Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. The following financial instruments are instruments traded in the market money except A. Malaysian Government Securities (MGS) B. Bankers' acceptance C. Negotiable instruments of





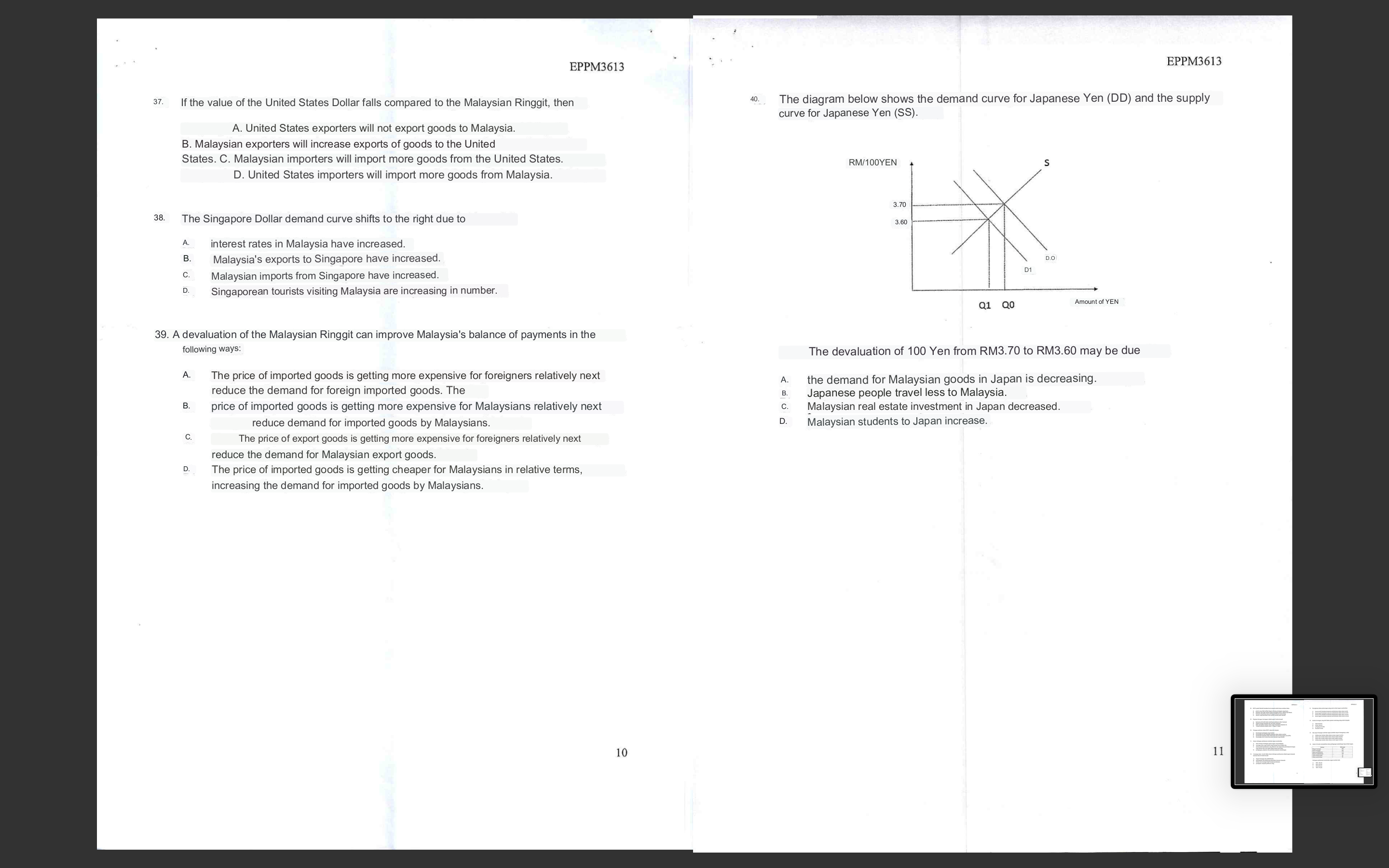 1. The following financial instruments are instruments traded in the market money except A. Malaysian Government Securities (MGS) B. Bankers' acceptance C. Negotiable instruments of deposits D. Corporate bonds 2. The payment system in the financial system in Malaysia consists of the following: I. Wholesale Payment System II. Retail Payment System III. Periodic Payment System IV. Regular Payment System A. I, II B. I, III C. II, III, IV D. I, II, III, IV 3. Financial institutions are important participants that move the financial system in a country. Which of the following is a participant in the Malaysian financial system? I. Bank Negara Malaysia II. Alliance Bank Berhad III. Employees' Provident Fund (EPF) IV. CIMB Principal Asset Management Berhad A. I, II B. I, III C. II, III, IV D. I, II, III, IV 37. If the value of the United States Dollar falls compared to the Malaysian Ringgit, then A. United States exporters will not export goods to Malaysia. B. Malaysian exporters will increase exports of goods to the United States. C. Malaysian importers will import more goods from the United States. D. United States importers will import more goods from Malaysia. 38. The Singapore Dollar demand curve shifts to the right due to A. interest rates in Malaysia have increased. B. Malaysia's exports to Singapore have increased. C. Malaysian imports from Singapore have increased. D. Singaporean tourists visiting Malaysia are increasing in number. 39. A devaluation of the Malaysian Ringgit can improve Malaysia's balance of payments in the following ways: A. The price of imported goods is getting more expensive for foreigners relatively next reduce the demand for foreign imported goods. The B. price of imported goods is getting more expensive for Malaysians relatively next reduce demand for imported goods by Malaysians. c. The price of export goods is getting more expensive for foreigners relatively next reduce the demand for Malaysian export goods. D. The price of imported goods is getting cheaper for Malaysians in relative terms, increasing the demand for imported goods by Malaysians. 40. The diagram below shows the demand curve for Japanese Yen (DD) and the supply curve for Japanese Yen (SS). The devaluation of 100 Yen from RM3.70 to RM3.60 may be due A. the demand for Malaysian goods in Japan is decreasing. B. Japanese people travel less to Malaysia. C. Malaysian real estate investment in Japan decreased. D. Malaysian students to Japan increase. 11. Treasury bills are one of the short-term financial instruments that are usually traded in the money market. Which of the following is correct about treasury bills in Malaysia? A. This instrument is a short-term debt obligation of the government to finance annual operating expenses. B. This instrument is issued by the government through its investment company, Khazanah Nasional Berhad C. This instrument is exposed to the risk of default and changes in the D. inflation rate. This instrument cannot be traded and cannot be transferred. 14. Choose the most accurate statement about Bankers' Acceptance. A. Banker's Acceptance is a financial instrument issued by a company and guaranteed by a bank. B. Banker's Acceptance is a financial instrument issued by a bank and used by a company in payment matters international trade. c. Bankers' Acceptances cannot be traded in the secondary or secondary market due to their non-transferable nature. D. A Banker's Acceptance is a debt paper with a certain coupon rate and sold at face value (par value). 12. The main characteristics of the money market are as follows: I. Instruments traded are short-term instruments II. Instruments traded have high liquidity III. The existence of the interbank market IV. Instruments such as bonds, sukuk and shares are traded in the money market A. I, II, III B. II, III, IV C. II, III D. III, IV 13. Which of the following is not the main function of the money market in Malaysia? A. Providing investment opportunities on the part that has B. excess funds. Give space to parties with deficits to increase investment. c. Assist economic units in their respective liquidity management for ensure liquidity risk can be minimized. D. Financing the company's working capital and providing short-term financing to the government other than tax collection. 15. The following are the main drivers for the existence of the Islamic money market in Malaysia except A. Islamic financial institutions are also exposed to liquidity risk which creates dependence on short-term instruments. B. Financial instruments that exist in the conventional money market prevent Islamic financial institutions from obtaining financing or making investments. The return c. on investment instruments in the conventional money market is not competitive although it requires a high investment capital. To D. enable market participants to carry out functions similar to conventional money market participants 16. The capital market is a market that A. carry out transactions for short-term securities such as treasury bills and Bank loan. carry out transactions for equity securities which are ordinary shares and preference c. shares. carry out transactions for various types of long-term securities, especially B shares. and bonds. D. conducting transactions for new securities, especially initial public offerings (IPOs). 17. An investor who intends to have ownership in a company will make the following transaction: A. Giving debt to the company. B. Buying common shares issued by the company. C. Buying bonds issued by the company. D. Become the CEO of the company. 4. Non-bank institutions are participants in the market that play an important role in fund mobility (fund mobility) from those who have excess funds to those who need those funds. The following institutions are non-bank institutions in the Malaysian money market except Export-Import Bank Malaysia Berhad Bank Simpanan Nasional Bank Kerjasama Rakyat Malaysia Berhad D. Malayan Banking Berhad 5. Commercial papers (commercial papers) refer to A. Instruments that are secured (secured) and can be redeemed at B. any time. Instruments issued for short-term financing purposes. C. Instruments that have a maturity period between 1 year and 3 years. D. Instruments that can only be issued by government-linked companies (GLCs). 6. The Islamic interbank money market (IIMM) was introduced in January 1994 to assist in the development of the Islamic financial system in Malaysia. Following are the main activities in IIMM except A. Buying and selling Islamic financial instruments among IIMM participants. B. Buying and selling sukuk, which is one of the Islamic financing instruments in Malaysia. C. Investment activities between banks through the mudharabah investment scheme between banks (MII). D. Check clearing through the Islamic interbank Check Clearing System (IICCS). 