Question
1. The design of a singly-linked list below is a picture of the function that needs to be used below is the code of the
1. The design of a singly-linked list
below is a picture of the function that needs to be used
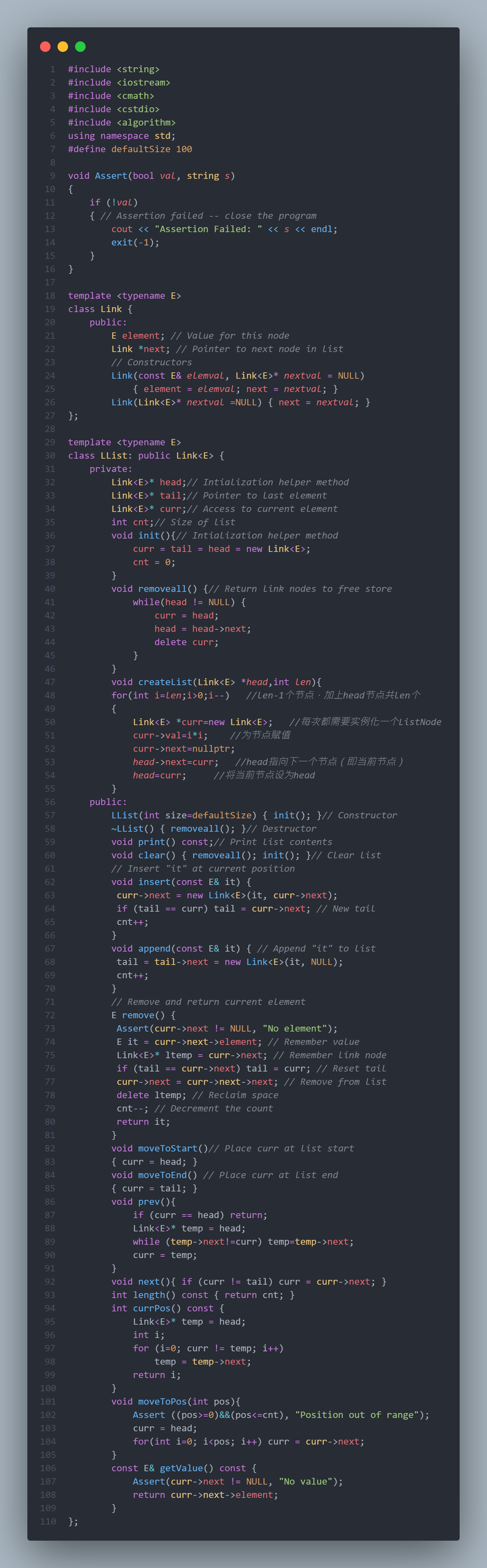
below is the code of the above picture:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define defaultSize 100
void Assert(bool val, string s)
{
if (!val)
{ // Assertion failed -- close the program
cout
exit(-1);
}
}
template
class Link {
public:
E element; // Value for this node
Link *next; // Pointer to next node in list
// Constructors
Link(const E& elemval, Link
{ element = elemval; next = nextval; }
Link(Link
};
template
class LList: public Link
private:
Link
Link
Link
int cnt;// Size of list
void init(){// Intialization helper method
curr = tail = head = new Link
cnt = 0;
}
void removeall() {// Return link nodes to free store
while(head != NULL) {
curr = head;
head = head->next;
delete curr;
}
}
public:
LList(int size=defaultSize) { init(); }// Constructor
~LList() { removeall(); }// Destructor
void print() const;// Print list contents
void clear() { removeall(); init(); }// Clear list
// Insert "it" at current position
void insert(const E& it) {
curr->next = new Link
if (tail == curr) tail = curr->next; // New tail
cnt++;
}
void append(const E& it) { // Append "it" to list
tail = tail->next = new Link
cnt++;
}
// Remove and return current element
E remove() {
Assert(curr->next != NULL, "No element");
E it = curr->next->element; // Remember value
Link
if (tail == curr->next) tail = curr; // Reset tail
curr->next = curr->next->next; // Remove from list
delete ltemp; // Reclaim space
cnt--; // Decrement the count
return it;
}
void moveToStart()// Place curr at list start
{ curr = head; }
void moveToEnd() // Place curr at list end
{ curr = tail; }
void prev(){
if (curr == head) return;
Link
while (temp->next!=curr) temp=temp->next;
curr = temp;
}
void next(){ if (curr != tail) curr = curr->next; }
int length() const { return cnt; }
int currPos() const {
Link
int i;
for (i=0; curr != temp; i++)
temp = temp->next;
return i;
}
void moveToPos(int pos){
Assert ((pos>=0)&&(pos
curr = head;
for(int i=0; i
}
const E& getValue() const {
Assert(curr->next != NULL, "No value");
return curr->next->element;
}
};
completed this code to fulfill the requirement below:
Write a function to insert an integer into a singly-linked list of elements arranged from largest to smallest. Requires that elements remain ordered after insertion.
