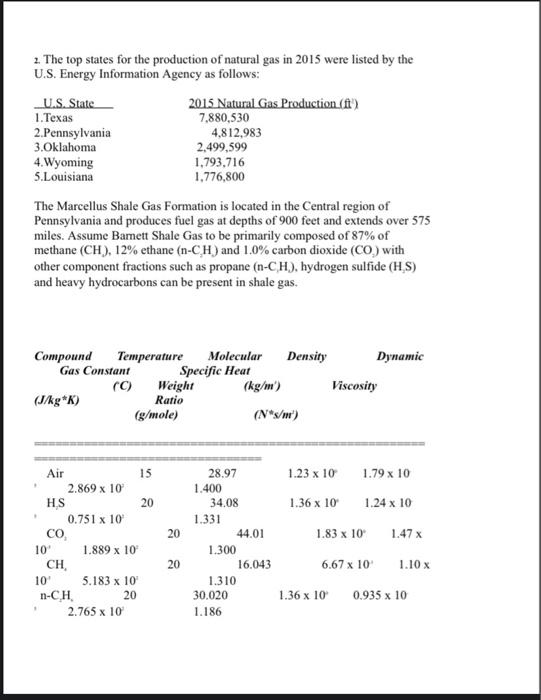
1. Red Bull Stratos - Space Jump On October 14, 2012, Austrian BASE jumper and professional skydiver *Fearless' Felix Baumgartner was elevated to a height of 38,969 m (127,851 ft) into the Earth's stratosphere and performed a freefall jump over the Roswell International Air Center in Roswell, New Mexico. During this freefall jump, Felix Baumgartner reached a maximum speed of March 1.25 (377.12 m/s or 843.6 miles/hr) and deployed his parachute after 4 minutes and 19 seconds and landed in the New Mexico desert approximately 10 minutes after beginning the jump. Please answer these questions. a.) Using tabulated reference information and calculated methods, determine the percent change in air density from the New Mexico desert to the launch point of Baumgartner's space jump. Please include all given information and state all assumptions. b.) Using the information from Part (a.), determine two relationships for air density as a function of elevation. Assuming constant gravity acceleration, derive two pressure distribution equations in the Earth's stratosphere. Please include all given information and state all assumptions. c.) Using the information from Part (b.), determine the effects on the air density (in kg/m) on the pressure distribution using these two new relationships. Using MS Excel plot both air density distributions and the pressure distribution as functions of elevation on two separate graphs. Please include all given information and state all assumptions. d.) Using Newton's Equations of Motion, estimate the distance that Felix Baumgartner traveled and his velocity profile before the deployment of his parachute. Using MS Excel, plot the velocity profile of Baumgartner before parachute deployment as functions of time and elevation. Please include all given information and state all assumptions. 2. The top states for the production of natural gas in 2015 were listed by the U.S. Energy Information Agency as follows: U.S. State 2015 Natural Gas Production (ft) 1.Texas 7,880,530 2.Pennsylvania 4,812,983 3.Oklahoma 2.499,599 4. Wyoming 1.793,716 5.Louisiana 1.776,800 The Marcellus Shale Gas Formation is located in the Central region of Pennsylvania and produces fuel gas at depths of 900 feet and extends over 575 miles. Assume Barnett Shale Gas to be primarily composed of 87% of methane (CH), 12% ethane (n-CH) and 1.0% carbon dioxide (CO) with other component fractions such as propane (n-CH), hydrogen sulfide (HS) and heavy hydrocarbons can be present in shale gas. Compound Temperature Molecular Density Gas Constant Specific Heat (C) Weight (kg/m) (J/kg *K) Ratio (g/mole) (N*s/) Dynamic Viscosity 1.23 x 10 1.79 x 10 1.36 x 10 1.24 x 10 20 1.83 x 10 1.47 x Air 15 2.869 x 10 HS 20 0.751 x 10 CO 10 1.889 x 10 CH 5.183 x 10 n-CH 20 2.765 x 10 28.97 1.400 34.08 1.331 44.01 1.300 16.043 1.310 30.020 1.186 20 6.67 x 10 1.10 10 1.36 x 10 0.935 x 10 20 n-CH 1.885 x 10 44.097 1.126 2.01 x 100.815 x 10 Location of Marcellus Shale Fields (U.S.A.) Marcellus to Atlantic Coast Pipeline Planned Route a.) If the natural gas extracted from the Marcellus Shale Gas Formation is compressed at standard temperature to 25 MPa (3,626 psia), estimate the average molecular weight and gas density of the compressed natural gas (CNG) assuming Ideal Gas conditions. Calculate the annual moles and metric tons of natural gas produced in Pennsylvania back in 2015. b.)If the natural gas produced in (a.) is directed through a steel piping with inner diameter 75 centimeters, calculate the volumetric flow rate required of the CNG to create a Mach number of 1.65 and the Reynolds Number 3. The intraocular pressure (IOP), or eye pressure, of an elderly patient previously diagnosed with pseudoexfoliation glaucoma is measured using tonometry. Pseudoexfoliation (PEX) glaucoma is a disease that causes the production of small protein fibers in the eye that impairs vision and can lead to blindness. Ocular tonometry uses various techniques to apply a force with to the cross-sectional area of the eye's membrane wall (or cornea) and this force can be calculated using the Imbert-Fick Law Intraocular Pressure (IOP) Eve Contact Force Area of Eye Contact healthy test patient was tested using ocular tonometry and her reading was 18.4 mmHg (760 mmHg = 101.325 kPa = 14.71 psia = 1.0142188 x 10 dynes/cm). Later a PEX patient was tested and the recorded reading was 11.75 mmHg. Ocular Tonometry System Inclined Manometry System (a.) If the intraocular pressure was measured using an inclined manometer using Red Palm Oil at Points A and B with a mercury manometer fluid, determine the differential readings along the manometer in inches for both patients. Use the physical properties from the table from Class Activity #1. State assumptions. Assume constant fluid density. (I foot - 12 inches = 30.48 cm -0.3048 m). (b.) If the average cornea surface area in humans is 153 mm (1 m=10 cm= 10' mm), determine the eye contact force for both patients in dynes (I dyne = 1 g*cm/s = 2.2481 x 10* Ib-force = 10 Newtons) and also calculate the percent change in eye contact force. 