Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Which of the following is not an advantage of multupnogrammung? (A) Increased throughput (C) Decreased operating system overhead (B) Shorter risponse time (D) Ability


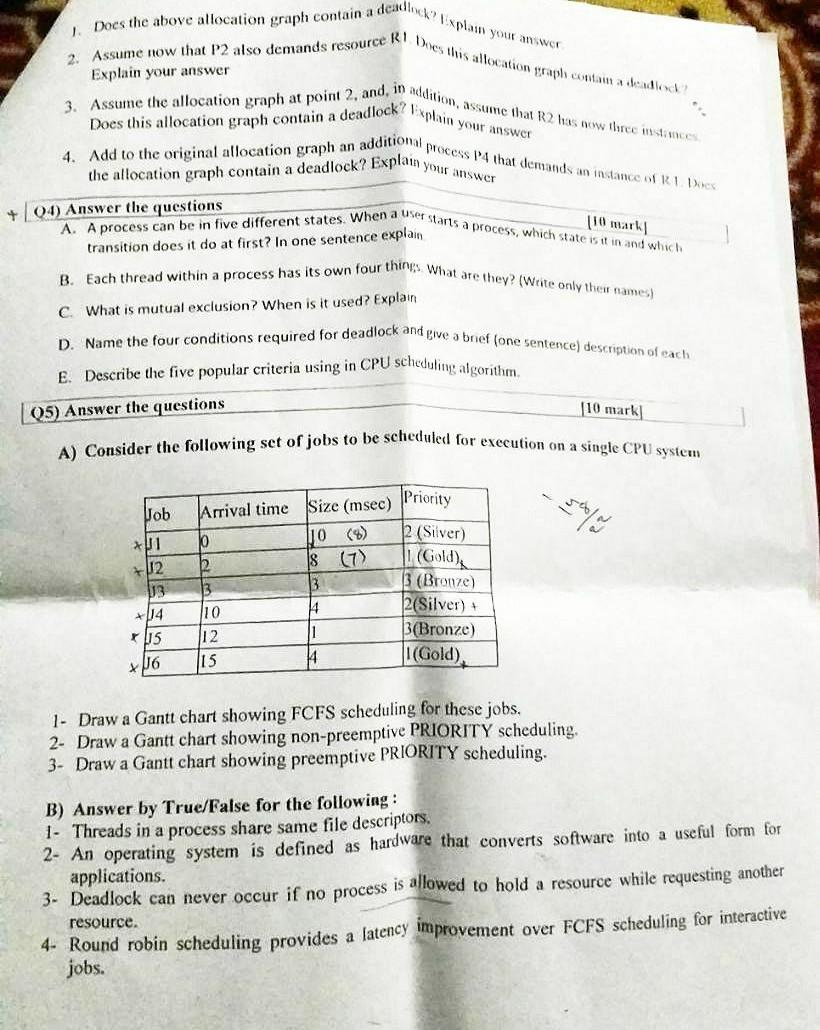
1. Which of the following is not an advantage of multupnogrammung? (A) Increased throughput (C) Decreased operating system overhead (B) Shorter risponse time (D) Ability to assign priorities to jobs 2. Context switching between processes is carried out by the (A) interrupt handler (B) short term (C) Dispateher (D) thread ntantiger 3. The Hardware mechanism that enables a device to notify the CPU is called (A) Polling (B) Interrupt (C) System Call (D) None of the previous 4. The threads. (A) many-to-one (B) one-to-one (C) many-to-many (D) many-to-some 5. When a process performs I/O, its PCB is moved to the (A) Ready queue (B) Wait queue (C) Terminate queue (D) Running quewe (E) 6. When was the first operating system developed? (A) 1948 (B) 1949 (C) 1950 (D) 1951 7. is the number of processes that are completed per time unit. (A) CPU utilization (B) Response time (C) Turnaround time (D) Throughput Which of the following is true of multilevel queue scheduling? (A) Processes can move between queues. (ip. Each queue has its own scheduling algorithm. (C) A queve cannot have absolute priority over (D) It is the most general CPU-scheduling algorithm. lower-priority queues. A thread control block (A) is managed by the parent process (B) contains the same information as the process control block (C) has the identical structure as the process control (D) does not include information about the parent block process resource allocation The state transition from READY to RUNNING happens when a process A) is interrupted (B) performs an (C) completes an [/O or (D) is dispatched by IO or event event handling the scheduler handling 11. Among CPU seheduling policies, Stortest Renaining processing Time (SRIT) is attractive because- (A) it is simple to implement (B) it is fair to all processes in the system (C) it minimizes the average waiting time in the (D) it minin system 12. Which of the following condition is required for a deadock to be possible? (A) mutual exelusion (B) a process may hold allocated resources (C) no resource can be forcibly removed from a awaiting assignment of 13. A problem encountered in multitasking when a process is perpetually deried necessary resources is aalled (A)deadlock(B)inversion(D)aging (B) starvation (C) inversion 14. A resource type, R is represented by 3 -dots, it has (A) 2 instances (B) 3 instances (C) 4 instances (D) 6 insteuees 15. What does API stand for? (A) address programming interface (B)application programming interface (C) accessing periph oral (D)address pregramating interface through interface D) hon af above Q2) Answer the questions A) For each of the following thread state transitions, say whether the transition is legal and how the transition occurs or why it cannot. i. Change from thread state BLOCKED to thread state RUNNING IIlegal. ii. Change from thread state RUNNING to thread state BLOCKED Legal. iii. Change from thread state RUNNABLE to thread state BLOCKED Illegal. B) Consider the Sollowing CPU processes witl arival times and length of CPU bursts (in mitliseconds) as given beiow: If the pre-emptive shortest remaining time tirst scheduling algorithm is used to schedule the processes, then calculate the average waiting time. Q3) Answer the questions [10 mark A) Explain the Differences between the light-weight process and the heavy-weight process in details? B) Consider the following resource allocation graph: 0 0 1. Does the above allocation graph contain a deadlock?' Xplain your answer 3. Assume the allocation graph at point Does this allocation graph contain a deadlock? I xplain your answer 4. Add to the original allocation graph an additional process p 4 that demands an instance of k biner the allocation graph contain a deadlock? Explait your answer Q4) Answer the questions A. A process can be in five different states. When a user starts a process, which state is wing ind transition does it do at first? In one sentence explain B. Each thread within a process has its own four things. What are they? (Weite only their names) C. What is mutual exclusion? When is it used? Explain D. Name the four conditions required for deadlock and give a brief (one sentence) description of each E. Describe the five popular criteria using in CPU scheduling algorithm. Q5) Answer the questions [10 mark] A) Consider the following set of jobs to be scheduled for execution on a single CPU system 1- Draw a Gantt chart showing FCFS scheduling for these jobs. 2- Draw a Gantt chart showing non-preemptive PRIORITY scheduling. 3- Draw a Gantt chart showing preemptive PRIORITY scheduling. B) Answer by True/False for the following : 1- Threads in a process share same file descriptors. 2- An operating system is defined as hardivare that converts software into a useful form for applications. 3. Deadlock can never occur if no process is allowed to hold a resource while requesting another resource. 4. Round robin scheduling provides a latency improvement over FCFS scheduling for interactive jobs
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


