Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
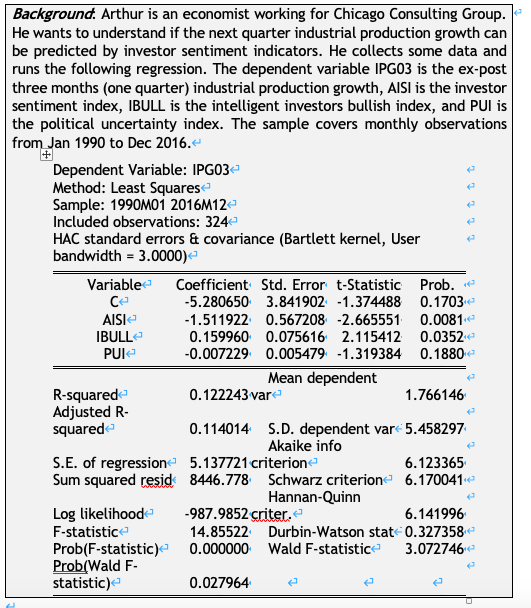
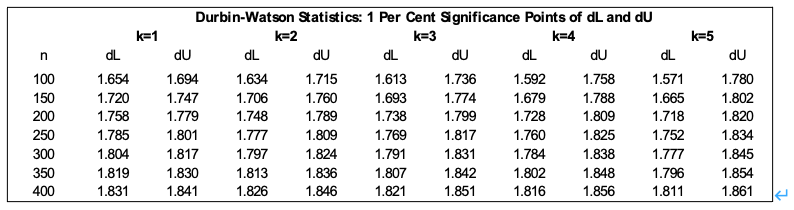
1) With the following extract of the Durbin Watson table, please help Arthur to understand if the regression residuals are suffered from serial correlation problem.
1) With the following extract of the Durbin Watson table, please help Arthur to understand if the regression residuals are suffered from serial correlation problem. Find the correct critical values, state the null hypothesis, and state your decision.
2) Arthur decides to drop PUI from above regression and add a search engine-based sentiment index (FEARS) in the regression. What potential problem should Arthur pay attention to? What test should Arthur do to check for such potential problem?.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