1. Red Bull Stratos - Space Jump On October 14, 2012, Austrian BASE jumper and professional skydiver *Fearless' Felix Baumgartner was elevated to a height of 38,969 m (127,851 ft) into the Earth's stratosphere and performed a freefall jump over the Roswell International Air Center in Roswell, New Mexico. During this freefall jump, Felix Baumgartner reached a maximum speed of March 1.25 (377.12 m/s or 843.6 miles/hr) and deployed his parachute after 4 minutes and 19 seconds and landed in the New Mexico desert approximately 10 minutes after beginning the jump. Please answer these questions. a.) Using tabulated reference information and calculated methods, determine the percent change in air density from the New Mexico desert to the launch point of Baumgartner's space jump. Please include all given information and state all assumptions. b.) Using the information from Part (a.), determine two relationships for air density as a function of elevation. Assuming constant gravity acceleration, derive two pressure distribution equations in the Earth's stratosphere. Please include all given information and state all assumptions. c.) Using the information from Part (b.), determine the effects on the air density (in kg/m) on the pressure distribution using these two new relationships. Using MS Excel plot both air density distributions and the pressure distribution as functions of elevation on two separate graphs. Please include all given information and state all assumptions. d.) Using Newton's Equations of Motion, estimate the distance that Felix Baumgartner traveled and his velocity profile before the deployment of his parachute. Using MS Excel, plot the velocity profile of Baumgartner before parachute deployment as functions of time and elevation. Please include all given information and state all assumptions. 2. The top states for the production of natural gas in 2015 were listed by the U.S. Energy Information Agency as follows: U.S. State 2015 Natural Gas Production (ft) 1.Texas 7,880,530 2.Pennsylvania 4,812,983 3.Oklahoma 2.499,599 4. Wyoming 1.793,716 5.Louisiana 1.776,800 The Marcellus Shale Gas Formation is located in the Central region of Pennsylvania and produces fuel gas at depths of 900 feet and extends over 575 miles. Assume Barnett Shale Gas to be primarily composed of 87% of methane (CH), 12% ethane (n-CH) and 1.0% carbon dioxide (CO) with other component fractions such as propane (n-CH), hydrogen sulfide (HS) and heavy hydrocarbons can be present in shale gas. Compound Temperature Molecular Density Gas Constant Specific Heat (C) Weight (kg/m) (J/kg *K) Ratio (g/mole) (N*s/) Dynamic Viscosity 1.23 x 10 1.79 x 10 1.36 x 10 1.24 x 10 20 1.83 x 10 1.47 x Air 15 2.869 x 10 HS 20 0.751 x 10 CO 10 1.889 x 10 CH 5.183 x 10 n-CH 20 2.765 x 10 28.97 1.400 34.08 1.331 44.01 1.300 16.043 1.310 30.020 1.186 20 6.67 x 10 1.10 10 1.36 x 10 0.935 x 10 20 n-CH 1.885 x 10 44.097 1.126 2.01 x 100.815 x 10 Location of Marcellus Shale Fields (U.S.A.) Marcellus to Atlantic Coast Pipeline Planned Route a.) If the natural gas extracted from the Marcellus Shale Gas Formation is compressed at standard temperature to 25 MPa (3,626 psia), estimate the average molecular weight and gas density of the compressed natural gas (CNG) assuming Ideal Gas conditions. Calculate the annual moles and metric tons of natural gas produced in Pennsylvania back in 2015. b.)If the natural gas produced in (a.) is directed through a steel piping with inner diameter 75 centimeters, calculate the volumetric flow rate required of the CNG to create a Mach number of 1.65 and the Reynolds Number 3. The intraocular pressure (IOP), or eye pressure, of an elderly patient previously diagnosed with pseudoexfoliation glaucoma is measured using tonometry. Pseudoexfoliation (PEX) glaucoma is a disease that causes the production of small protein fibers in the eye that impairs vision and can lead to blindness. Ocular tonometry uses various techniques to apply a force with to the cross-sectional area of the eye's membrane wall (or cornea) and this force can be calculated using the Imbert-Fick Law Intraocular Pressure (IOP) Eve Contact Force Area of Eye Contact healthy test patient was tested using ocular tonometry and her reading was 18.4 mmHg (760 mmHg = 101.325 kPa = 14.71 psia = 1.0142188 x 10 dynes/cm). Later a PEX patient was tested and the recorded reading was 11.75 mmHg. Ocular Tonometry System Inclined Manometry System (a.) If the intraocular pressure was measured using an inclined manometer using Red Palm Oil at Points A and B with a mercury manometer fluid, determine the differential readings along the manometer in inches for both patients. Use the physical properties from the table from Class Activity #1. State assumptions. Assume constant fluid density. (I foot - 12 inches = 30.48 cm -0.3048 m). (b.) If the average cornea surface area in humans is 153 mm (1 m=10 cm= 10' mm), determine the eye contact force for both patients in dynes (I dyne = 1 g*cm/s = 2.2481 x 10* Ib-force = 10 Newtons) and also calculate the percent change in eye contact force