Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. In this problem we will investigate image aberration due to a spherical lens surface, otherwise known as spherical aberration. In the figure below
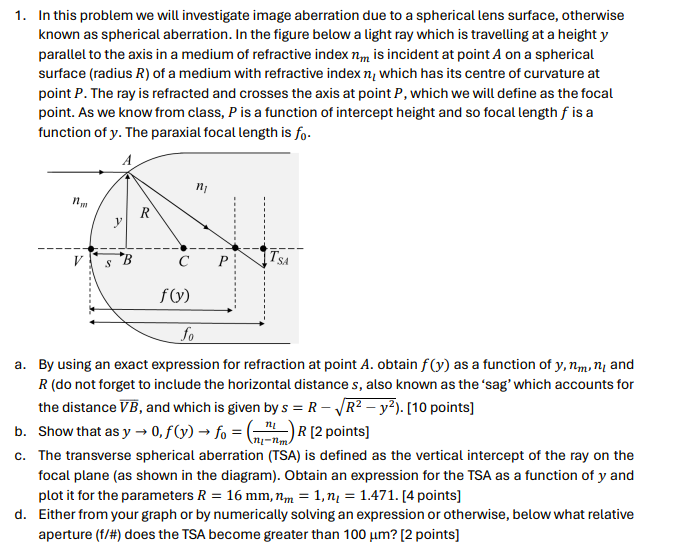
1. In this problem we will investigate image aberration due to a spherical lens surface, otherwise known as spherical aberration. In the figure below a light ray which is travelling at a height y parallel to the axis in a medium of refractive index nm is incident at point A on a spherical surface (radius R) of a medium with refractive index n, which has its centre of curvature at point P. The ray is refracted and crosses the axis at point P, which we will define as the focal point. As we know from class, P is a function of intercept height and so focal length f is a function of y. The paraxial focal length is fo. A y R V B C P ISA S f(y) fo a. By using an exact expression for refraction at point A. obtain f(y) as a function of y, nm, n, and R (do not forget to include the horizontal distance s, also known as the 'sag' which accounts for the distance VB, and which is given by s = R - R - y). [10 points] b. Show that as y 0, f(y) fo = (nm) R [2 points] c. The transverse spherical aberration (TSA) is defined as the vertical intercept of the ray on the focal plane (as shown in the diagram). Obtain an expression for the TSA as a function of y and plot it for the parameters R = 16 mm, nm = 1, n = 1.471. [4 points] d. Either from your graph or by numerically solving an expression or otherwise, below what relative aperture (f/#) does the TSA become greater than 100 m? [2 points]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