7. Which of the following is a risk inherent in the money market? . Political risk II. Default risk III. Risk of inflation rate increase IV. Market risk 8. Among the following, which statement is correct? A. Bank Negara Malaysia has no role in the money market in Malaysia due to the issuance of short-term instruments regulated by the Malaysian Securities Commission. B. The government issues treasury bills through government-linked companies (GLCs) c. The money market aims to distribute savings in the economy efficiently to support the economic growth D. of a country. The Islamic Check Clearing System is based on the principle of musyarakah and introduced to facilitate transactions in among Islamic banking institutions 9. The following statements are true about participants in the money market in Malaysia except A. Cagamas was established in 1986 and is a leader in securitization activities in Malaysia, including short-term instruments. B. RAM Holdings (RAM) is the only local credit rating agency in Malaysia. c. Permodalan Nasional Berhad (PNB) was established to encourage the ownership of shares by Bumiputeras in the corporate sector. The D. main role of the Employees' Provident Fund (EPF) is to provide retirement benefits to each of its members. 10. What is meant by financial instruments traded in the money market? A. Is a document published by an institution or organization for obtain short-term financing or purchase short-term assets. B. Is a document published by an institution or organization to obtain short-term investment and also buy short-term assets. C. Is a document published by the government and sold to agencies government only to obtain short-term financing. D. Is a document published by the government to obtain short-term investment and also buy short-term assets. A. II, III B. III, IV C. I, II, III D. I, II, III, IV 18. The main secondary capital market in Malaysia is A. Bank Negara Malaysia B. Securities Commission C. Bursa Malaysia D. CIMB Bank Berhad. 19. The following statements explain the characteristics of the capital market except A. Instruments traded are long or medium term instruments secured or unsecured. B. Traded instruments have higher liquidity than money market instruments. c. The risk of the instrument is higher, but the return is also relatively higher compared to money market instruments. D. Its secondary market is more active than the secondary market for the market money. 20. One of the following securities is not a capital market instrument ie A. Common stock. B. Priority share. C. Bonds. D. Treasury bills. 21. Sukuk is A. Shariah compliant bonds B. Islamic bank loan C. Shares Shariah compliant D. Shariah compliant preference shares. 22. The following statements explain the characteristics of the bond market in Malaysia except A. includes the government and private debt securities (PDS) markets. B. dominated by government debt securities. C. includes sukuk and bond debt securities transactions. D. including sukuk and rights securities transactions. 23. Shariah compliant shares are Shares issued with Islamic banking financing. Shares issued for Muslim investors only. Shares issued by Shariah compliant companies. D. Shares traded on Bursa Islam Malaysia Berhad (BIMB). 24. The price of trust units is based on A. Net asset value B. Net present value C. Time value of D. money Net profit value 25. The following are fund management firms in Malaysia except A. Amanah Saham Nasional Berhad B. Public Mutual Berhad C. RHB Asset Management Sdn. Bhd. D. Al-Rajhi Asset Management Berhad 26. One of the following statements is not related to unit trusts in Malaysia. A. Most unit trusts are traded on Bursa Malaysia like ordinary shares. B. Unit trust investors have the option to invest in Shariah compliant unit trusts and/or conventional unit trusts. c. The return from investment in unit trusts is usually higher than investment in fixed deposits. D. unit trusts that are offered in various types such as equity trust units, bonds, balanced and money market. 27. The following statement best explains the difference between unit trust and REITs. A. Funds in unit trusts can be invested in shares of various types of companies while REITs can only be invested in company bonds. B. Funds in unit trusts can be invested in securities of various types of companies while REITs can only be invested in securities of real estate companies. c. Unit trusts are investments for retail investors (individuals) while REITs is an investment for institutional investors -. only. Unit trusts involve a small investment value while REITs involve a D value. only. Unit trusts involve a a huge investment. 28. Shariah compliant REITS means that the unit trust only invests in A. premises that are not involved in any illegal business. B. properties that are not involved in the casino, alcohol and pork business. C. properties built without any type of debt financing. D. securities issued by Shariah compliant companies. 29. Secured loans (mortgages) are as follows except A. Derivative instruments to finance investments in the real B. estate sector. Secured by real estate or fixed assets. C. Banks are the main institutions that provide these loans. D. The loan period is between 1 and 30 years. 30. Investment returns in REITs are derived from A. The profit of the business ventured. B. Dividend gains from investing in company shares. C. Profit from the sale of new shares i.e. initial public offering (IPO) D. Profit from the rental and sale of properties owned. 31. A country's balance of payments account records A. the flow of goods among trading countries. official B. transactions that occur between governments and other governments. c. all total payments made abroad and financial receipts received from abroad within one year. D. international trade, lending and lending. 32. The main transactions recorded in a country's balance of payments account include all the items below except A. export of goods and services. B. spending by foreign tourists in the domestic economy. C. federal government budget surplus or deficit. D. income from foreign investment. 33. An increase in foreign tourism for a given country A. positive effect on the service component in the capital account. B. negative impact on the service component in the capital account. C. positive impact on the service component in the current account. D. negative impact on the service component in the current account. 34. Financial institutions that are active in the foreign exchange market consist of A. commercial banks. B. securities broker. C. commodity traders. D. all of the above. 35. If the import of goods of a country exceeds its export of goods, then A. a surplus will occur in the country's current account. B. a deficit will occur in the country's current account. C. a deficit will occur in the country's capital account. D. the surplus will occur in the country's capital account. 