2. The design of array-based stack
below is a picture of the function that needs to be used
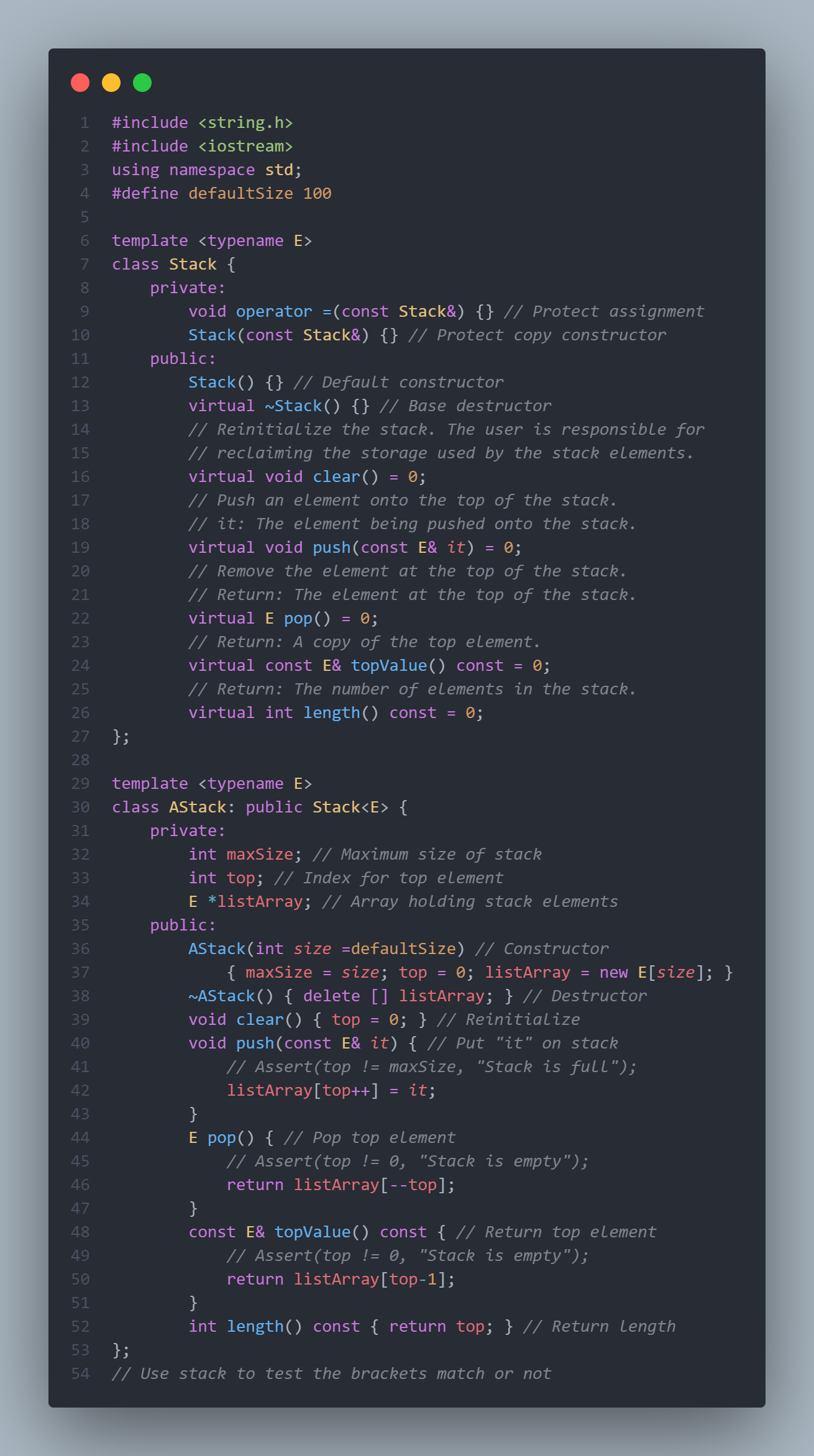
below is the code of the above picture:
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define defaultSize 100
template
class Stack {
private:
void operator =(const Stack&) {} // Protect assignment
Stack(const Stack&) {} // Protect copy constructor
public:
Stack() {} // Default constructor
virtual ~Stack() {} // Base destructor
// Reinitialize the stack. The user is responsible for
// reclaiming the storage used by the stack elements.
