Question: 1. In the lab, you will be analyzing the collisions of two pucks on an air table. The pucks are connected to an electric pulsing
1. In the lab, you will be analyzing the collisions of two pucks on an air table. The pucks are connected to an electric pulsing system that provides a brief electric pulse 60 times per second. Each pulse results in a spark being produced between the puck and the table. By placing a sheet of paper between the puck and the table, we can use the sparks to record the position of the pucks at regular intervals. The trails of spark marks look like this:
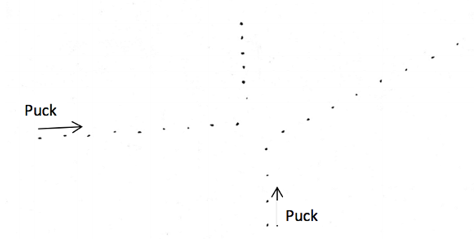
2. How much time passes between two consecutive marks, in MILLISECONDS?
3. Using a ruler, we determine that the distance between points X and Y in the figure is ____ cm. What
is the speed of puck 2 after the collision, in cm/s?
However, we will measure distances with a cheap plastic ruler, and that imposes limitations to the precision of the measurement. A safe estimation of the uncertainty to our measurement of the distance between points X and Y due to the precision of the ruler is plus or minus 0.1 cm (both due to the cheap construction of the measuring tool and due to reading errors). As discussed in previous labs, this uncertainty needs to be propagated through calculations.
6. What is the uncertainty in the speed of puck 2 after the collision, in cm/s? Round up your result to two significant figures.
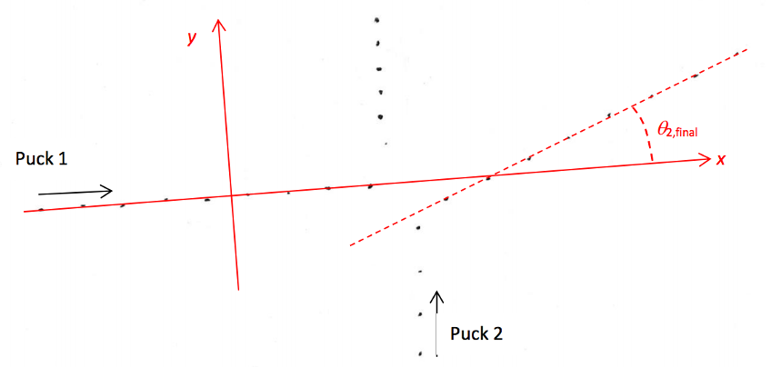
Using this angle(23 degrees), we can now determine the components of the velocity of puck 2 after the collision. For instance, find the component in the x direction, vx , in cm/s:
Let us take the uncertainty in theta 2 final,final to be ?0.5cm. Using this and the uncertainty in the speed from question 6, what is then the uncertainty in the x compoment of the velocity, in cm/s?
X & y are below
Since velocities are vectors, we need to worry about direction. Let us take the x axis along the initial direction of puck 1, and y axis perpendicular to that and pointing up. Using a protractor, we determine the angle between the x-axis and the direction of motion of puck 2 after the collision, ? 2,final = 23?.
Puck Puck Puck 1 Puck 2 2,final
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (142 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To solve these questions lets go step by step 2 Time Between Consecutive Marks Question How much time passes between two consecutive marks in millisec... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


