Question
1. The national debt and budget deficit are different names for the same thing. Circle one: TRUE FALSE 2. If government outlays and taxes revenues
1. The national debt and budget deficit are different names for the same thing.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
2. If government outlays and taxes revenues increase by the same amount, the government's budget balance does not change.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
3. Social Security and Medicare obligations are less than U.S. GDP.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
4. For the past decade, the U.S. federal government has had a budget deficit.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
5. Automatic stabilizers are features of fiscal policy that work to stabilize real GDP without explicit action by the government.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
6. The cyclical deficit is larger when the economy is in a recession.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
7. The government expenditure multiplier is the magnification effect that a change in aggregate demand has on government expenditures on goods and services.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
8. A tax cut is a possible fiscal stimulus designed to increase GDP.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
9. Estimating potential GDP is a limitation of automatic fiscal policy.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
10. Income taxes create wedge between the wage rate paid by firms and the wage rate workers take home.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
11. An income tax hike decreases the supply of labor but has no effect on employment or potential GDP.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
12. An income tax cut increases potential GDP by shifting the nation's production function upward.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
13. Taxes on interest income can drive a wedge between the interest rate borrowers pay and the interest rate lenders receive.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
14. An increase in the budget deficit can raise the real interest rate and crowd out private investment.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
15. A tax cut increases aggregate demand and decreases aggregate supply.
Circle one: TRUE FALSE
1. The annual statement of the outlays, tax revenues, and surplus or deficit of the government of the United States is the federal:
A. surplus record
B. deficit record
C. budget
D. spending
E. debt to the public
2. When government outlays are less than tax revenues, the government has:
A. a budget with a positive balance
B. a budget deficit
C. a budget surplus
D. a budget with a negative debt
E. an illegal budget because outlays must exceed tax revenues
3. National debt decreases in a given year when a country has:
A. a budget deficit
B. a balanced budget
C. a budget supplement
D. a budget surplus
E. no government budget
4. The ____ view says that fiscal stimulus has a multiplier effect that makes it a ____ tool to fight a deep recession.
A. mainstream; powerful
B. "free lunch"; powerful
C. Keynesian; powerful
D. Keynesian; weak
E. None of the above answers is correct
5. An example of automatic fiscal policy is:
A. an interest rate cut, initiated by an act of Congress
B. an increase in the quantity of money
C. a tax cut, initiated by an act of Congress
D. a decrease in tax revenues, triggered by the state of the economy
E. any change tax revenues, regardless of the cause
6. If the structural deficit is $800 billion and the cyclical deficit is $600 billion, the actual budget deficit is ____.
A. $200 billion
B. $600 billion
C. $800 billion
D. $1,400 billion
E. None of the above answers are correct
7. The government expenditure multiplier reflects the magnification effect on ____ from a change in government expenditure on goods and services.
A. aggregate demand
B. the budget deficit
C. tax revenues
D. aggregate supply
E. potential GDP
8. The magnitude of the tax multiplier is ____ the magnitude of the government expenditure multiplier.
A. equal to
B. greater than
C. smaller than
D. the inverse of
E. exactly one half
9. An example of a discretionary fiscal stimulus policy is:
A. the automatic increase in needs-tested spending in a recession
B. induced taxes
C. decreasing government expenditure
D. decreasing needs-tested spending
E. cutting taxes
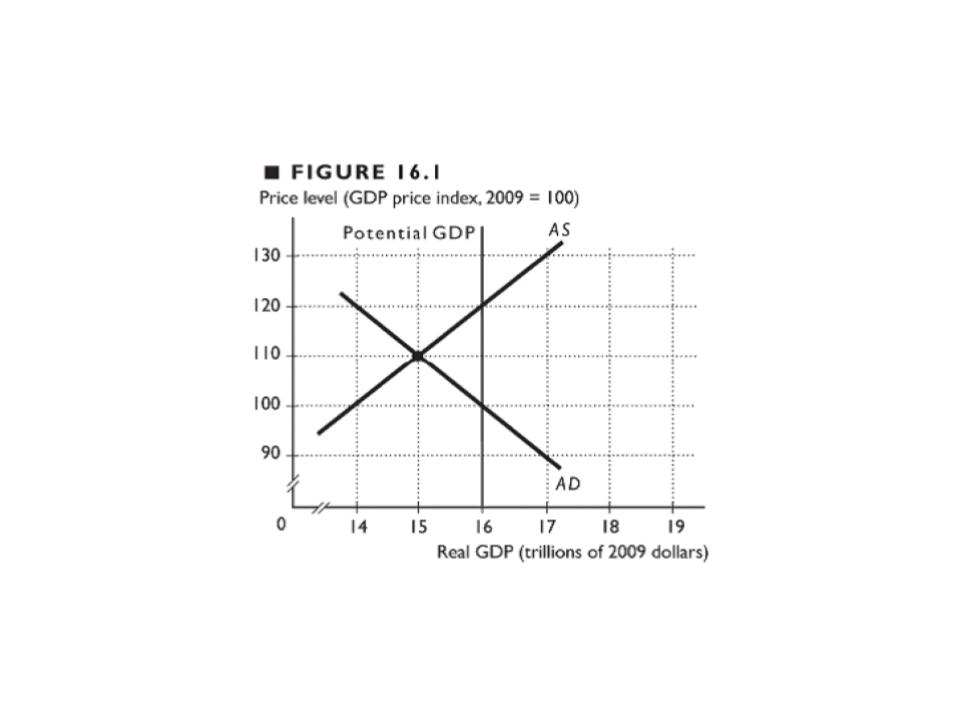
10. A fiscal stimulus works to close a recessionary gap by shifting the
A. AD curve leftward
B. AS curve leftward
C. AD curve leftward and the AS curve leftward
D. AD curve rightward
E. potential GDP line leftward
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


