Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
10. The Coca-Cola Company is a global soft drink beverage company (ticker symbol = KO). The data in the exhibits that follow include the



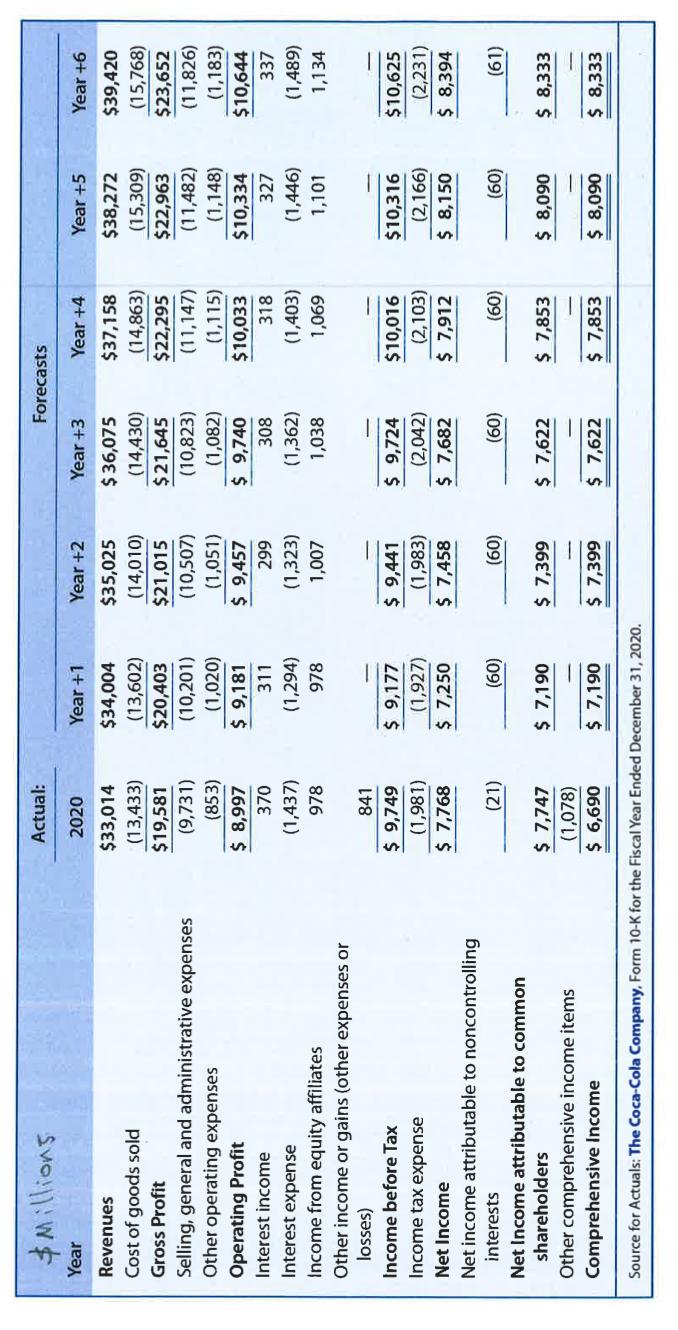
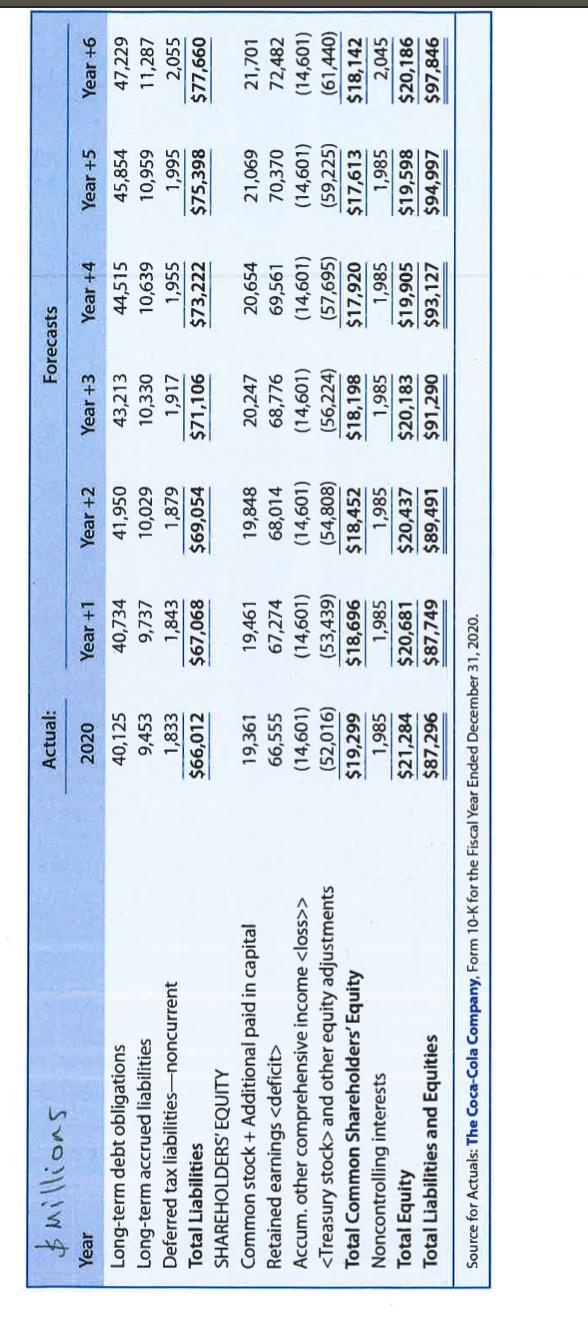
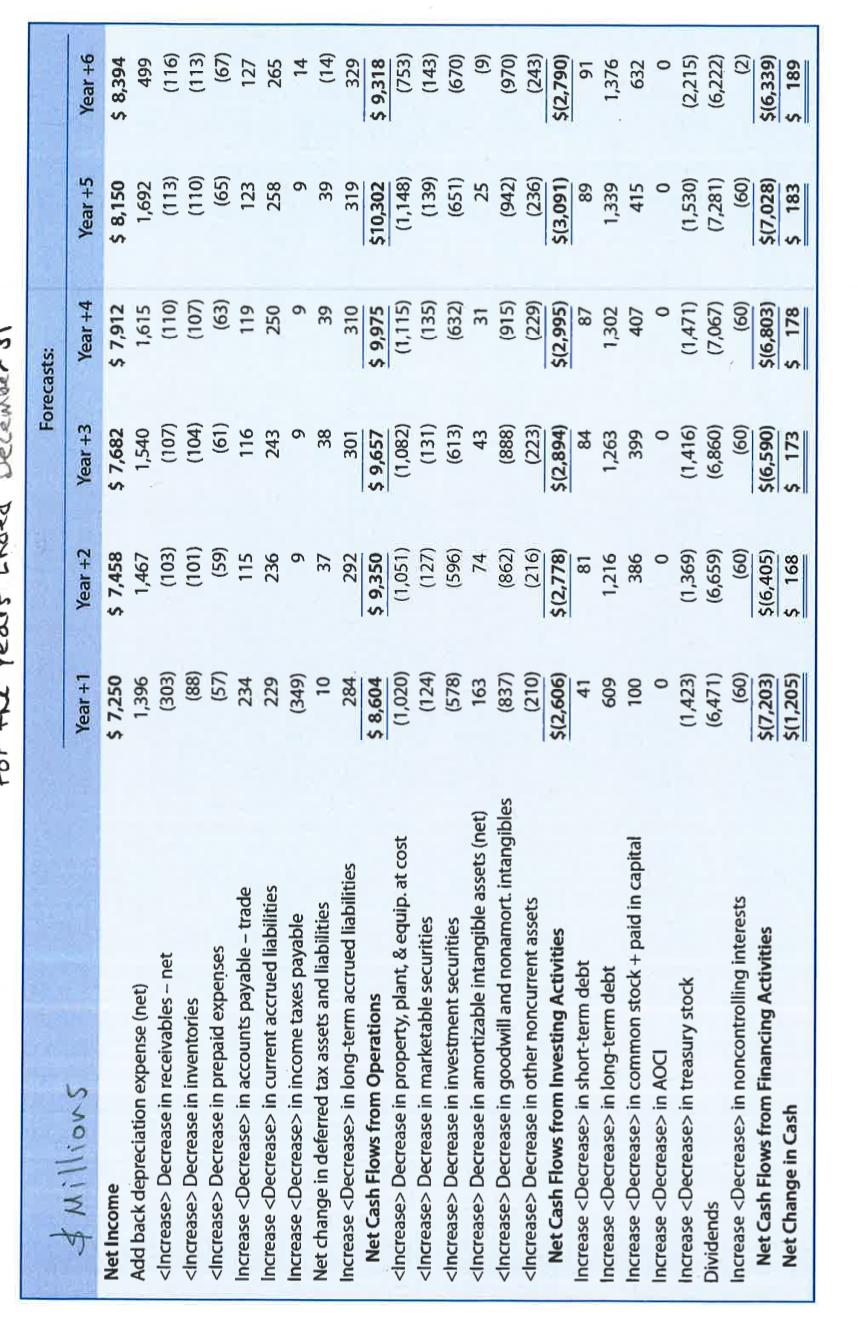
10. The Coca-Cola Company is a global soft drink beverage company (ticker symbol = KO). The data in the exhibits that follow include the actual amounts for fiscal 2020 and the projected amounts for Years +1 to +6 for the income statements, balance sheets, and statement of cash flows for Coca-Cola (in millions). The market equity beta for Coca-Cola at the end of 2020 is 0.60. Assume that the risk-free rate is 3.0% and the market risk premium is 5.0%. Coca-Cola has 4,302 million shares outstanding at the end of 2020, when the stock price was $54.39. Consider the above information as well as the exhibits at the end of this package, and utilize the templates that follow to complete requirements a -k, contained in Parts 1-3 of this problem. Required: Part 1 - Computing Coca-Cola's share value using Free Cash Flows to Common Equity Shareholders a. Derive the projected cash flows for common equity shareholders for Coca-Cola for Years +1 through +6 based on the projected financial statements. Assume that Coca-Cola's changes in cash each year are necessary for operating liquidity purposes. Note that the financial statement forecasts for Year +6 assume that Coca-Cola will experience a steady-state long-run growth rate of 3% in Year +6 and beyond. Complete/document your work on Template A. b. Using the required rate of return on common equity