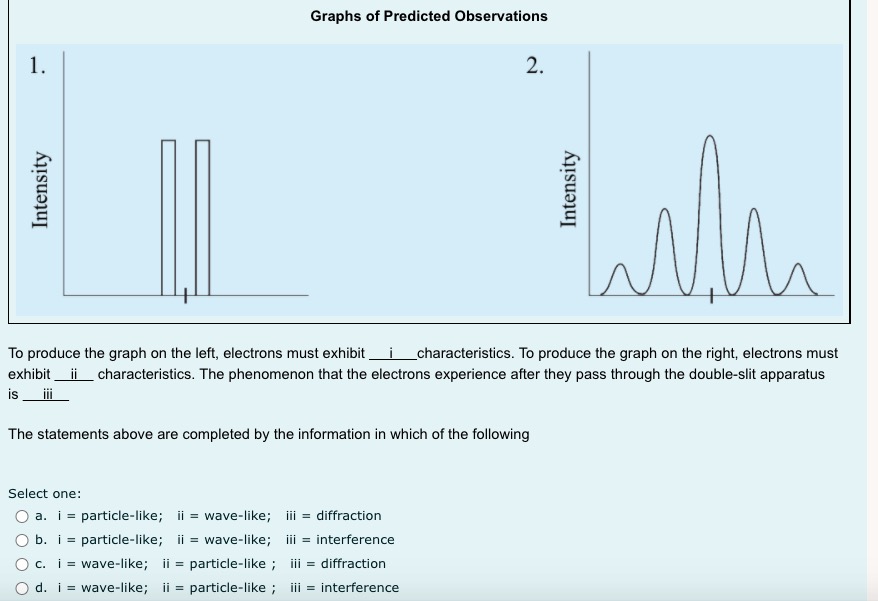




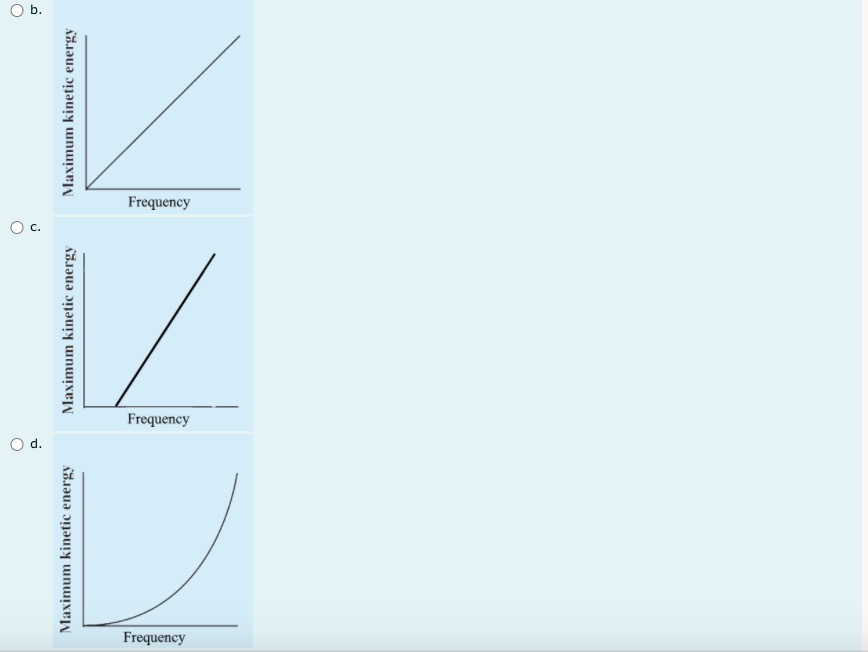


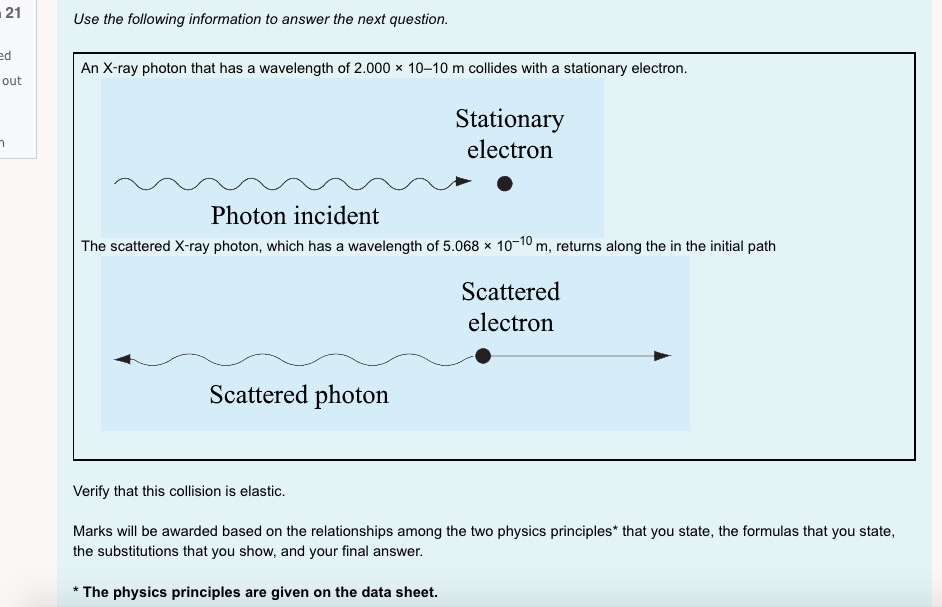
1 I understand d . that this is an open book non-supervised quiz. ded . that I am allowed access to my course material and calculator. . this quiz is to be done independently without the assistance of tutors, friends or parents. . that I need to upload my written response question prior to the time running out . that if I am caught for academic dishonesty that I will receive zero on this quiz. Select true if you understand these statements. Select one: O True O False 2 Which of the following sentences is not a property of electromagnetic radiation? Pi Select one: out a. An electromagnetic wave can not refract O b. Electromagnetic waves travel at c = 3 x 10* m/s in a vacuum. O c. Electromagnetic radiation is produced by an accelerating charge. O d. The electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.3 a) If electromagnetic radiation has a wavelength of 2.2 x 10 m, then the period of this electromagnetic radiation expressed in scientific notation is a.b x 10 . out Record a,b and c in the space below, no decimals or commas, please :) b) The type of electromagnetic radiation from part a) is A. microwave B. visible C. radio D. ultraviolet Record your response in the space below4 Use the following information to answer the next question. In a Michelson-type experiment, the path followed by a beam of light when the out 8-sided mirror is at rest is as shown below. The detector indicates a maximum signal. As the 8-sided mirror begins to rotate, the beam of light no longer follows this path, and the detector indicates a decreased signal. Light source Stationary Path of Light Beam Mirror 35.0 km 8-sided rotating mirror Light detector Note: This diagram is not drawn to scale. Once the 8-sided mirror is rotating, the frequency of rotation for which the detector will first indicate a maximum signal isOnce the 8-sided mirror is rotating, the frequency of rotation for which the detector will first indicate a maximum signal is Select one: O a. 5.36 x 10- revolutions per second O b. 1.07 x 10 revolutions per second O c. 4.29 x 10" revolutions per second O d. 8.57 x 104 revolutions per second Use the following information to answer the next question An object that is 100 cm tall is placed 35 cm in front of a particular mirror, its real image in the mirror is inverted and 45 cm tall. The mirror is_i , and the object's image is located _ ii away from the mirror. The statement above is completed by Select one: O a. i = convex, ii = 16 cm O b. i = convex, ii = 78 cm O c. i = concave, li = 16 cm O d. i = concave, ii = 78 cmUse the diagram belowto answer the following question 2FF which of the following descriptions describes the image formed by the blue object and lens. Select one: Q a. real, inverted, larger than the object, opposite side of the lens to the object O b. real, inverted, smaller than the object, opposite side of the lens to the object. O c. imaginary, upright, smaller than the object, same side of the lens as the object. Q d. no image is formed. Visible light that has a wavelength of 6.50 x 10"/m in air, is directed into