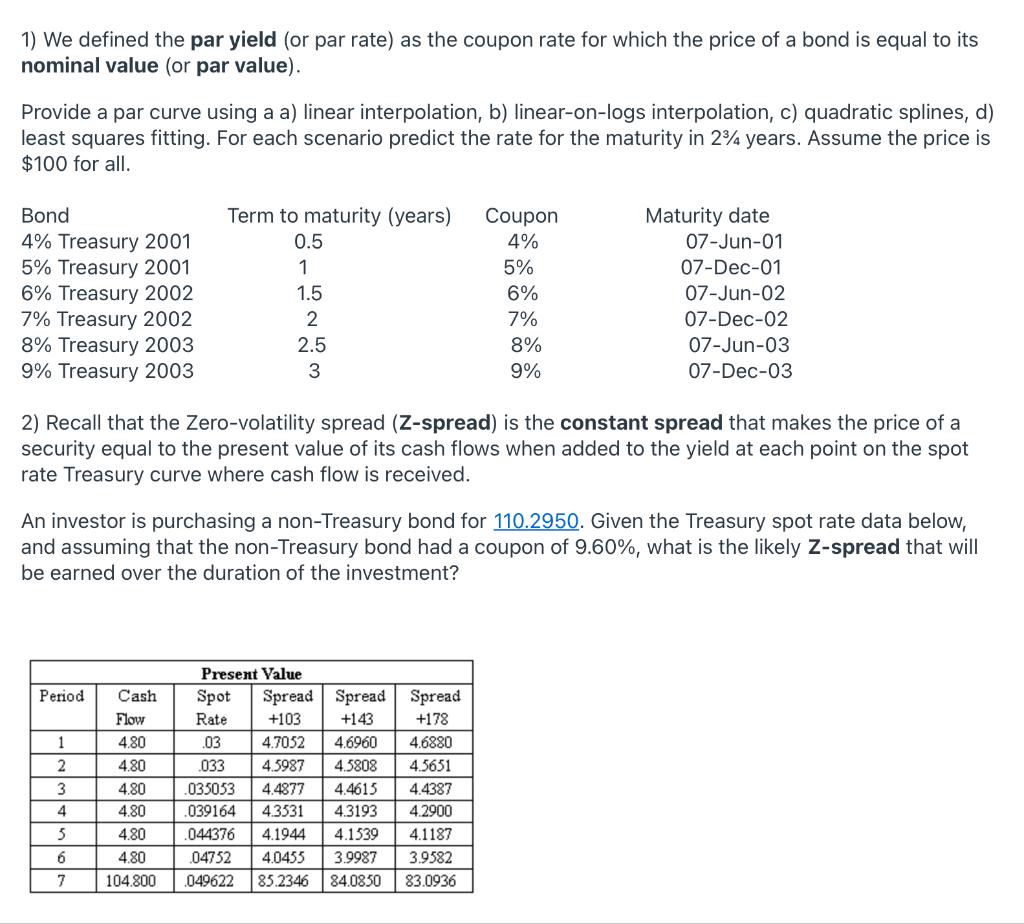
1) We defined the par yield (or par rate) as the coupon rate for which the price of a bond is equal to its nominal value (or par value). Provide a par curve using a a) linear interpolation, b) linear-on-logs interpolation, c) quadratic splines, d) least squares fitting. For each scenario predict the rate for the maturity in 24 years. Assume the price is $100 for all. Bond 4% Treasury 2001 5% Treasury 2001 6% Treasury 2002 7% Treasury 2002 8% Treasury 2003 9% Treasury 2003 Term to maturity (years) 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 Coupon 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% Maturity date 07-Jun-01 07-Dec-01 07-Jun-02 07-Dec-02 07-Jun-03 07-Dec-03 2) Recall that the Zero-volatility spread (Z-spread) is the constant spread that makes the price of a security equal to the present value of its cash flows when added to the yield at each point on the spot rate Treasury curve where cash flow is received. An investor is purchasing a non-Treasury bond for 110.2950. Given the Treasury spot rate data below, and assuming that the non-Treasury bond had a coupon of 9.60%, what is the likely Z-spread that will be earned over the duration of the investment? Period 1 2 Present Value Spot Spread Spread Spread Rate +103 +143 +178 .03 4.7052 4.6960 4.6880 .033 4.5987 4.5808 4.5651 .035053 4.4877 4.4615 4.4387 .039164 43531 4.3193 4.2900 .044376 4.1944 4.1539 4.1187 04752 4.0455 3.9987 3.9582 049622 85.2346 84.0850 83.0936 Cash Flow 4.80 4.80 4.80 4.80 4.80 4.80 104.800 3 4 5 6 7 1) We defined the par yield (or par rate) as the coupon rate for which the price of a bond is equal to its nominal value (or par value). Provide a par curve using a a) linear interpolation, b) linear-on-logs interpolation, c) quadratic splines, d) least squares fitting. For each scenario predict the rate for the maturity in 24 years. Assume the price is $100 for all. Bond 4% Treasury 2001 5% Treasury 2001 6% Treasury 2002 7% Treasury 2002 8% Treasury 2003 9% Treasury 2003 Term to maturity (years) 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 Coupon 4% 5% 6% 7% 8% 9% Maturity date 07-Jun-01 07-Dec-01 07-Jun-02 07-Dec-02 07-Jun-03 07-Dec-03 2) Recall that the Zero-volatility spread (Z-spread) is the constant spread that makes the price of a security equal to the present value of its cash flows when added to the yield at each point on the spot rate Treasury curve where cash flow is received. An investor is purchasing a non-Treasury bond for 110.2950. Given the Treasury spot rate data below, and assuming that the non-Treasury bond had a coupon of 9.60%, what is the likely Z-spread that will be earned over the duration of the investment? Period 1 2 Present Value Spot Spread Spread Spread Rate +103 +143 +178 .03 4.7052 4.6960 4.6880 .033 4.5987 4.5808 4.5651 .035053 4.4877 4.4615 4.4387 .039164 43531 4.3193 4.2900 .044376 4.1944 4.1539 4.1187 04752 4.0455 3.9987 3.9582 049622 85.2346 84.0850 83.0936 Cash Flow 4.80 4.80 4.80 4.80 4.80 4.80 104.800 3 4 5 6 7







