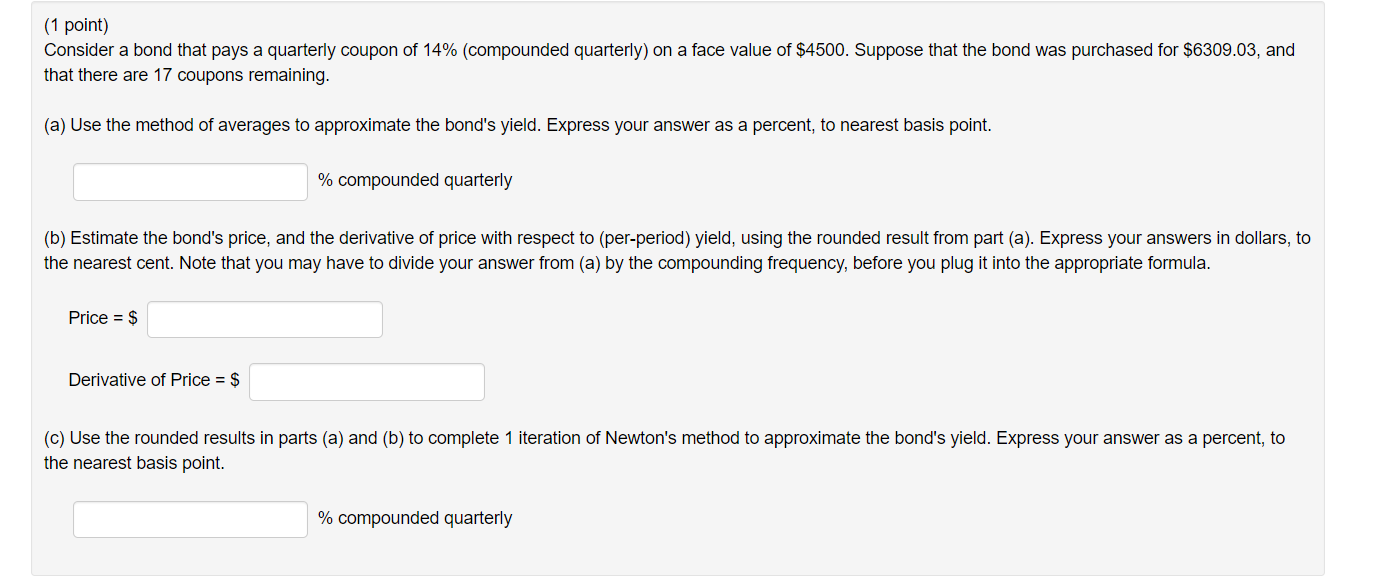
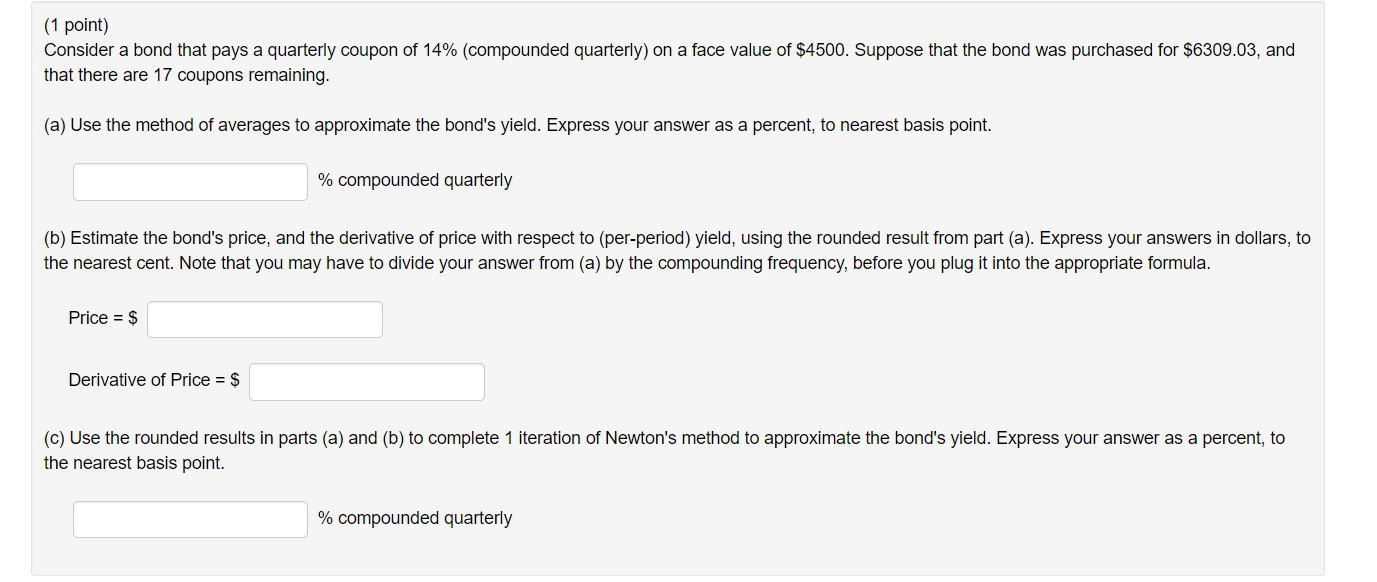
(1 point) Consider a bond that pays a quarterly coupon of 14% (compounded quarterly) on a face value of $4500. Suppose that the bond was purchased for $6309.03, and that there are 17 coupons remaining. (a) Use the method of averages to approximate the bond's yield. Express your answer as a percent, to nearest basis point. % compounded quarterly (b) Estimate the bond's price, and the derivative of price with respect to (per-period) yield, using the rounded result from part (a). Express your answers in dollars, to the nearest cent. Note that you may have to divide your answer from (a) by the compounding frequency, before you plug it into the appropriate formula. Price = $ Derivative of Price = $ (c) Use the rounded results in parts (a) and (b) to complete 1 iteration of Newton's method to approximate the bond's yield. Express your answer as a percent, to the nearest basis point. % compounded quarterly (1 point) Consider a bond that pays a quarterly coupon of 14% (compounded quarterly) on a face value of $4500. Suppose that the bond was purchased for $6309.03, and that there are 17 coupons remaining. (a) Use the method of averages to approximate the bond's yield. Express your answer as a percent, to nearest basis point. % compounded quarterly (b) Estimate the bond's price, and the derivative of price with respect to (per-period) yield, using the rounded result from part (a). Express your answers in dollars, to the nearest cent. Note that you may have to divide your answer from (a) by the compounding frequency, before you plug it into the appropriate formula. Price = $ Derivative of Price = $ (c) Use the rounded results in parts (a) and (b) to complete 1 iteration of Newton's method to approximate the bond's yield. Express your answer as a percent, to the nearest