virtual void clear() = 0;
// Push an element onto the top of the stack.
// it: The element being pushed onto the stack.
virtual void push(const E& it) = 0;
// Remove the element at the top of the stack.
// Return: The element at the top of the stack.
virtual E pop() = 0;
// Return: A copy of the top element.
virtual const E& topValue() const = 0;
// Return: The number of elements in the stack.
virtual int length() const = 0;
};
template
class AStack: public Stack
private:
int maxSize; // Maximum size of stack
int top; // Index for top element
E *listArray; // Array holding stack elements
public:
AStack(int size =defaultSize) // Constructor
{ maxSize = size; top = 0; listArray = new E[size]; }
~AStack() { delete [] listArray; } // Destructor
void clear() { top = 0; } // Reinitialize
void push(const E& it) { // Put "it" on stack
// Assert(top != maxSize, "Stack is full");
listArray[top++] = it;
}
E pop() { // Pop top element
// Assert(top != 0, "Stack is empty");
return listArray[--top];
}
const E& topValue() const { // Return top element
// Assert(top != 0, "Stack is empty");
return listArray[top-1];
}
int length() const { return top; } // Return length
};
completed this code to fulfill the requirement below:
Write a function that uses the stack to check whether the parentheses in the string are balanced. For example, "(()(()))" is balanced, and "(()()" and "())" are unbalanced.
3. The design of array-based queue
below is a picture of the function that needs to be used
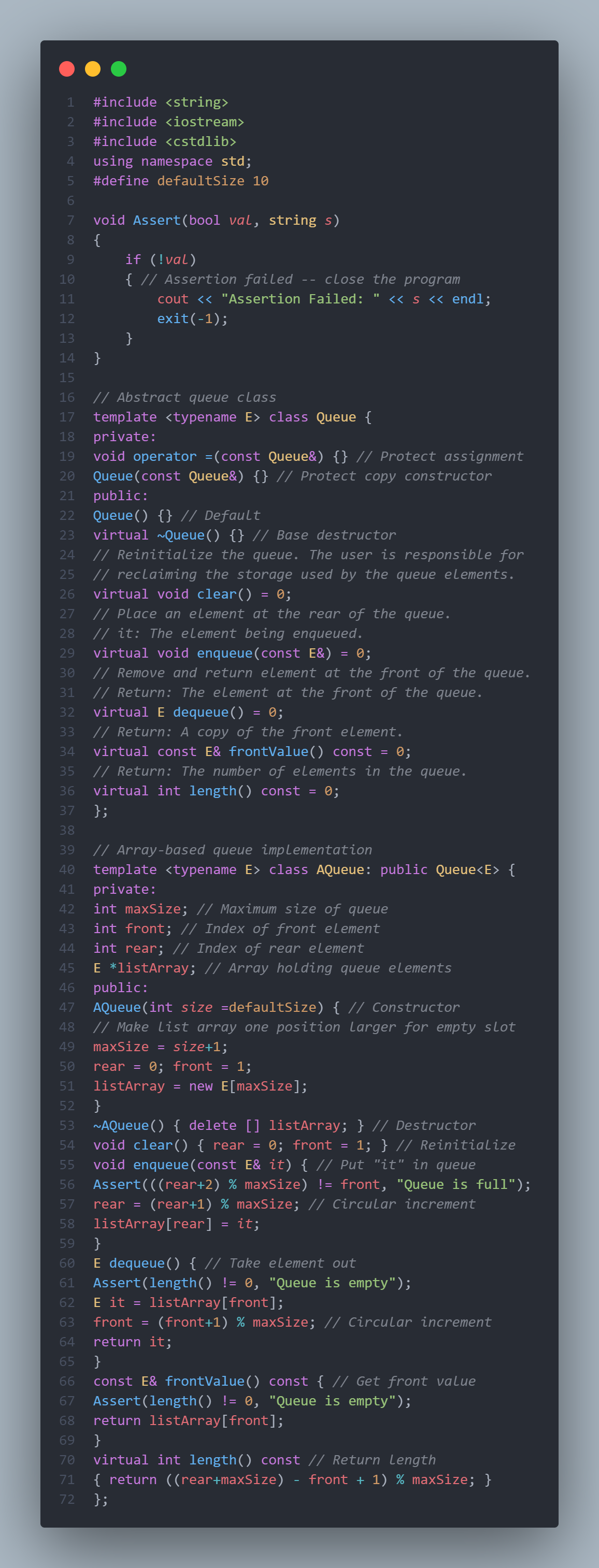
below is the code of the above picture:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define defaultSize 10
void Assert(bool val, string s)
{
if (!val)
{ // Assertion failed -- close the program
cout
exit(-1);
}
}
// Abstract queue class
template
private:
void operator =(const Queue&) {} // Protect assignment
Queue(const Queue&) {} // Protect copy constructor
public:
Queue() {} // Default
virtual ~Queue() {} // Base destructor
// Reinitialize the queue. The user is responsible for
// reclaiming the storage used by the queue elements.
