Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Predict/explain how you think the total momentum of an elastic collision between 2 objects is conserved. 2. Utilizing the Law of Conservation of
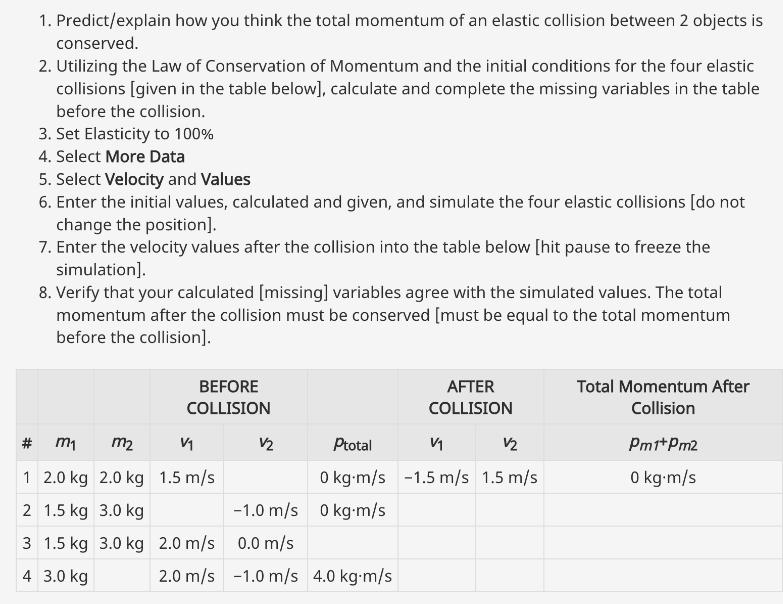

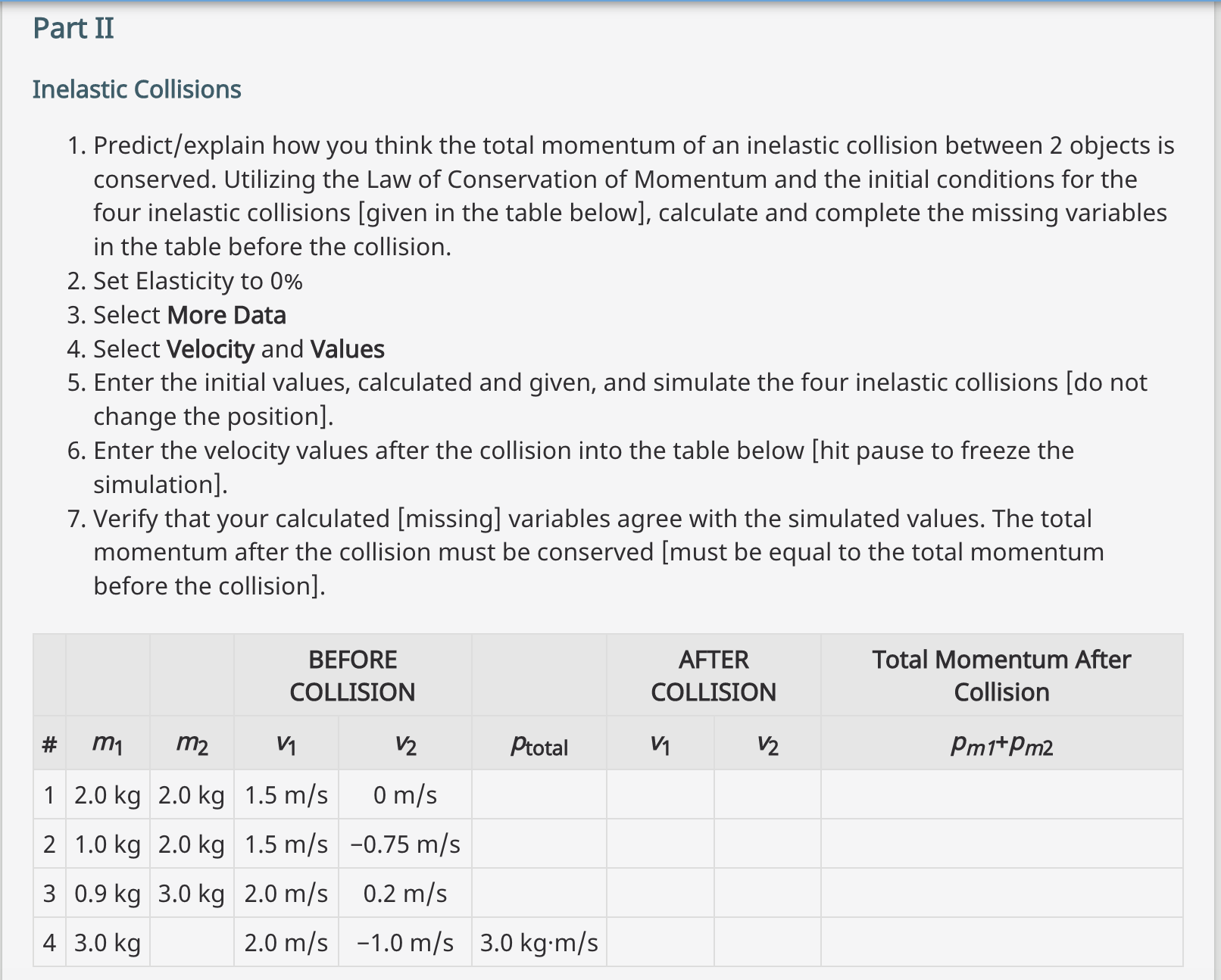

1. Predict/explain how you think the total momentum of an elastic collision between 2 objects is conserved. 2. Utilizing the Law of Conservation of Momentum and the initial conditions for the four elastic collisions [given in the table below], calculate and complete the missing variables in the table before the collision. 3. Set Elasticity to 100% 4. Select More Data 5. Select Velocity and Values 6. Enter the initial values, calculated and given, and simulate the four elastic collisions [do not change the position]. 7. Enter the velocity values after the collision into the table below [hit pause to freeze the simulation]. 8. Verify that your calculated [missing] variables agree with the simulated values. The total momentum after the collision must be conserved [must be equal to the total momentum before the collision]. BEFORE COLLISION AFTER COLLISION Total Momentum After # m m2 V V Ptotal V1 V2 Collision Pm1+Pm2 1 2.0 kg 2.0 kg 1.5 m/s 0 kg m/s -1.5 m/s 1.5 m/s 0 kg.m/s 2 1.5 kg 3.0 kg -1.0 m/s 0 kg.m/s 3 1.5 kg 3.0 kg 2.0 m/s 0.0 m/s 4 3.0 kg 2.0 m/s -1.0 m/s 4.0 kg-m/s Questions 1. Show mathematically that the total momentum [Trial #1] before the collision is conserved after the collision. 2. Two objects with the same mass move towards each other with the same speed and experience an elastic collision. Compare the final velocities of each object to their initial velocities. 3. A less-massive moving object has an elastic collision with a more-massive object that is not moving. Compare the initial velocity (speed and direction) of the less-massive object to its final velocity. 4. In your opinion, what defines a collision as being elastic? 