
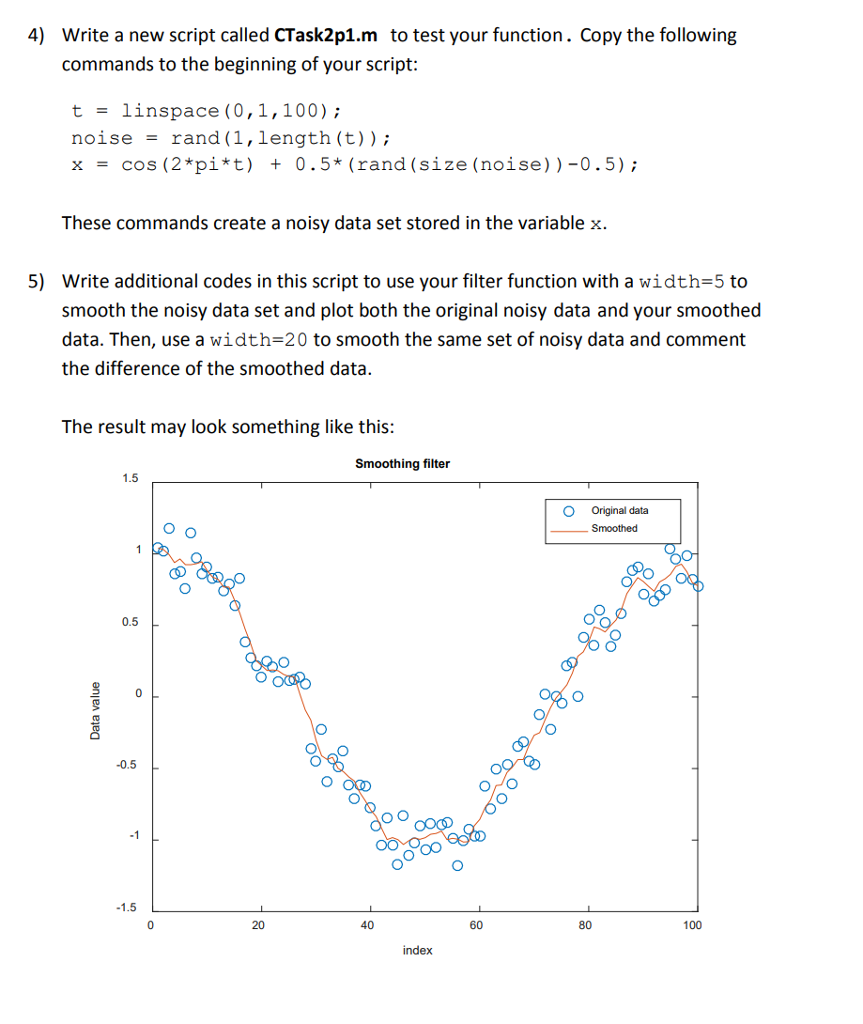
1. Smoothing filter A smoothing filter averages out rapid changes from a data set and is typically used to remove high-frequency fluctuations (e.g., measurement noise) from a signal or to reduce the amount of intensity variation between one pixel and the next one in images In this task, you will design a smoothing filter by writing a custom function with the declaration: smoothed- CTask2p1 f (x, width) and save it in a file named CTask2p1 f.m. The filter should take a vector of noisy data (x) and smooth it by doing a symmetric moving average with a window of the specified width. For points near the beginning and the end of the data set, use a smaller number of samples on either side of the samples in the average calculation, but be sure to keep an equal number of samples on either side of the sample under test. For example: If width-5 and length (x) -100 Then for n-3:98, smoothed (n) mean (x (n-2:n+2) ; for n98, x (98) , x (99 , x (100)) Note: You must write your own code to implement the smoothing algorithm rather than use any built-in MATLAB functions such as smooth. Your code should also meet the following requirements: The lengths of x and smoothed should be equal. For symmetry to work, make sure that width is odd. If it isn't, increase it by 1 to make it odd and display a warning in command window, but still do the smoothing You can use a loop and mean (which should be easy but may be slow), or more efficiently by using conv (if you are familiar withconvolution) 1) 2) 3) 1. Smoothing filter A smoothing filter averages out rapid changes from a data set and is typically used to remove high-frequency fluctuations (e.g., measurement noise) from a signal or to reduce the amount of intensity variation between one pixel and the next one in images In this task, you will design a smoothing filter by writing a custom function with the declaration: smoothed- CTask2p1 f (x, width) and save it in a file named CTask2p1 f.m. The filter should take a vector of noisy data (x) and smooth it by doing a symmetric moving average with a window of the specified width. For points near the beginning and the end of the data set, use a smaller number of samples on either side of the samples in the average calculation, but be sure to keep an equal number of samples on either side of the sample under test. For example: If width-5 and length (x) -100 Then for n-3:98, smoothed (n) mean (x (n-2:n+2) ; for n98, x (98) , x (99 , x (100)) Note: You must write your own code to implement the smoothing algorithm rather than use any built-in MATLAB functions such as smooth. Your code should also meet the following requirements: The lengths of x and smoothed should be equal. For symmetry to work, make sure that width is odd. If it isn't, increase it by 1 to make it odd and display a warning in command window, but still do the smoothing You can use a loop and mean (which should be easy but may be slow), or more efficiently by using conv (if you are familiar withconvolution) 1) 2) 3)