obsidian. The index of refraction of obsidian 1.76. The wavelength of this light inside the obsidian expressed in scientific notation, is a.bc x 107 m. Record a, b and c in the space below out 8 Light travelling through water into glass air experiences a decrease in speed. Glass has a refractive index i than water so the light ray will bend _ ii the normal. out Select one: O a. i = greater; /i = toward O b. i = greater; ji = away from O c. i = less; ii = toward O d. i = less; ii = away from9 At what distance above this page would a convex magnifying lens that has a focal length of 10.0 cm have to be held for the image of the letters to appear upright and 2.5 times as tall? out Select one: O a. 8.00 cm O b. 4.00 cm O c. 16.0 cm O d. 12.5 cm 10 Use the following information to answer the next question. Light from a source passes through a diffraction grating and the following spectrum is observed. d out The diffraction grating separates the colours because Select one: O a. different wavelengths refract to different angles O b. different wavelengths diffract to different angles O c. there is no change in frequency in refraction O d. there is no change in frequency in diffraction11 In a laboratory experiment, a microwave generator is used to produce a beam of monochromatic microwaves. These waves d are incident on a series of metal tubes that forms a diffraction grating. The metal tubes are spaced 1.60 cm apart. out When the microwave signal passes through the grating, a receiver placed 57.0 cm from the grating detects a maximum signal. A first-order maximum signal is also detected at each of positions I and II, as labelled in the diagram below. The angle from the central maximum to either Position I or II is 25.00 Grating Position I Receiver Microwave generator Position II Note: This diagram is not drawn to scale. The experimental wavelength of the microwaves, in centimetres, is a.bc x 10 - cm. Record a, b, c and d in the space provided. Answer:Use the foiloudng information to answer me next question. In certain situations, electrons demonstrate particle-like characteristics, and in other situations, they demonstrate 1irratIe-lilte characteristics. The following diagram illustrates the apparatus used to investigate the particle-like and wave-like characteristics of electrons. Detection screen Beam of electrons Doubleslit apparatus Electron source Graphs of Predicted Observations 1. 2* e 35" s E a. .5 To produce the graph on the left, electrons must exhibit i characteristics. To produce the graph on the right, electrons must exhibit ii characteristics. The phenomenon that the electrons experience alter they pass through the double~slit apparatus is iii The statements above are completed by the information in which of the following Select one: Q a. i = particle-like; ii a wave-like; iii a diffraction O b. i = particle-like; ii 2 wave-like; iii 2 interference C} c. i =- wave-like; ii In particle-like ; iii 2: diffraction Q d. i - wave-like; ii - particle-like ; iii - interference 13 A metal has a work function of 3.10 x 10 20 J. Light with a frequency of 6.28 x 1014 Hz is incident on the metal. The stopping voltage is ........... d out Record your three-dig