36. The table below shows the international trade account for a country. The country's overall balance of payments is A. -RM 60 million B. -RM 140 million C. -RM 250 million D. RM 170 million 1. The following financial instruments are instruments traded in the market money except A. Malaysian Government Securities (MGS) B. Bankers' acceptance C. Negotiable instruments of deposits D. Corporate bonds 2. The payment system in the financial system in Malaysia consists of the following: I. Wholesale Payment System II. Retail Payment System III. Periodic Payment System IV. Regular Payment System A. I, II B. I, III C. II, III, IV D. I, II, III, IV 3. Financial institutions are important participants that move the financial system in a country. Which of the following is a participant in the Malaysian financial system? I. Bank Negara Malaysia II. Alliance Bank Berhad III. Employees' Provident Fund (EPF) IV. CIMB Principal Asset Management Berhad A. I, II B. I, III C. II, III, IV D. I, II, III, IV 37. If the value of the United States Dollar falls compared to the Malaysian Ringgit, then A. United States exporters will not export goods to Malaysia. B. Malaysian exporters will increase exports of goods to the United States. C. Malaysian importers will import more goods from the United States. D. United States importers will import more goods from Malaysia. 38. The Singapore Dollar demand curve shifts to the right due to A. interest rates in Malaysia have increased. B. Malaysia's exports to Singapore have increased. C. Malaysian imports from Singapore have increased. D. Singaporean tourists visiting Malaysia are increasing in number. 39. A devaluation of the Malaysian Ringgit can improve Malaysia's balance of payments in the following ways: A. The price of imported goods is getting more expensive for foreigners relatively next reduce the demand for foreign imported goods. The B. price of imported goods is getting more expensive for Malaysians relatively next reduce demand for imported goods by Malaysians. c. The price of export goods is getting more expensive for foreigners relatively next reduce the demand for Malaysian export goods. D. The price of imported goods is getting cheaper for Malaysians in relative terms, increasing the demand for imported goods by Malaysians. 40. The diagram below shows the demand curve for Japanese Yen (DD) and the supply curve for Japanese Yen (SS). The devaluation of 100 Yen from RM3.70 to RM3.60 may be due A. the demand for Malaysian goods in Japan is decreasing. B. Japanese people travel less to Malaysia. C. Malaysian real estate investment in Japan decreased. D. Malaysian students to Japan increase. 11. Treasury bills are one of the short-term financial instruments that are usually traded in the money market. Which of the following is correct about treasury bills in Malaysia? A. This instrument is a short-term debt obligation of the government to finance annual operating expenses. B. This instrument is issued by the government through its investment company, Khazanah Nasional Berhad C. This instrument is exposed to the risk of default and changes in the D. inflation rate. This instrument cannot be traded and cannot be transferred. 14. Choose the most accurate statement about Bankers' Acceptance. A. Banker's Acceptance is a financial instrument issued by a company and guaranteed by a bank. B. Banker's Acceptance is a financial instrument issued by a bank and used by a company in payment matters international trade. c. Bankers' Acceptances cannot be traded in the secondary or secondary market due to their non-transferable nature. D. A Banker's Acceptance is a debt paper with a certain coupon rate and sold at face value (par value). 12. The main characteristics of the money market are as follows: I. Instruments traded are short-term instruments II. Instruments traded have high liquidity III. The existence of the interbank market IV. Instruments such as bonds, sukuk and shares are traded in the money market A. I, II, III B. II, III, IV C. II, III D. III, IV 13. Which of the following is not the main function of the money market in Malaysia? A. Providing investment opportunities on the part that has B. excess funds. Give space to parties with deficits to increase investment. c. Assist economic units in their respective liquidity management for ensure liquidity risk can be minimized. D. Financing the company's working capital and providing short-term financing to the government other than tax collection. 15. The following are the main drivers for the existence of the Islamic money market in Malaysia except A. Islamic financial institutions are also exposed to liquidity risk which creates dependence on short-term instruments. B. Financial instruments that exist in the conventional money market prevent Islamic financial institutions from obtaining financing or making investments. The return c. on investment instruments in the conventional money market is not competitive although it requires a high investment capital. To D. enable market participants to carry out functions similar to conventional money market participants 16. The capital market is a market that A. carry out transactions for short-term securities such as treasury bills and Bank loan. carry out transactions for equity securities which are ordinary shares and preference c. shares. carry out transactions for various types of long-term securities, especially B shares. and bonds. D. conducting transactions for new securities, especially initial public offerings (IPOs). 17. An investor who intends to have ownership in a company will make the following transaction: A. Giving debt to the company. B. Buying common shares issued by the company. C. Buying bonds issued by the company. D. Become the CEO of the company. 4. Non-bank institutions are participants in the market that play an important role in fund mobility (fund mobility) from those who have excess funds to those who need those funds. The following institutions are non-bank institutions in the Malaysian money market except Export-Import Bank Malaysia Berhad Bank Simpanan Nasional Bank Kerjasama Rakyat Malaysia Berhad D. Malayan Banking Berhad 5. Commercial papers (commercial papers) refer to A. Instruments that are secured (secured) and can be redeemed at B. any time. Instruments issued for short-term financing purposes. C. Instruments that have a maturity period between 1 year and 3 years. D. Instruments that can only be issued by government-linked companies (GLCs). 6. The Islamic interbank money market (IIMM) was introduced in January 1994 to assist in the development of the Islamic financial system in Malaysia. Following are the main activities in IIMM except A. Buying and selling Islamic financial instruments among IIMM participants. B. Buying and selling sukuk, which is one of the Islamic financing instruments in Malaysia. C. Investment activities between banks through the mudharabah investment scheme between banks (MII). D. Check clearing through the Islamic interbank Check Clearing System (IICCS). 