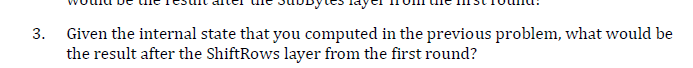
1. - - Problems 1 through 5 will used hexadecimal notation to represent bytes. The following table can be used to perform an XOR operation on hexadecimal digits: 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f -1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f 1 1 0 3 2 5 4 7 6 9 8 badcfe 212 3 0 16 7 4 5 a b 8 9 efcd 313 2 1 0 7 6 5 4 6 a 9 8 fedc 4/4 5 6 7 0 123 cdef 89 a b 515 4 7 6 1 0 3 2 dcfe98 b a 616 7 4 5 2 3 0 1 fcd a b 8 9 717 6 5 4 3 2 1 0fedcba 98 889 a b c d e f 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 998 b a dcfe 10 3 2 5 4 7 6 ala b89efcd 230 16 7 4 5 bb a 98fedc3 210 7 6 5 4 ccdef 89 a b 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 dldcfe98 b a 5 4 7 6 1 0 3 2 elefcd a b 8 9 6 7 4 5 2 3 0 1 f|fedcba 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 For example, 5 dwould give the entry in row 5 column d, which is 8 Given a plaintext block P and a round key K, with the following values: P=0001020304050607 08090A0B OCODOEOF Ko = 46369cf7 9345246d 450856fb 70c62e3e what would the internal state be after the initial AES AddRoundKey layer? 2. The AES byte substitution layer can be defined using the following table: | 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 ea ob oc od de of ------- 00163 7 77 7b f2 6b 6f c5 30 01 67 2b fe d7 ab 76 10|ca 82 9 7d fa 59 47 fo ad d4 a2 af 9c a4 72 CO 20b7 fd 93 26 36 3f f7 cc 34 a5 e5 f1 71 d8 31 15 3004 7 23 3 18 96 05 9a 07 12 80 e2 eb 27 62 75 40 | 09 83 2c 1a 1b 6e 5a a 52 36 db b3 29 e3 2f 84 5053 d1 00 ed 20 fc b1 5b 6a cb be 39 4a 4c 58 cf 60 do ef aa fb 43 4d 33 85 45 79 02 7f 50 30 9f a8 7051 a3 40 8f 92 9d 38 f5 bc b6 da 21 10 ff f3 d2 80 cd Oc 13 ec 5f 97 44 17 c4 a7 7e 3d 64 5d 19 73 9060 81 45 dc 22 2a 90 88 46 ee b8 14 de 5e ob db a0e0 32 3a Oa 49 06 24 5c c2 d3 ac 62 91 95 e4 79 bole7 08 37 6d 8d d5 4e a9 6c 56 f4 ea 65 7a ae 08 coba 78 25 2e 1c a6 b4 c6 e8 dd 74 1f 4b bd 8b 8a do 70 3e 65 66 48 03 f6 De 61 35 57 69 86 c1 1d 9e ebel f8 98 11 69 d9 8e 94 9b le 87 9 ce 55 28 df f08c al 89 od bf e6 42 68 41 99 2d of bo 54 bb 16 The row headings represent the first four bits of the input byte while the column headings represent the last four bits of the input byte. The entries in the table are the corresponding output bytes for an input byte whose first four bits match the row heading and whose last four bits match the column heading. For example, the input byte b4 would translate to the entry in row bo and column 04, which is 8d. Given the resulting internal state that you computed in the previous problem, what would be the result after the SubBytes layer from the first round? 3. Given the internal state that you computed in the previous problem, what would be the result after the ShiftRows layer from the first round