Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1) The attached figure shows a conceptual design for an infrared astronomical satellite, consisting of an optical telescope assembly and an attached spacecraft bus,


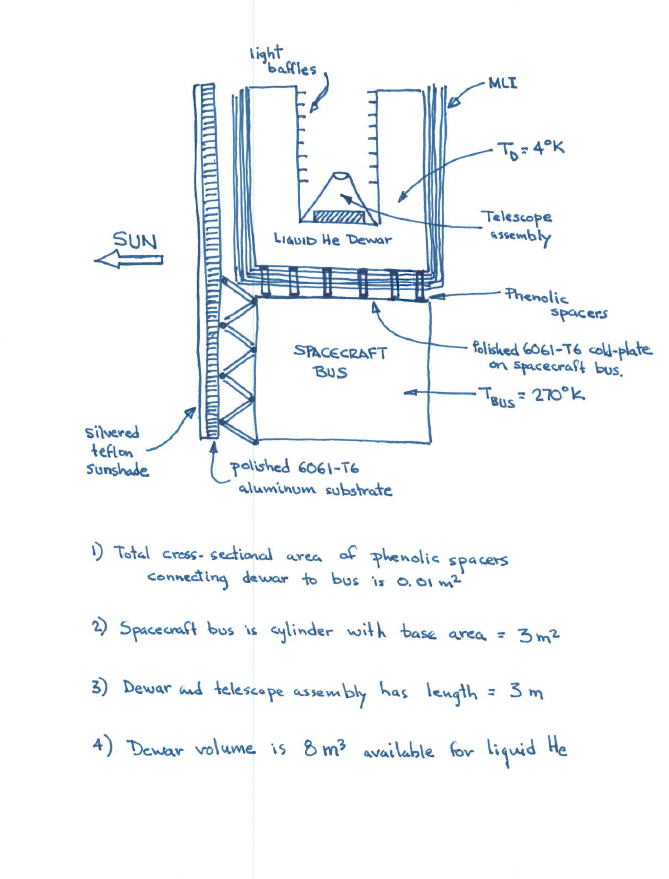
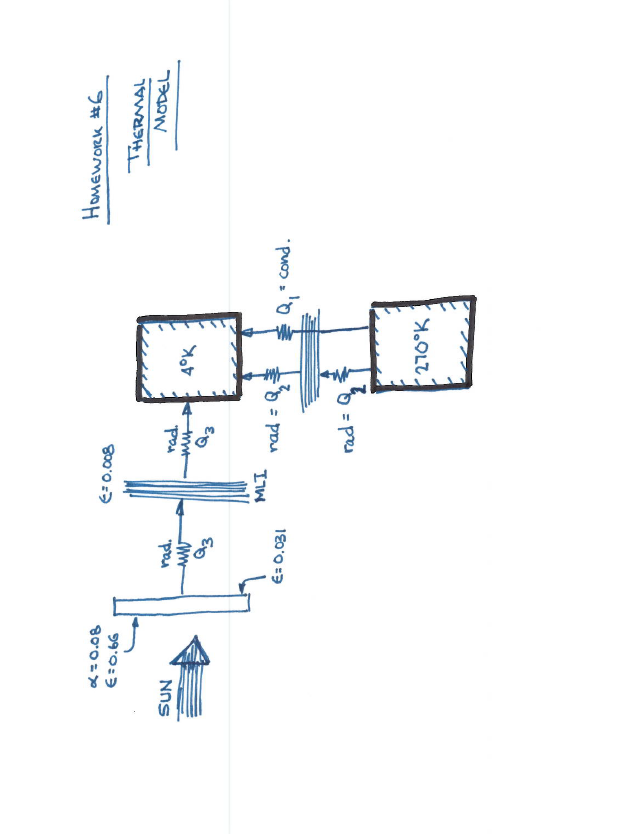
1) The attached figure shows a conceptual design for an infrared astronomical satellite, consisting of an optical telescope assembly and an attached spacecraft bus, which supplies all the non-optical functions. Because the telescope is designed to function in the far infrared, it must operate at very low temperatures. To effect this, the entire telescope assembly is surrounded by a dewar containing 8 m of liquid helium at 4 K. The liquid helium keeps the dewar walls and the telescope mirrors at this temperature by evaporating the helium in response to heat input to the system. The evaporated helium is expelled overboard; the rate of evaporation determines the operating lifetime of the system. It is therefore necessary to minimize heat input from extraneous sources. To this end, the spacecraft is deployed into geostationary orbit, where Earth radiation into the system is minimized. A sunshade, comprised of silvered teflon on a substrate of polished 6061-T6 aluminum, is used the protect the spacecraft from solar radiation. The spacecraft bus is attached to the optical telescope assembly through a set of phenolic support struts or spacers, each 10 cm long and having a total area, for all the struts, of 0.01 m2. Multilayer insulation (MLI) surrounds the dewar assembly both on its base and sides. The MLI may be taken to be of average effectiveness. The telescope has a base area of 3 m and a height of 3 m for the dewar alone. The top of the spacecraft bus, where it faces the bottom of the MLI-covered dewar, is maintained as a "cold plate" at a temperature of 270 K through the use of active cooling. This cold plate is comprised of 6061-T6 polished aluminum, just like the back of the sunshade. The spacecraft bus radiates excess heat to dark space through side-mounted radiators which do not "see" the dewar and telescope assembly. Spacing between the bus and the dewar is sufficiently small that a radiation view factor of unity between the two may be assumed. A similar assumption may be made for the view factor from the dewar to the sunshade and vice-versa. As a first approximation, we will neglect the heat flow into the telescope assembly through any wires connecting the spacecraft bus to instrumentation in the dewar and telescope. The vehicle is flown in a solar inertial orientation, with the sunshade oriented approximately perpendicular to the sun vector at all times. Observation of various IR targets is accomplished by slewing the spacecraft around the sun vector, with appropriate software logic provided to maintain keep-out zones around Earth and Moon. With the concept design shown, what length of observing time can be provided on orbit? Assume all heat flux into the dewar is from the spacecraft bus and the sunshade, i.e.; neglect any contribution from deep space black body radiation. k = thermal conductivity of phenolic = 0.0332 W/mK &B = bus emissivity = 0.031 EM = effective emissivity of MLI=0.008 qs=solar flux = 1358 W/m as = solar absorptivity of sunshade = 0.08 si = emissivity of aluminum sunshade = 0.031 E$2 emissivity of silvered teflon = 0.66 Heat of vaporization of liquid helium = 21,000 J/kg Density of liquid helium = 125.1 kg/m SUN silvered teflon Sunshade light "baffles LIQUID He Dewar SPACECRAFT BUS polished 6061-T6 aluminum substrate 1) Total cross-sectional area MLI -To=4K Telescope assembly Phenolic spacers Polished 6061-T6 cold-plate on spacecraft bus, -TBUS = 270k of phenolic spacers connecting dewar to bus is 0.01 m 2) Spacecraft bus is cylinder with base area = 3m 3) Dewar and telescope assembly has length = 3m 4) Dewar volume is 8 m available for liquid He x=0.08 =0.66 SUN rad. Q3 = 0.031 =0.008 MLI rad. my Q3 rad = 4K rad = Q 270K Q = cond. Homework #6 THERMAL MODEL
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
To estimate the observing time of the infrared astronomical satellite well need to make several assu...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