7. Which of the following is a risk inherent in the money market? . Political risk II. Default risk III. Risk of inflation rate increase IV. Market risk 8. Among the following, which statement is correct? A. Bank Negara Malaysia has no role in the money market in Malaysia due to the issuance of short-term instruments regulated by the Malaysian Securities Commission. B. The government issues treasury bills through government-linked companies (GLCs) c. The money market aims to distribute savings in the economy efficiently to support the economic growth D. of a country. The Islamic Check Clearing System is based on the principle of musyarakah and introduced to facilitate transactions in among Islamic banking institutions 9. The following statements are true about participants in the money market in Malaysia except A. Cagamas was established in 1986 and is a leader in securitization activities in Malaysia, including short-term instruments. B. RAM Holdings (RAM) is the only local credit rating agency in Malaysia. c. Permodalan Nasional Berhad (PNB) was established to encourage the ownership of shares by Bumiputeras in the corporate sector. The D. main role of the Employees' Provident Fund (EPF) is to provide retirement benefits to each of its members. 10. What is meant by financial instruments traded in the money market? A. Is a document published by an institution or organization for obtain short-term financing or purchase short-term assets. B. Is a document published by an institution or organization to obtain short-term investment and also buy short-term assets. C. Is a document published by the government and sold to agencies government only to obtain short-term financing. D. Is a document published by the government to obtain short-term investment and also buy short-term assets. A. II, III B. III, IV C. I, II, III D. I, II, III, IV 18. The main secondary capital market in Malaysia is A. Bank Negara Malaysia B. Securities Commission C. Bursa Malaysia D. CIMB Bank Berhad. 19. The following statements explain the characteristics of the capital market except A. Instruments traded are long or medium term instruments secured or unsecured. B. Traded instruments have higher liquidity than money market instruments. c. The risk of the instrument is higher, but the return is also relatively higher compared to money market instruments. D. Its secondary market is more active than the secondary market for the market money. 20. One of the following securities is not a capital market instrument ie A. Common stock. B. Priority share. C. Bonds. D. Treasury bills. 21. Sukuk is A. Shariah compliant bonds B. Islamic bank loan C. Shares Shariah compliant D. Shariah compliant preference shares. 22. The following statements explain the characteristics of the bond market in Malaysia except A. includes the government and private debt securities (PDS) markets. B. dominated by government debt securities. C. includes sukuk and bond debt securities transactions. D. including sukuk and rights securities transactions. 23. Shariah compliant shares are Shares issued with Islamic banking financing. Shares issued for Muslim investors only. Shares issued by Shariah compliant companies. D. Shares traded on Bursa Islam Malaysia Berhad (BIMB). 24. The price of trust units is based on A. Net asset value B. Net present value C. Time value of D. money Net profit value 25. The following are fund management firms in Malaysia except A. Amanah Saham Nasional Berhad B. Public Mutual Berhad C. RHB Asset Management Sdn. Bhd. D. Al-Rajhi Asset Management Berhad 26. One of the following statements is not related to unit trusts in Malaysia. A. Most unit trusts are traded on Bursa Malaysia like ordinary shares. B. Unit trust investors have the option to invest in Shariah compliant unit trusts and/or conventional unit trusts. c. The return from investment in unit trusts is usually higher than investment in fixed deposits. D. unit trusts that are offered in various types such as equity trust units, bonds, balanced and money market. 27. The following statement best explains the difference between unit trust and REITs. A. Funds in unit trusts can be invested in shares of various types of companies while REITs can only be invested in company bonds. B. Funds in unit trusts can be invested in securities of various types of companies while REITs can only be invested in securities of real estate companies. c. Unit trusts are investments for retail investors (individuals) while REITs is an investment for institutional investors -. only. Unit trusts involve a small investment value while REITs involve a D value. only. Unit trusts involve a a huge investment. 28. Shariah compliant REITS means that the unit trust only invests in A. premises that are not involved in any illegal business. B. properties that are not involved in the casino, alcohol and pork business. C. properties built without any type of debt financing. D. securities issued by Shariah compliant companies. 29. Secured loans (mortgages) are as follows except A. Derivative instruments to finance investments in the real B. estate sector. Secured by real estate or fixed assets. C. Banks are the main institutions that provide these loans. D. The loan period is between 1 and 30 years. 30. Investment returns in REITs are derived from A. The profit of the business ventured. B. Dividend gains from investing in company shares. C. Profit from the sale of new shares i.e. initial public offering (IPO) D. Profit from the rental and sale of properties owned. 31. A country's balance of payments account records A. the flow of goods among trading countries. official B. transactions that occur between governments and other governments. c. all total payments made abroad and financial receipts received from abroad within one year. D. international trade, lending and lending. 32. The main transactions recorded in a country's balance of payments account include all the items below except A. export of goods and services. B. spending by foreign tourists in the domestic economy. C. federal government budget surplus or deficit. D. income from foreign investment. 33. An increase in foreign tourism for a given country A. positive effect on the service component in the capital account. B. negative impact on the service component in the capital account. C. positive impact on the service component in the current account. D. negative impact on the service component in the current account. 34. Financial institutions that are active in the foreign exchange market consist of A. commercial banks. B. securities broker. C. commodity traders. D. all of the above. 35. If the import of goods of a country exceeds its export of goods, then A. a surplus will occur in the country's current account. B. a deficit will occur in the country's current account. C. a deficit will occur in the country's capital account. D. the surplus will occur in the country's capital account. 36. The table below shows the international trade account for a country. The country's overall balance of payments is A. -RM 60 million B. -RM 140 million C. -RM 250 million D. RM 170 million
