Question
1. Which is easier for nucleation in solids, homogeneous or heterogeneous nucleation? What are the common defects present in solid solution (list at least five
1. Which is easier for nucleation in solids, homogeneous or heterogeneous nucleation? What are the common defects present in solid solution (list at least five kinds of defects)? Are the defects generally harmful for nucleation and explain why?
2. The following figure shows the phase diagram and the corresponding homogeneous nucleation rates of composition X0 at different temperatures. Te indicates the equilibrium temperature for ???? and ???? at X0.
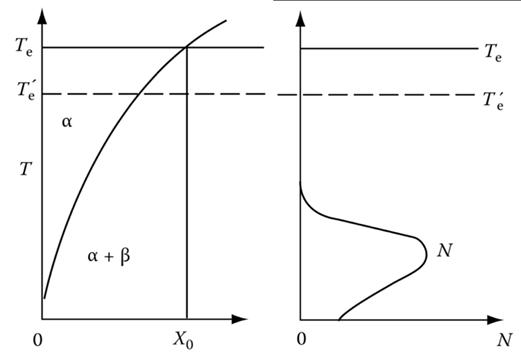
Explain why the peak of nucleation rate happens at a temperature lower than Te
3. For the following nucleation on grain boundaries, if misfit train energy can be ignored, how the optimum embryo shape is determined? What is the condition to achieve mechanical equilibrium for such an embryo shape? Can you derive the excess free energy associated with the embryo (using the defined interface energy and interface area A) ?
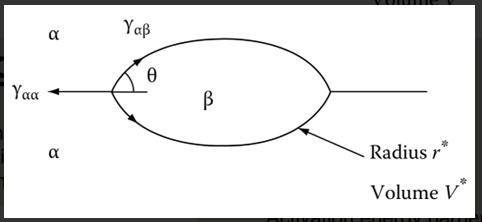
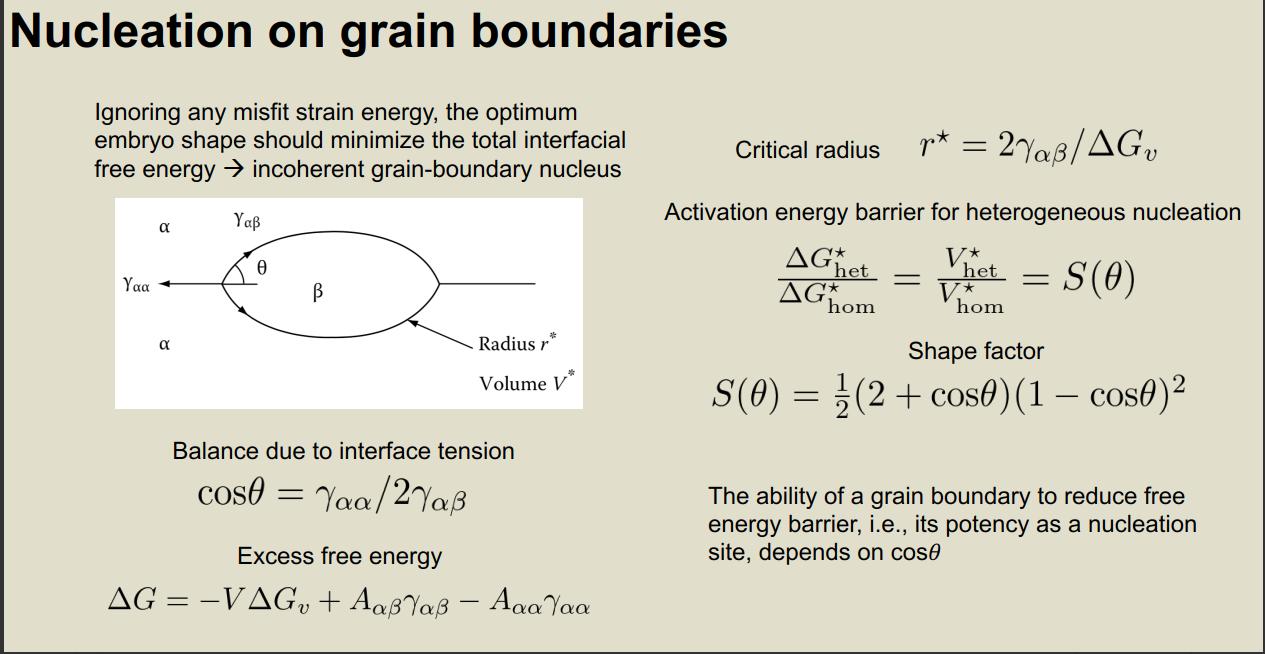
Te T Te T T + 0 0 N N
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


