Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. The rate law for the reaction 2NO2(g) + F2(g) are two proposed mechanisms for this reaction. plausible. (a) Step 1: NO2 + F2
![1. The rate law for the reaction 2NO2(g) F2(g) 2NO2F(g) is rate kNO2][F2]. Below are two proposed mechanisms for this reactio](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2022/08/6308b52b60f78_0516308b52b1821f.jpg)
![Step l: NO (g) + Br2 (g) NOBr2 (g) Step 2: NOBr2 (g) + NO (g) 2 NOBr (g) The rate law for the reaction is rate kINO [Br2] A.](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2022/08/6308b52c4eef9_0516308b52bec50f.jpg)
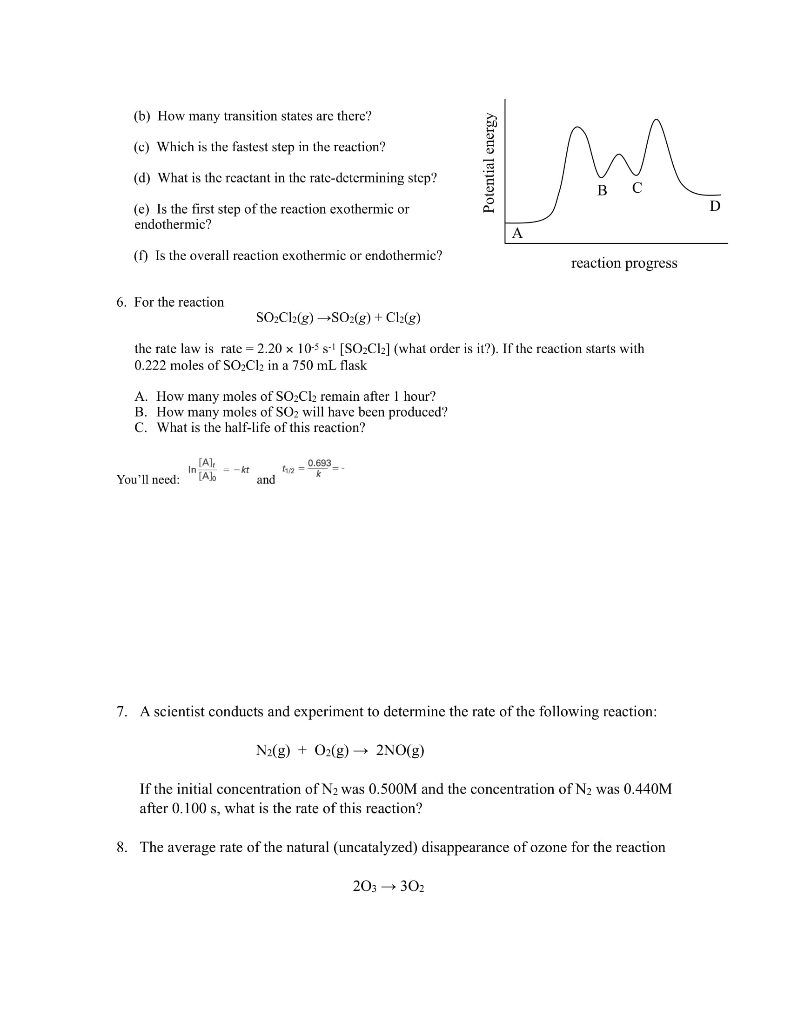
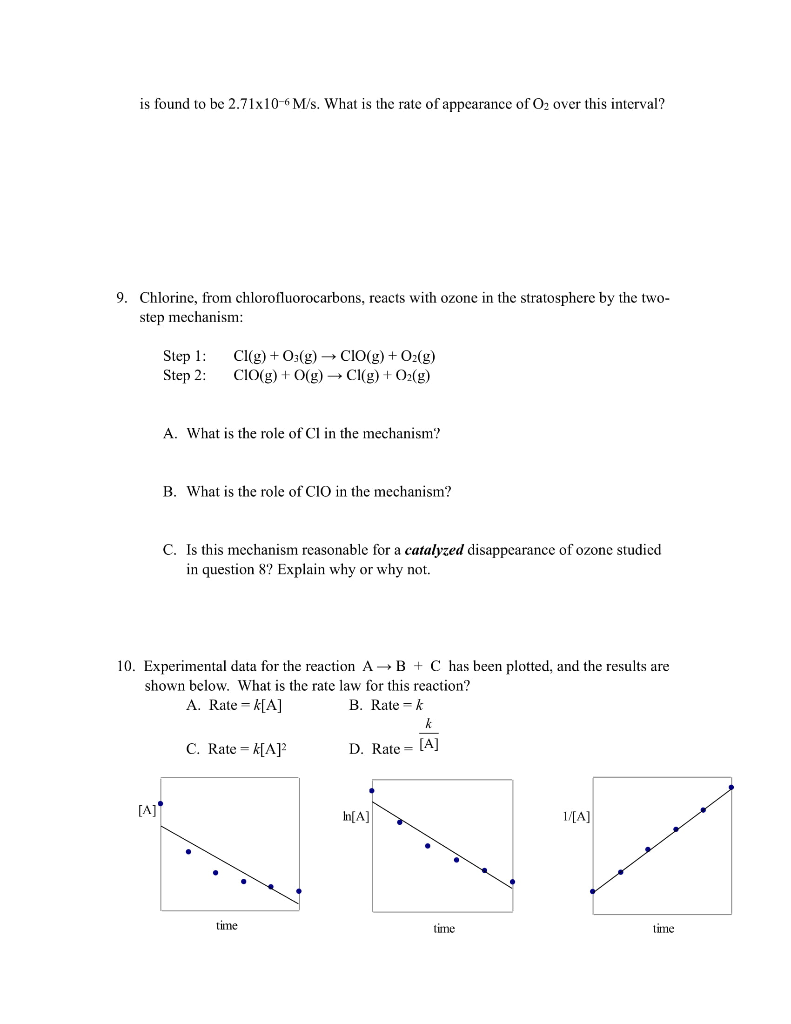
1. The rate law for the reaction 2NO2(g) + F2(g) are two proposed mechanisms for this reaction. plausible. (a) Step 1: NO2 + F2 Step 2: NO+ F (b) Step 1: NO2 + F2 Step 2: NOF2 Step 3: F+NO (a) I2 I + H HI + I k2 k3 k NOF+F (Slow) k NOF k k3 2NOF(g) is rate = k[NO2][F2]. Below Show that both of these mechanisms are NOF2 (Fast) NOF (Fast) NOF + F (Slow) 2. Derive the overall reaction and the rate law for each mechanism shown below. k K 21 K (fast) HI (fast) 2HI (slow) (Fast) (b) NO + Brz NOBr2 + NO k NOBrz (slow) 2NOBr (fast) 3. The reaction 2 NO (g) + Brz (g) 2 NOBr (g) is believed to follow the mechanism: Step 1: Step 2: The rate law for the reaction is rate = k[NO][Br]. NO (g) + Br2 (g) NOBr2 (g) NOBr2 (g) + NO (g) - 2 NOBr (g) A. Which is the rate-determining step in the mechanism? B. Why is it believed that the overall reaction is NOT an elementary process? (Hint: collision state theory) 4. For the reaction 4A + B + C A2B + 2AC, the following initial rates of reaction were found. Determine the rate law and the value of k (with units!) for this reaction. Experiment 1 2 3 4 [A]o (mol/L) 0.20 0.20 0.30 0.20 [B]o (mol/L) 0.30 0.60 0.30 0.60 [C]0 (mol/L) 0.20 0.20 0.20 0.60 Initial Rate (mol/ L-s) 6.8 x 10-6 2.7 x 10-5 1.0 x 10-5 2.7 x 10-5 5. Below is the reaction profile for the reaction of A to D. Use