1. The following financial instruments are instruments traded in the market money except A. Malaysian Government Securities (MGS) B. Bankers' acceptance C. Negotiable instruments of deposits D. Corporate bonds 2. The payment system in the financial system in Malaysia consists of the following: I. Wholesale Payment System II. Retail Payment System III. Periodic Payment System IV. Regular Payment System A. I, II B. I, III C. II, III, IV D. I, II, III, IV 3. Financial institutions are important participants that move the financial system in a country. Which of the following is a participant in the Malaysian financial system? I. Bank Negara Malaysia II. Alliance Bank Berhad III. Employees' Provident Fund (EPF) IV. CIMB Principal Asset Management Berhad A. I, II B. I, III C. II, III, IV D. I, II, III, IV 37. If the value of the United States Dollar falls compared to the Malaysian Ringgit, then A. United States exporters will not export goods to Malaysia. B. Malaysian exporters will increase exports of goods to the United States. C. Malaysian importers will import more goods from the United States. D. United States importers will import more goods from Malaysia. 38. The Singapore Dollar demand curve shifts to the right due to A. interest rates in Malaysia have increased. B. Malaysia's exports to Singapore have increased. C. Malaysian imports from Singapore have increased. D. Singaporean tourists visiting Malaysia are increasing in number. 39. A devaluation of the Malaysian Ringgit can improve Malaysia's balance of payments in the following ways: A. The price of imported goods is getting more expensive for foreigners relatively next reduce the demand for foreign imported goods. The B. price of imported goods is getting more expensive for Malaysians relatively next reduce demand for imported goods by Malaysians. c. The price of export goods is getting more expensive for foreigners relatively next reduce the demand for Malaysian export goods. D. The price of imported goods is getting cheaper for Malaysians in relative terms, increasing the demand for imported goods by Malaysians. 40. The diagram below shows the demand curve for Japanese Yen (DD) and the supply curve for Japanese Yen (SS). The devaluation of 100 Yen from RM3.70 to RM3.60 may be due A. the demand for Malaysian goods in Japan is decreasing. B. Japanese people travel less to Malaysia. C. Malaysian real estate investment in Japan decreased. D. Malaysian students to Japan increase. 11. Treasury bills are one of the short-term financial instruments that are usually traded in the money market. Which of the following is correct about treasury bills in Malaysia? A. This instrument is a short-term debt obligation of the government to finance annual operating expenses. B. This instrument is issued by the government through its investment company, Khazanah Nasional Berhad C. This instrument is exposed to the risk of default and changes in the D. inflation rate. This instrument cannot be traded and cannot be transferred. 14. Choose the most accurate statement about Bankers' Acceptance. A. Banker's Acceptance is a financial instrument issued by a company and guaranteed by a bank. B. Banker's Acceptance is a financial instrument issued by a bank and used by a company in payment matters international trade. c. Bankers' Acceptances cannot be traded in the secondary or secondary market due to their non-transferable nature. D. A Banker's Acceptance is a debt paper with a certain coupon rate and sold at face value (par value). 12. The main characteristics of the money market are as follows: I. Instruments traded are short-term instruments II. Instruments traded have high liquidity III. The existence of the interbank market IV. Instruments such as bonds, sukuk and shares are traded in the money market A. I, II, III B. II, III, IV C. II, III D. III, IV 13. Which of the following is not the main function of the money market in Malaysia? A. Providing investment opportunities on the part that has B. excess funds. Give space to parties with deficits to increase investment. c. Assist economic units in their respective liquidity management for ensure liquidity risk can be minimized. D. Financing the company's working capital and providing short-term financing to the government other than tax collection. 15. The following are the main drivers for the existence of the Islamic money market in Malaysia except A. Islamic financial institutions are also exposed to liquidity risk which creates dependence on short-term instruments. B. Financial instruments that exist in the conventional money market prevent Islamic financial institutions from obtaining financing or making investments. The return c. on investment instruments in the conventional money market is not competitive although it requires a high investment capital. To D. enable market participants to carry out functions similar to conventional money market participants 16. The capital market is a market that A. carry out transactions for short-term securities such as treasury bills and Bank loan. carry out transactions for equity securities which are ordinary shares and preference c. shares. carry out transactions for various types of long-term securities, especially B shares. and bonds. D. conducting transactions for new securities, especially initial public offerings (IPOs). 17. An investor who intends to have ownership in a company will make the following transaction: A. Giving debt to the company. B. Buying common shares issued by the company. C. Buying bonds issued by the company. D. Become the CEO of the company. 4. Non-bank institutions are participants in the market that play an important role in fund mobility (fund mobility) from those who have excess funds to those who need those funds. The following institutions are non-bank institutions in the Malaysian money market except Export-Import Bank Malaysia Berhad Bank Simpanan Nasional Bank Kerjasama Rakyat Malaysia Berhad D. Malayan Banking Berhad 5. Commercial papers (commercial papers) refer to A. Instruments that are secured (secured) and can be redeemed at B. any time. Instruments issued for short-term financing purposes. C. Instruments that have a maturity period between 1 year and 3 years. D. Instruments that can only be issued by government-linked companies (GLCs). 6. The Islamic interbank money market (IIMM) was introduced in January 1994 to assist in the development of the Islamic financial system in Malaysia. Following are the main activities in IIMM except A. Buying and selling Islamic financial instruments among IIMM participants. B. Buying and selling sukuk, which is one of the Islamic financing instruments in Malaysia. C. Investment activities between banks through the mudharabah investment scheme between banks (MII). D. Check clearing through the Islamic interbank Check Clearing System (IICCS). 