5. Was your original hypothesis from Part I supported, or not, upon completing the simulation? [Justify your response] Part II Inelastic Collisions 1. Predict/explain how you think the total momentum of an inelastic collision between 2 objects is conserved. Utilizing the Law of Conservation of Momentum and the initial conditions for the four inelastic collisions [given in the table below], calculate and complete the missing variables in the table before the collision. 2. Set Elasticity to 0% 3. Select More Data 4. Select Velocity and Values 5. Enter the initial values, calculated and given, and simulate the four inelastic collisions [do not change the position]. 6. Enter the velocity values after the collision into the table below [hit pause to freeze the simulation]. 7. Verify that your calculated [missing] variables agree with the simulated values. The total momentum after the collision must be conserved [must be equal to the total momentum before the collision]. BEFORE COLLISION AFTER COLLISION Total Momentum After Collision # m1 m2 Vi V2 Ptotal Vi V Pm1+Pm2 1 2.0 kg 2.0 kg 1.5 m/s 0 m/s 2 1.0 kg 2.0 kg 1.5 m/s -0.75 m/s 3 0.9 kg 3.0 kg 2.0 m/s 0.2 m/s 4 3.0 kg 2.0 m/s -1.0 m/s 3.0 kgm/s Questions 1. Show mathematically that the total momentum [Trial #1] before the collision is conserved after the collision. 2. Two objects moving toward each other with different momentums experience an inelastic collision. In which direction will both objects travel after the collision? 3. A less-massive object is moving in the same direction as a more-massive object, but with a higher speed. They experience an inelastic collision. Describe the speed of the more-massive object after the collision. 4. In your opinion, what defines a collision as being inelastic? 5. Was your original hypothesis from Part II 1) supported, or not, upon completing the simulation? [Justify your response] Submit 1. Completed table from Part I. 2. Responses to questions from Part I. 3. Completed table from Part II. 4. Responses to questions from Part II. 5. Explain a real-world societal issue or technological innovation that applies the knowledge of the physics principle(s) investigated in this activity.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