as a discount rate, compute the sum of the present value of free cash flows for common equity shareholders, for Coca-Cola for Years +1 through +5. Complete/document your work on Template A. c. Using the same required rate of return on common equity and the long-run growth rate noted in Requirement "a", compute the continuing value of Coca-Cola as of the start of the Year +6 based on Coca-Cola's continuing free cash flows for common equity shareholders in Year +6 and beyond. After computing continuing value as of the start of Year +6, discount it to present value at the start of Year +1. Complete/document your work on Template A. d. Compute the value of a share of Coca-Cola common stock. Specifically: i. Compute the total sum of the present value of all future free cash flows for equity shareholders (from requirements "b" and "c"). Complete/document your work on Template A ii. Adjust the total sum of the present value using the midyear discounting adjustment factor. Complete/document your work on Template A. iii. Compute the per-share value estimate. Complete/document your work on Template A. c. Using the same required rate of return on common equity and the long-run growth rate noted in Requirement "a", compute the continuing value of Coca-Cola as of the start of the Year +6 based on Coca-Cola's continuing free cash flows for common equity shareholders in Year +6 and beyond. After computing continuing value as of the start of Year +6, discount it to present value at the start of Year +1. Complete/document your work on Template A. d. Compute the value of a share of Coca-Cola common stock. Specifically: i. Compute the total sum of the present