7. Which of the following is a risk inherent in the money market? . Political risk II. Default risk III. Risk of inflation rate increase IV. Market risk 8. Among the following, which statement is correct? A. Bank Negara Malaysia has no role in the money market in Malaysia due to the issuance of short-term instruments regulated by the Malaysian Securities Commission. B. The government issues treasury bills through government-linked companies (GLCs) c. The money market aims to distribute savings in the economy efficiently to support the economic growth D. of a country. The Islamic Check Clearing System is based on the principle of musyarakah and introduced to facilitate transactions in among Islamic banking institutions 9. The following statements are true about participants in the money market in Malaysia except A. Cagamas was established in 1986 and is a leader in securitization activities in Malaysia, including short-term instruments. B. RAM Holdings (RAM) is the only local credit rating agency in Malaysia. c. Permodalan Nasional Berhad (PNB) was established to encourage the ownership of shares by Bumiputeras in the corporate sector. The D. main role of the Employees' Provident Fund (EPF) is to provide retirement benefits to each of its members. 10. What is meant by financial instruments traded in the money market? A. Is a document published by an institution or organization for obtain short-term financing or purchase short-term assets. B. Is a document published by an institution or organization to obtain short-term investment and also buy short-term assets. C. Is a document published by the government and sold to agencies government only to obtain short-term financing. D. Is a document published by the government to obtain short-term investment and also buy short-term assets. A. II, III B. III, IV C. I, II, III D. I, II, III, IV 18. The main secondary capital market in Malaysia is A. Bank Negara Malaysia B. Securities Commission C. Bursa Malaysia D. CIMB Bank Berhad. 19. The following statements explain the characteristics of the capital market except A. Instruments traded are long or medium term instruments secured or unsecured. B. Traded instruments have higher liquidity than money market instruments. c. The risk of the instrument is higher, but the return is also relatively higher compared to money market instruments. D. Its secondary market is more active than the secondary market for the market money. 20. One of the following securities is not a capital market instrument ie A. Common stock. B. Priority share. C. Bonds. D. Treasury bills. 21. Sukuk is A. Shariah compliant bonds B. Islamic bank loan C. Shares Shariah compliant D. Shariah compliant preference shares. 22. The following statements explain the characteristics of the bond market in Malaysia except A. includes the government and private debt securities (PDS) markets. B. dominated by government debt securities. C. includes sukuk and bond debt securities transactions. D. including sukuk and rights securities transactions. 23. Shariah compliant shares are Shares issued with Islamic banking financing. Shares issued for Muslim investors only. Shares issued by Shariah compliant companies. D. Shares traded on Bursa Islam Malaysia Berhad (BIMB). 24. The price of trust units is based on A. Net asset value B. Net present value C. Time value of D. money Net profit value 25. The following are fund management firms in Malaysia except A. Amanah Saham Nasional Berhad B. Public Mutual Berhad C. RHB Asset Management Sdn. Bhd. D. Al-Rajhi Asset Management Berhad 26. One of the following statements is not related to unit trusts in Malaysia. A. Most unit trusts are traded on Bursa Malaysia like ordinary shares. B. Unit trust investors have the option to invest in Shariah compliant unit trusts and/or conventional unit trusts. c. The return from investment in unit trusts is usually higher than investment in fixed deposits. D. unit trusts that are offered in various types such as equity trust units, bonds, balanced and money market. 27. The following statement best explains the difference between unit trust and REITs. A. Funds in unit trusts can be invested in shares of various types of companies while REITs can only be invested in company bonds. B. Funds in unit trusts can be invested in securities of various types of companies while REITs can only be invested in securities of real estate companies. c. Unit trusts are investments for retail investors (individuals) while REITs is an investment for institutional investors -. only. Unit trusts involve a small investment value while REITs involve a D value. only. Unit trusts involve a a huge investment. 28. Shariah compliant REITS means that the unit trust only invests in A. premises that are not involved in any illegal business. B. properties that are not involved in the casino, alcohol and pork business. C. properties built without any type of debt financing. D. securities issued by Shariah compliant companies. 29. Secured loans (mortgages) are as follows except A. Derivative instruments to finance investments in the real B. estate sector. Secured by real estate or fixed assets. C. Banks are the main institutions that provide these loans. D. The loan period is between 1 and 30 years. 30. Investment returns in REITs are derived from A. The profit of the business ventured. B. Dividend gains from investing in company shares. C. Profit from the sale of new shares i.e. initial public offering (IPO) D. Profit from the rental and sale of properties owned. 31. A country's balance of payments account records A. the flow of goods among trading countries. official B. transactions that occur between governments and other governments. c. all total payments made abroad and financial receipts received from abroad within one year. D. international trade, lending and lending. 32. The main transactions recorded in a country's balance of payments account include all the items below except A. export of goods and services. B. spending by foreign tourists in the domestic economy. C. federal government budget surplus or deficit. D. income from foreign investment. 33. An increase in foreign tourism for a given country A. positive effect on the service component in the capital account. B. negative impact on the service component in the capital account. C. positive impact on the service component in the current account. D. negative impact on the service component in the current account. 34. Financial institutions that are active in the foreign exchange market consist of A. commercial banks. B. securities broker. C. commodity traders. D. all of the above. 35. If the import of goods of a country exceeds its export of goods, then A. a surplus will occur in the country's current account. B. a deficit will occur in the country's current account. C. a deficit will occur in the country's capital account. D. the surplus will occur in the country's capital account. 