virtual void clear() = 0;
// Place an element at the rear of the queue.
// it: The element being enqueued.
virtual void enqueue(const E&) = 0;
// Remove and return element at the front of the queue.
// Return: The element at the front of the queue.
virtual E dequeue() = 0;
// Return: A copy of the front element.
virtual const E& frontValue() const = 0;
// Return: The number of elements in the queue.
virtual int length() const = 0;
};
// Array-based queue implementation
template
private:
int maxSize; // Maximum size of queue
int front; // Index of front element
int rear; // Index of rear element
E *listArray; // Array holding queue elements
public:
AQueue(int size =defaultSize) { // Constructor
// Make list array one position larger for empty slot
maxSize = size+1;
rear = 0; front = 1;
listArray = new E[maxSize];
}
~AQueue() { delete [] listArray; } // Destructor
void clear() { rear = 0; front = 1; } // Reinitialize
void enqueue(const E& it) { // Put "it" in queue
Assert(((rear+2) % maxSize) != front, "Queue is full");
rear = (rear+1) % maxSize; // Circular increment
listArray[rear] = it;
}
E dequeue() { // Take element out
Assert(length() != 0, "Queue is empty");
E it = listArray[front];
front = (front+1) % maxSize; // Circular increment
return it;
}
const E& frontValue() const { // Get front value
Assert(length() != 0, "Queue is empty");
return listArray[front];
}
virtual int length() const // Return length
{ return ((rear+maxSize) - front + 1) % maxSize; }
};
completed this code to fulfill the requirement below:
Write a function that the user selects queue i (0i9), and then inserts any number of numbers into queue i. Input "#" to indicate that the user does not select any queue. At the end of the program, the non-empty queue among the 10 queues is output in the order of queue number from the smallest to the largest.
For example
Input
0(queue number)
1 3 5 7 9 8
1(queue number)
2 4 6
9(queue number)
111 222 333
#
Output
1 3 5 7 9 8 2 4 6 111 222 333
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