answer in the space below. If applicable, remember to include the decimal.14 Use the following information to answer the next question. A satellite in orbit around Earth is exposed to radiation from the Sun. This radiation may cause the satellite to become positively charged, in other words, lose electrons. out Some Wavelengths Incident on a Satellite 1 2.81 x 10-7 m 11 2.91 x 10-7 m Ill 4.18x 10-7 m IV 5.35 x 10-7 m Titanium is commonly used to coat satellites and has a work function of 6.6 x 10-19 J. Which of the wavelengths listed above would cause a satellite with a titanium coating to become positively charged? Select one: O a. Wavelength I only O b. Wavelength IV only O c. Wavelengths I and II O d. Wavelengths Ill and IV15 If the stopping potential of a photocell is 8.90 V, then the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron emitted is Select one: out O a. 1.42 x 10 18 J O b. 8.90 ] O c. 5.56 x 1019 ] O d. 1.80 x 10-2016 Electromagnetic radiation of constant wavelength is incident on a metal cathode, and the photoelectric effect is observed. Which of the following graphs represents the relationship between the maximum kinetic energy of the emitted photoelectrons and the d frequency of the incident radiation? out Select one: O a. Maximum kinetic energy FrequencyO b. Maximum kinetic energy Frequency O c. Maximum kinetic energy Frequency O d. Maximum kinetic energy Frequency17 A proton is moving at 2.5x 10 m/s to the right across your screen when it encounters a 3.7 x 10" T magnetic field that is perpendicular to its direction of travel. d What is the radius of the circular path the proton makes? out Select one: O a. 3.9 x 10 5 m O b. 1.1 x 10 5 m O c. 2.5 x 10-2 m O d. 7.1 m 18 Supported by the Compton effect, deBroglie hypothesized the concept of Select one: out O a. wave-particle duality O b. the wave nature of matter O c. the particle nature of light O d. the particle nature of matter 19 The significance of Michelson's experiment was that it provided evidence that light has d Select one: out O a. Mass O b. Momentum O c. Wave properties O d. a speed close to 3.00 x 108 m/s20 Solar wind is hot plasma ejected from the surface of the Sun. The plasma consists, in part, of electrons. de Broglie hypothesized that a moving particle has a wavelength that relates to its momentum, given by the formula below. d 1 = h out The wavelength of one solar-wind electron that has a measured speed of 1.7 x 10 m/s is Select one: O a. 4.3 x 10 10 m O b. 7.3 x 10* m O c. 6.4 x 10-13 m O d. 4.0 x 10' m21 Use the following information to answer the next question. An X-ray photon that has a wavelength of 2.000 x 10-10 m collides with a stationary electron. out Stationary electron Photon incident The scattered X-ray photon, which has a wavelength of 5.068 x 10-1 m, returns along the in the initial path Scattered electron Scattered photon Verify that this collision is elastic. Marks will be awarded based on the relationships among the two physics principles* that you state, the formulas that you state, the substitutions that you show, and your final answer. * The physics principles are given on the data sheet
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


