Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. The reaction: CO+O2CO2+O is a minor, but non-trivial oxidation reaction for CO in high-temperature flames (e.g., oxyfuel combustion). A mixture of CO and O2
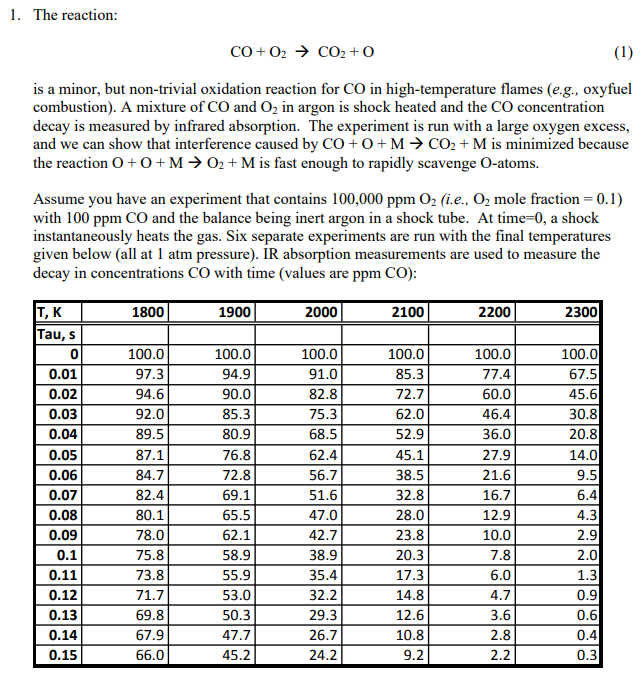
 1. The reaction: CO+O2CO2+O is a minor, but non-trivial oxidation reaction for CO in high-temperature flames (e.g., oxyfuel combustion). A mixture of CO and O2 in argon is shock heated and the CO concentration decay is measured by infrared absorption. The experiment is run with a large oxygen excess, and we can show that interference caused by CO+O+MCO2+M is minimized because the reaction O+O+MO2+M is fast enough to rapidly scavenge O-atoms. Assume you have an experiment that contains 100,000ppmO2 (i.e., O2 mole fraction = 0.1) with 100ppmCO and the balance being inert argon in a shock tube. At time=0, a shock instantaneously heats the gas. Six separate experiments are run with the final temperatures given below (all at 1atm pressure). IR absorption measurements are used to measure the decay in concentrations CO with time (values are ppmCO ): Find A(cm3/ mole-s ) and EA(kJ/mole). Also decide if n=0 or not. Hint: A reactant that is present in large excess will not change its concentration appreciable during the reaction, and its concentration can be assumed constant. This significantly simplifies the analysis. You can check your answer against the tables in the text
1. The reaction: CO+O2CO2+O is a minor, but non-trivial oxidation reaction for CO in high-temperature flames (e.g., oxyfuel combustion). A mixture of CO and O2 in argon is shock heated and the CO concentration decay is measured by infrared absorption. The experiment is run with a large oxygen excess, and we can show that interference caused by CO+O+MCO2+M is minimized because the reaction O+O+MO2+M is fast enough to rapidly scavenge O-atoms. Assume you have an experiment that contains 100,000ppmO2 (i.e., O2 mole fraction = 0.1) with 100ppmCO and the balance being inert argon in a shock tube. At time=0, a shock instantaneously heats the gas. Six separate experiments are run with the final temperatures given below (all at 1atm pressure). IR absorption measurements are used to measure the decay in concentrations CO with time (values are ppmCO ): Find A(cm3/ mole-s ) and EA(kJ/mole). Also decide if n=0 or not. Hint: A reactant that is present in large excess will not change its concentration appreciable during the reaction, and its concentration can be assumed constant. This significantly simplifies the analysis. You can check your answer against the tables in the text Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


