Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
(1) Refer to light intensity vs angle plot for the table 1, is the diode laser beam polarized? Explain. (2) What is the shape


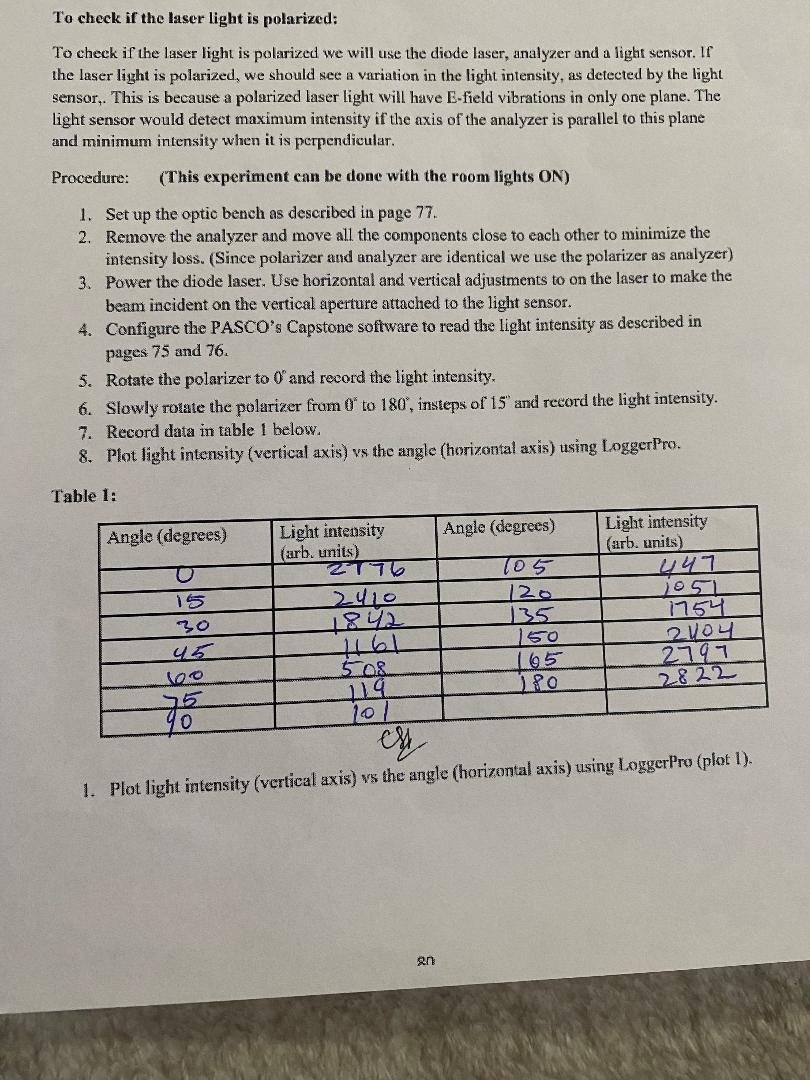
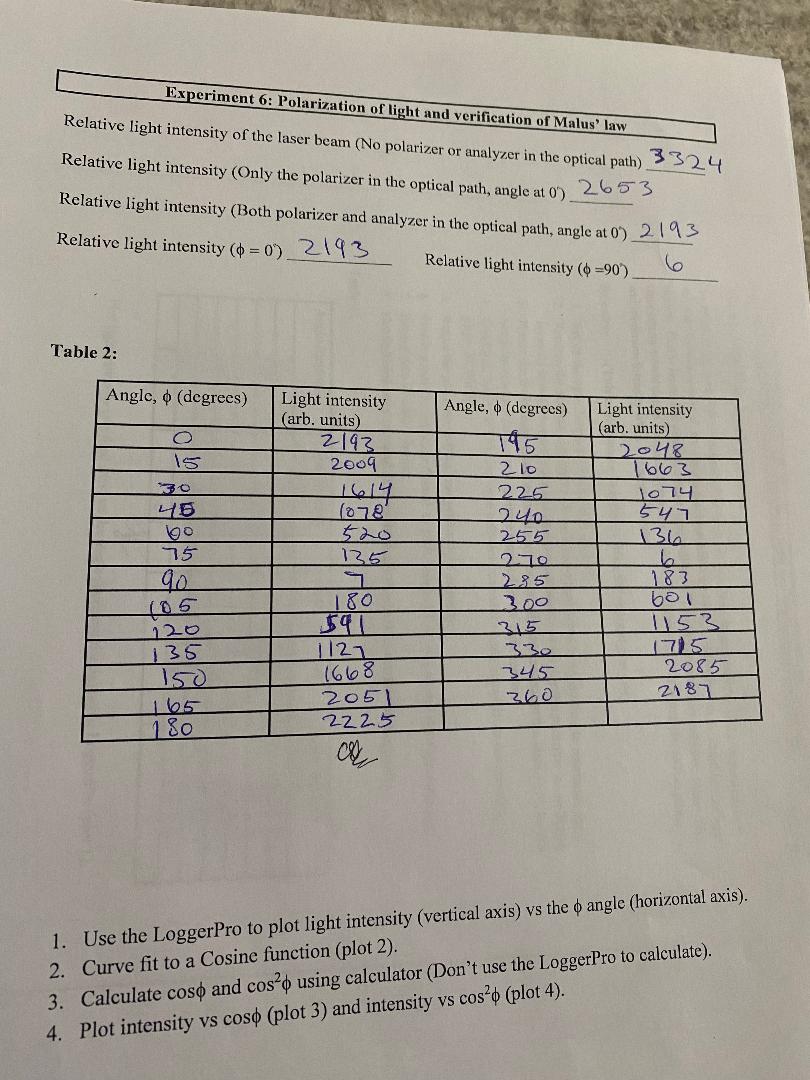
(1) Refer to light intensity vs angle plot for the table 1, is the diode laser beam polarized? Explain. (2) What is the shape of the light intensity vs angle plot? (3) Refer to the data from table-2, does your data support Malus law of polarization. Explain qualitatively and then support your answer with numbers. (4) Use the preliminary observations to answer these questions; Compared to no polarizer or analyzer in the optical path, by what percent does the light intensity decrease when (a) The polarizer is introduced into the optical path? (b) The both polarizer and analyzer are introduced into the optical path? To check if the laser light is polarized: To check if the laser light is polarized we will use the diode laser, analyzer and a light sensor. If the laser light is polarized, we should see a variation in the light intensity, as detected by the light sensor,. This is because a polarized laser light will have E-field vibrations in only one plane. The light sensor would detect maximum intensity if the axis of the analyzer is parallel to this plane and minimum intensity when it is perpendicular. Procedure: (This experiment can be done with the room lights ON) 1. Set up the optic bench as described in page 77. 2. Remove the analyzer and move all the components close to each other to minimize the intensity loss. (Since polarizer and analyzer are identical we use the polarizer as analyzer) 3. Power the diode laser. Use horizontal and vertical adjustments to on the laser to make the beam incident on the vertical aperture attached to the light sensor. 