36. The table below shows the international trade account for a country. The country's overall balance of payments is A. -RM 60 million B. -RM 140 million C. -RM 250 million D. RM 170 million 1. The following financial instruments are instruments traded in the market money except A. Malaysian Government Securities (MGS) B. Bankers' acceptance C. Negotiable instruments of deposits D. Corporate bonds 2. The payment system in the financial system in Malaysia consists of the following: I. Wholesale Payment System II. Retail Payment System III. Periodic Payment System IV. Regular Payment System A. I, II B. I, III C. II, III, IV D. I, II, III, IV 3. Financial institutions are important participants that move the financial system in a country. Which of the following is a participant in the Malaysian financial system? I. Bank Negara Malaysia II. Alliance Bank Berhad III. Employees' Provident Fund (EPF) IV. CIMB Principal Asset Management Berhad A. I, II B. I, III C. II, III, IV D. I, II, III, IV 37. If the value of the United States Dollar falls compared to the Malaysian Ringgit, then A. United States exporters will not export goods to Malaysia. B. Malaysian exporters will increase exports of goods to the United States. C. Malaysian importers will import more goods from the United States. D. United States importers will import more goods from Malaysia. 38. The Singapore Dollar demand curve shifts to the right due to A. interest rates in Malaysia have increased. B. Malaysia's exports to Singapore have increased. C. Malaysian imports from Singapore have increased. D. Singaporean tourists visiting Malaysia are increasing in number. 39. A devaluation of the Malaysian Ringgit can improve Malaysia's balance of payments in the following ways: A. The price of imported goods is getting more expensive for foreigners relatively next reduce the demand for foreign imported goods. The B. price of imported goods is getting more expensive for Malaysians relatively next reduce demand for imported goods by Malaysians. c. The price of export goods is getting more expensive for foreigners relatively next reduce the demand for Malaysian export goods. D. The price of imported goods is getting cheaper for Malaysians in relative terms, increasing the demand for imported goods by Malaysians. 40. The diagram below shows the demand curve for Japanese Yen (DD) and the supply curve for Japanese Yen (SS). The devaluation of 100 Yen from RM3.70 to RM3.60 may be due A. the demand for Malaysian goods in Japan is decreasing. B. Japanese people travel less to Malaysia. C. Malaysian real estate investment in Japan decreased. D. Malaysian students to Japan increase. 11. Treasury bills are one of the short-term financial instruments that are usually traded in the money market. Which of the following is correct about treasury bills in Malaysia? A. This instrument is a short-term debt obligation of the government to finance annual operating expenses. B. This instrument is issued by the government through its investment company, Khazanah Nasional Berhad C. This instrument is exposed to the risk of default and changes in the D. inflation rate. This instrument cannot be traded and cannot be transferred. 14. Choose the most accurate statement about Bankers' Acceptance. A. Banker's Acceptance is a financial instrument issued by a company and guaranteed by a bank. B. Banker's Acceptance is a financial instrument issued by a bank and used by a company in payment matters international trade. c. Bankers' Acceptances cannot be traded in the secondary or secondary market due to their non-transferable nature. D. A Banker's Acceptance is a debt paper with a certain coupon rate and sold at face value (par value). 12. The main characteristics of the money market are as follows: I. Instruments traded are short-term instruments II. Instruments traded have high liquidity III. The existence of the interbank market IV. Instruments such as bonds, sukuk and shares are traded in the money market A. I, II, III B. II, III, IV C. II, III D. III, IV 13. Which of the following is not the main function of the money market in Malaysia? A. Providing investment opportunities on the part that has B. excess funds. Give space to parties with deficits to increase investment. c. Assist economic units in their respective liquidity management for ensure liquidity risk can be minimized. D. Financing the company's working capital and providing short-term financing to the government other than tax collection. 15. The following are the main drivers for the existence of the Islamic money market in Malaysia except A. Islamic financial institutions are also exposed to liquidity risk which creates dependence on short-term instruments. B. Financial instruments that exist in the conventional money market prevent Islamic financial institutions from obtaining financing or making investments. The return c. on investment instruments in the conventional money market is not competitive although it requires a high investment capital. To D. enable market participants to carry out functions similar to conventional money market participants 16. The capital market is a market that A. carry out transactions for short-term securities such as treasury bills and Bank loan. carry out transactions for equity securities which are ordinary shares and preference c. shares. carry out transactions for various types of long-term securities, especially B shares. and bonds. D. conducting transactions for new securities, especially initial public offerings (IPOs). 17. An investor who intends to have ownership in a company will make the following transaction: A. Giving debt to the company. B. Buying common shares issued by the company. C. Buying bonds issued by the company. D. Become the CEO of the company. 4. Non-bank institutions are participants in the market that play an important role in fund mobility (fund mobility) from those who have excess funds to those who need those funds. The following institutions are non-bank institutions in the Malaysian money market except Export-Import Bank Malaysia Berhad Bank Simpanan Nasional Bank Kerjasama Rakyat Malaysia Berhad D. Malayan Banking Berhad 5. Commercial papers (commercial papers) refer to A. Instruments that are secured (secured) and can be redeemed at B. any time. Instruments issued for short-term financing purposes. C. Instruments that have a maturity period between 1 year and 3 years. D. Instruments that can only be issued by government-linked companies (GLCs). 6. The Islamic interbank money market (IIMM) was introduced in January 1994 to assist in the development of the Islamic financial system in Malaysia. Following are the main activities in IIMM except A. Buying and selling Islamic financial instruments among IIMM participants. B. Buying and selling sukuk, which is one of the Islamic financing instruments in Malaysia. C. Investment activities between banks through the mudharabah investment scheme between banks (MII). D. Check clearing through the Islamic interbank Check Clearing System (IICCS). 