basis point. % compounded quarterly (1 point) Consider a bond that pays a quarterly coupon of 14% (compounded quarterly) on a face value of $4500. Suppose that the bond was purchased for $6309.03, and that there are 17 coupons remaining. (a) Use the method of averages to approximate the bond's yield. Express your answer as a percent, to nearest basis point. % compounded quarterly (b) Estimate the bond's price, and the derivative of price with respect to (per-period) yield, using the rounded result from part (a). Express your answers in dollars, to the nearest cent. Note that you may have to divide your answer from (a) by the compounding frequency, before you plug it into the appropriate formula. Price = $ Derivative of Price = $ (c) Use the rounded results in parts (a) and (b) to complete 1 iteration of Newton's method to approximate the bond's yield. Express your answer as a percent, to the nearest basis point. % compounded quarterly (1 point) Consider a bond that pays a quarterly coupon of 14% (compounded quarterly) on a face value of $4500. Suppose that the bond was purchased for $6309.03, and that there are 17 coupons remaining. (a) Use the method of averages to approximate the bond's yield. Express your answer as a percent, to nearest basis point. % compounded quarterly (b) Estimate the bond's price, and the derivative of price with respect to (per-period) yield, using the rounded result from part (a). Express your answers in dollars, to the nearest cent. Note that you may have to divide your answer from (a) by the compounding frequency, before you plug it into the appropriate formula. Price = $ Derivative of Price = $ (c) Use the rounded results in parts (a) and (b) to complete 1 iteration of Newton's method to approximate the bond's yield. Express your answer as a percent, to the nearest basis point. % compounded quarterly








