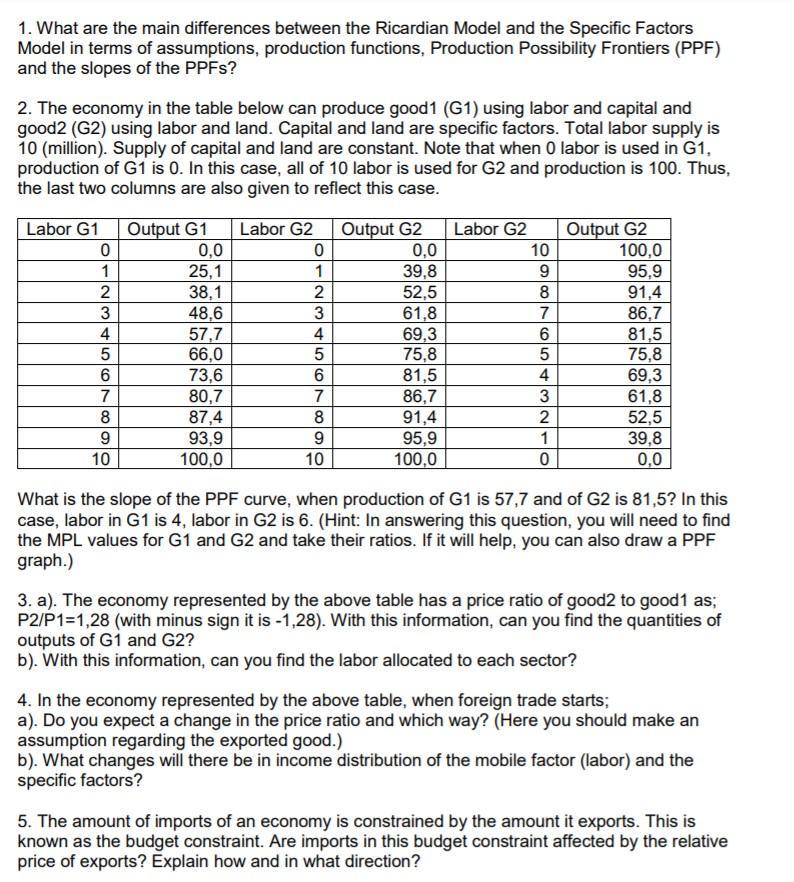
1. What are the main differences between the Ricardian Model and the Specific Factors Model in terms of assumptions, production functions, Production Possibility Frontiers (PPF) and the slopes of the PPFs? 2. The economy in the table below can produce good1 (G1) using labor and capital and good2 (G2) using labor and land. Capital and land are specific factors. Total labor supply is 10 (million). Supply of capital and land are constant. Note that when 0 labor is used in G1, production of G1 is 0. In this case, all of 10 labor is used for G2 and production is 100. Thus, the last two columns are also given to reflect this case. Labor G2 0 1 Labor G1 Output G1 0 0,0 1 25,1 2 38,1 3 48,6 4 57,7 5 66,0 6 73,6 7 80,7 8 87,4 9 93,9 10 100,0 OWN Output G2 0,0 39,8 52,5 61,8 69,3 75,8 81,5 86,7 91,4 95,9 100,0 Labor G2 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Output G2 100,0 95,9 91,4 86,7 81,5 75,8 69,3 61,8 52,5 39,8 0,0 7 8 9 10 What is the slope of the PPF curve, when production of G1 is 57,7 and of G2 is 81,5? In this case, labor in G1 is 4, labor in G2 is 6. (Hint: In answering this question, you will need to find the MPL values for G1 and G2 and take their ratios. If it will help, you can also draw a PPF graph.) 3. a). The economy represented by the above table has a price ratio of good2 to good1 as; P2/P1=1,28 (with minus sign it is -1,28). With this information, can you find the quantities of outputs of G1 and G2? b). With this information, can you find the labor allocated to each sector? 4. In the economy represented by the above table, when foreign trade starts; a). Do you expect a change in the price ratio and which way? (Here you should make an assumption regarding the exported good.) b). What changes will there be in income distribution of the mobile factor (labor) and the specific factors? 5. The amount of imports of an economy is constrained by the amount it exports. This is known as the budget constraint. Are imports in this budget constraint affected by the relative price of exports? Explain how and in what direction? 1. What are the main differences between the Ricardian Model and the Specific Factors Model in terms of assumptions, production functions, Production Possibility Frontiers (PPF) and the slopes of the PPFs? 2. The economy in the table below can produce good1 (G1) using labor and capital and good2 (G2) using labor and land. Capital and land are specific factors. Total labor supply is 10 (million). Supply of capital and land are constant. Note that when 0 labor is used in G1, production of G1 is 0. In this case, all of 10 labor is used for G2 and production is 100. Thus, the last two columns are also given to reflect this case. Labor G2 0 1 Labor G1 Output G1 0 0,0 1 25,1 2 38,1 3 48,6 4 57,7 5 66,0 6 73,6 7 80,7 8 87,4 9 93,9 10 100,0 OWN Output G2 0,0 39,8 52,5 61,8 69,3 75,8 81,5 86,7 91,4 95,9 100,0 Labor G2 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Output G2 100,0 95,9 91,4 86,7 81,5 75,8 69,3 61,8 52,5 39,8 0,0 7 8 9 10 What is the slope of the PPF curve, when production of G1 is 57,7 and of G2 is 81,5? In this case, labor in G1 is 4, labor in G2 is 6. (Hint: In answering this question, you will need to find the MPL values for G1 and G2 and take their ratios. If it will help, you can also draw a PPF graph.) 3. a). The economy represented by the above table has a price ratio of good2 to good1 as; P2/P1=1,28 (with minus sign it is -1,28). With this information, can you find the quantities of outputs of G1 and G2? b). With this information, can you find the labor allocated to each sector? 4. In the economy represented by the above table, when foreign trade starts; a). Do you expect a change in the price ratio and which way? (Here you should make an assumption regarding the exported good.) b). What changes will there be in income distribution of the mobile factor (labor) and the specific factors? 5. The amount of imports of an economy is constrained by the amount it exports. This is known as the budget constraint. Are imports in this budget constraint affected by the relative price of exports? Explain how and in what direction