7. Which of the following is a risk inherent in the money market? . Political risk II. Default risk III. Risk of inflation rate increase IV. Market risk 8. Among the following, which statement is correct? A. Bank Negara Malaysia has no role in the money market in Malaysia due to the issuance of short-term instruments regulated by the Malaysian Securities Commission. B. The government issues treasury bills through government-linked companies (GLCs) c. The money market aims to distribute savings in the economy efficiently to support the economic growth D. of a country. The Islamic Check Clearing System is based on the principle of musyarakah and introduced to facilitate transactions in among Islamic banking institutions 9. The following statements are true about participants in the money market in Malaysia except A. Cagamas was established in 1986 and is a leader in securitization activities in Malaysia, including short-term instruments. B. RAM Holdings (RAM) is the only local credit rating agency in Malaysia. c. Permodalan Nasional Berhad (PNB) was established to encourage the ownership of shares by Bumiputeras in the corporate sector. The D. main role of the Employees' Provident Fund (EPF) is to provide retirement benefits to each of its members. 10. What is meant by financial instruments traded in the money market? A. Is a document published by an institution or organization for obtain short-term financing or purchase short-term assets. B. Is a document published by an institution or organization to obtain short-term investment and also buy short-term assets. C. Is a document published by the government and sold to agencies government only to obtain short-term financing. D. Is a document published by the government to obtain short-term investment and also buy short-term assets. A. II, III B. III, IV C. I, II, III D. I, II, III, IV 18. The main secondary capital market in Malaysia is A. Bank Negara Malaysia B. Securities Commission C. Bursa Malaysia D. CIMB Bank Berhad. 19. The following statements explain the characteristics of the capital market except A. Instruments traded are long or medium term instruments secured or unsecured. B. Traded instruments have higher liquidity than money market instruments. c. The risk of the instrument is higher, but the return is also relatively higher compared to money market instruments. D. Its secondary market is more active than the secondary market for the market money. 20. One of the following securities is not a capital market instrument ie A. Common stock. B. Priority share. C. Bonds. D. Treasury bills. 21. Sukuk is A. Shariah compliant bonds B. Islamic bank loan C. Shares Shariah compliant D. Shariah compliant preference shares. 22. The following statements explain the characteristics of the bond market in Malaysia except A. includes the government and private debt securities (PDS) markets. B. dominated by government debt securities. C. includes sukuk and bond debt securities transactions. D. including sukuk and rights securities transactions. 23. Shariah compliant shares are Shares issued with Islamic banking financing. Shares issued for Muslim investors only. Shares issued by Shariah compliant companies. D. Shares traded on Bursa Islam Malaysia Berhad (BIMB). 24. The price of trust units is based on A. Net asset value B. Net present value C. Time value of D. money Net profit value 25. The following are fund management firms in Malaysia except A. Amanah Saham Nasional Berhad B. Public Mutual Berhad C. RHB Asset Management Sdn. Bhd. D. Al-Rajhi Asset Management Berhad 26. One of the following statements is not related to unit trusts in Malaysia. A. Most unit trusts are traded on Bursa Malaysia like ordinary shares. B. Unit trust investors have the option to invest in Shariah compliant unit trusts and/or conventional unit trusts. c. The return from investment in unit trusts is usually higher than investment in fixed deposits. D. unit trusts that are offered in various types such as equity trust units, bonds, balanced and money market. 27. The following statement best explains the difference between unit trust and REITs. A. Funds in unit trusts can be invested in shares of various types of companies while REITs can only be invested in company bonds. B. Funds in unit trusts can be invested in securities of various types of companies while REITs can only be invested in securities of real estate companies. c. Unit trusts are investments for retail investors (individuals) while REITs is an investment for institutional investors -. only. Unit trusts involve a small investment value while REITs involve a D value. only. Unit trusts involve a a huge investment. 28. Shariah compliant REITS means that the unit trust only invests in A. premises that are not involved in any illegal business. B. properties that are not involved in the casino, alcohol and pork business. C. properties built without any type of debt financing. D. securities issued by Shariah compliant companies. 29. Secured loans (mortgages) are as follows except A. Derivative instruments to finance investments in the real B. estate sector. Secured by real estate or fixed assets. C. Banks are the main institutions that provide these loans. D. The loan period is between 1 and 30 years. 30. Investment returns in REITs are derived from A. The profit of the business ventured. B. Dividend gains from investing in company shares. C. Profit from the sale of new shares i.e. initial public offering (IPO) D. Profit from the rental and sale of properties owned. 31. A country's balance of payments account records A. the flow of goods among trading countries. official B. transactions that occur between governments and other governments. c. all total payments made abroad and financial receipts received from abroad within one year. D. international trade, lending and lending. 32. The main transactions recorded in a country's balance of payments account include all the items below except A. export of goods and services. B. spending by foreign tourists in the domestic economy. C. federal government budget surplus or deficit. D. income from foreign investment. 33. An increase in foreign tourism for a given country A. positive effect on the service component in the capital account. B. negative impact on the service component in the capital account. C. positive impact on the service component in the current account. D. negative impact on the service component in the current account. 34. Financial institutions that are active in the foreign exchange market consist of A. commercial banks. B. securities broker. C. commodity traders. D. all of the above. 35. If the import of goods of a country exceeds its export of goods, then A. a surplus will occur in the country's current account. B. a deficit will occur in the country's current account. C. a deficit will occur in the country's capital account. D. the surplus will occur in the country's capital account. 36. The table below shows the international trade account for a country. The country's overall balance of payments is A. -RM 60 million B. -RM 140 million C. -RM 250 million D. RM 170 million Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