4. Configure the PASCO's Capstone software to read the light intensity as described in pages 75 and 76. 5. Rotate the polarizer to 0" and record the light intensity. 6. Slowly rotate the polarizer from 0 to 180, insteps of 15" and record the light intensity. 7. Record data in table 1 below. 8. Plot light intensity (vertical axis) vs the angle (horizontal axis) using LoggerPro. Table 1: Angle (degrees) Light intensity (arb. units) Angle (degrees) Light intensity (arb. units) 2776 105 447 15 2410 120 1051 30 1842 135 1754 45 1161 150 2004 100 508 165 2797 75 119 180 2822 0 101 er 1. Plot light intensity (vertical axis) vs the angle (horizontal axis) using LoggerPro (plot 1). 20 Experiment 6: Polarization of light and verification of Malus' law Relative light intensity of the laser beam (No polarizer or analyzer in the optical path) 3324 2653 Relative light intensity (Only the polarizer in the optical path, angle at 0). Relative light intensity (Both polarizer and analyzer in the optical path, angle at 0) 2193 Relative light intensity (= 0) 2193 Relative light intensity (=90) 6. Table 2: Angle, (degrees) Light intensity (arb. units) Angle, (degrees) O 15 2193 Light intensity (arb. units) 195 2048 2009 210 1663 30 45 1614 225 1074 1078 240 547 60 520 255 136 75 135 270 h 90 285 183 105 180 300 601 120 591 315 1153 135 1121 330 1715 150 1668 345 2085 165 2051 360 2187 180 2225 1. Use the LoggerPro to plot light intensity (vertical axis) vs the o angle (horizontal axis). 2. Curve fit to a Cosine function (plot 2). 3. Calculate cost and cos using calculator (Don't use the LoggerPro to calculate). 4. Plot intensity vs coso (plot 3) and intensity vs cos (plot 4).
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


