Question
1. Statistical analysis involves the following type(s) of analysis? a. Descriptive Analysis b. Differences Analysis c. Associative Analysis d. Predictive Analysis e. All of the

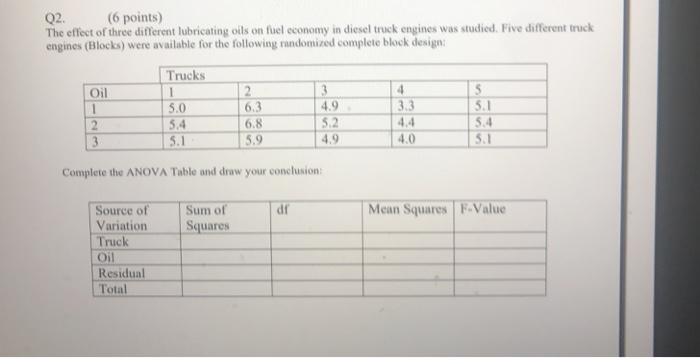


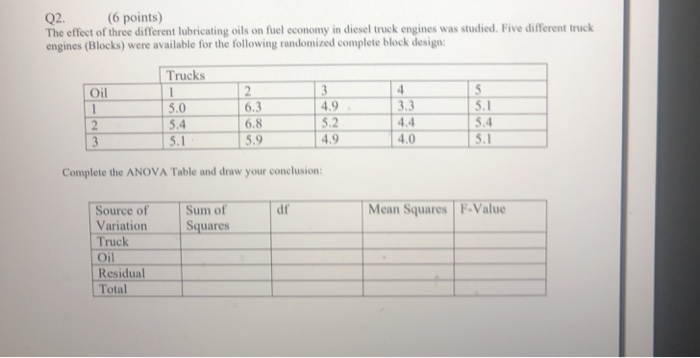
1. Statistical analysis involves the following type(s) of analysis? a. Descriptive Analysis b. Differences Analysis c. Associative Analysis d. Predictive Analysis e. All of the above 2. Differences analysis involves: a. Summarize the data b. Draw conclusions about population parameters from sample data c. Examine group differences in means d. Determine associations between two or more variables e. Forecast a variable, using other variables in a data set 3. Inferential analysis involves: a. Summarize the data b. Draw conclusions about population parameters from sample data c. Examine group differences d. Determine associations between two or more variables e. Forecast a variable, using other variables in a data set 4. Predictive analysis involves: a. Summarize the data b. Draw conclusions about population parameters from sample data c. Examine group differences d. Determine associations between two or more variables e. Forecast a variable, using other variables in a data set 5. What is a Hypothesis? a. Proposition b. Supposition c. Statement d. May include all a, b, and c but it is also empirically testable e. May include all a, b, and c but it is not empirically testable 6. What is a Null Hypothesis? a. A testable statement about no difference b. A testable proposition about no relationship c. A testable supposition about status quo d. All of the above 7. What is an Alternate Hypothesis? a. A testable statement about significant difference b. A testable proposition about significant relationship c. A testable supposition about no status quo d. All of the above 8. When representing a Hypothesis as a mathematical relationship, we use? a. Parameter Symbols b. Statistic Symbols c. Can use either d. None of the above 9. If sample size is 100, it is more appropriate to use? a. z- statistic approach b. t- statistic approach c. p- statistic approach d. Either a or b can be used with no difference 11. In one-sample t-test, we: a. Compare group mean for a variable with a test value, for statistical difference b. Compare means of two different variables from the same group, for statistical difference c. Compare means of two different groups for the same variable, for statistical difference d. All the above e. None of the above 12. In paired-sample t-test, we: a. Compare group mean for a variable with a test value, for statistical difference b. Compare means of two different variables from the same group, for statistical difference c. Compare means of two different groups for the same variable, for statistical difference d. All the above e. None of the above 13. In independent-sample t-test, we: a. Compare group mean for a variable with a test value, for statistical difference b. Compare means of two different variables from the same group, for statistical difference c. Compare means of two different groups for the same variable, for statistical difference d. All the above e. None of the above 14. What type of test is reported in the above SPSS output-1? a. one-sample t test b. paired sample t test c. independent sample t test d. dependent sample t test e. unpaired sample t test 15. What is the respective sample mean and test value in the above SPSS output-1? a. 37.865 and 50 b. 13.773 and 50 c. 89 and 88 d. -8.0312 and -12.1348 e. unpaired sample t test 16. Is the difference between sample mean and test value in the above SPSS output-1? a. Not significant b. Significant 17. Does the 95% confidence interval around the mean difference, between the sample mean and test value in the above SPSS output-1, captures the value of "0" or no difference? a. Yes b. No 18. What type of test is reported in the above SPSS output-2? a. one-sample t test b. paired sample t test c. independent sample t test d. dependent sample t test e. unpaired sample t test 19. Which two values we will be directly comparing for difference in the above SPSS output-2? a. 4.37 and 3.08 b. .68 and 1.40 c. 1.58 and 1.00 d. .0677 and .14 e. All the above 20. Is the difference between two means in the above SPSS output-2 significant and why? a. No, p > .05 b. Yes, p



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