it to answer the following questions. (a) How many intermediates are there in this reaction? (b) How many transition states are there? (c) Which is the fastest step in the reaction? (d) What is the reactant in the rate-determining step? (e) Is the first step of the reaction exothermic or endothermic? (f) Is the overall reaction exothermic or endothermic? 6. For the reaction A. How many moles of SOCl remain after 1 hour? B. How many moles of SO will have been produced? C. What is the half-life of this reaction? SOCl2(g) SO2(g) + Cl(g) the rate law is rate = 2.20 x 105 s- [SOCl2] (what order is it?). If the reaction starts with 0.222 moles of SOCl2 in a 750 mL flask You'll need: [A], [A] = kt and 11/2 = 0.693_ m reaction progress 203 302 7. A scientist conducts and experiment to determine the rate of the following reaction: N(g) + O(g) 2NO(g) If the initial concentration of N was 0.500M and the concentration of N was 0.440M after 0.100 s, what is the rate of this reaction? 8. The average rate of the natural (uncatalyzed) disappearance of ozone for the reaction D is found to be 2.71x10-6 M/s. What is the rate of appearance of O over this interval? 9. Chlorine, from chlorofluorocarbons, reacts with ozone in the stratosphere by the two- step mechanism: Step 1: Step 2: [A] Cl(g) + O3(g) CIO(g) + O(g) CIO(g) + O(g) Cl(g) + O(g) A. What is the role of Cl in the mechanism? B. What is the role of CIO in the mechanism? C. Is this mechanism reasonable for a catalyzed disappearance of ozone studied in question 8? Explain why or why not. 10. Experimental data for the reaction AB + C has been plotted, and the results are shown below. What is the rate law for this reaction? A. Rate = k[A] B. Rate k C. Rate = k[A] time k D. Rate: [A] In[A] time 1/[A] time
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.47 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Answer 1 For mechanism a the Rate determining step RDS is the slow step step 1 therefore rate k ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