value of all future free cash flows for equity shareholders (from requirements "b" and "c"). Complete/document your work on Template A. ii. Adjust the total sum of the present value using the midyear discounting adjustment factor. Complete/document your work on Template A. Compute the per-share value estimate. Complete/document your work on Template A. iii. Part 2 - Computing Coca-Cola's share value using free cash flows to all debt and equity shareholders. e. Compute the weighted-average cost of capital for Coca-Cola as of the start of Year +1. At the end of fiscal 2020, Coca-Cola had $42,793 million outstanding interest-bearing debt on the balance sheet and no preferred stock. Assume that the balance sheet value of Coca-Cola's debt is approximately equal to the market value of the debt. The forecasts assume that Coca- Cola will face an interest rate of 3.0% on debt capital and Coca-Cola's average tax rate will be 21% (based on the past five-year average effective tax rate). Coca-Cola also had noncontrolling interests of $1,985 million at that time. The forecasts assume a 3.0% cost of capital for noncontrolling interests. (The forecasts assume noncontrolling interests receive dividends equal to the required rate of return each year.) Your answer: based upon the following supporting calculations: k. Considering all of the valuation work that you completed in this problem, what reasonable range of share values would you have expected for Coca-Cola common stock? What investment strategy (buy, hold, or sell) would you have recommended? Provide the rationale for your strategy. $ Millions Year Actual: Forecasts 2020 Year +1 Year +2 Year +3 Year +4 Year +5 Year +6 Revenues $33,014 $34,004 $35,025 $36,075 $37,158 $38,272 $39,420 Cost of goods sold (13,433) (13,602) (14,010) (14,430) (14,863) (15,309) (15,768) Gross Profit $19,581 $20,403 $21,015 $21,645 $22,295 $22,963 $23,652 Selling, general and administrative expenses (9,731) (10,201) (10,507) (10,823) (11,147) (11,482) (11,826) Other operating expenses (853) (1,020) (1,051) (1,082) (1,115) (1,148) (1,183) Operating Profit $ 8,997 $ 9,181 $ 9,457 $ 9,740 $10,033 $10,334 $10,644 Interest income 370 311 299 308 318 327 337 Interest expense (1,437) (1,294) (1,323) (1,362) (1,403) (1,446) (1,489) Income from equity affiliates 978 978 1,007 1,038 1,069 1,101 1,134 Other income or gains (other expenses or losses) 841 Income before Tax $ 9,749 $ 9,177 $ 9,441 $ 9,724 $10,016 Income tax expense (1,981) (1,927) (1,983) (2,042) (2,103) $10,316 (2,166) $10,625 (2,231) Net Income $ 7,768 $ 7,250 $ 7,458 $ 7,682 $ 7,912 $ 8,150 $ 8,394 Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests (21) (60) (60) (60) (60) (60) (61) Net Income attributable to common shareholders $ 7,747 $ 7,190 $ 7,399 $ 7,622 $ 7,853 $ 8,090 $ 8,333 Other comprehensive income items (1,078) Comprehensive Income $ 6,690 $ 7,190 $ 7,399 $ 7,622 $ 7,853 $ 8,090 $ 8,333 Source for Actuals: The Coca-Cola Company, Form 10-K for the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2020. $ Millions Year Long-term debt obligations Actual: Forecasts 2020 Year +1 Year +2 Year +3 Year +4 Year +5 Year +6 40,125 40,734 41,950 43,213 44,515 45,854 47,229 Long-term accrued liabilities 9,453 9,737 10,029 10,330 10,639 10,959 11,287 Deferred tax liabilities-noncurrent 1,833 1,843 1,879 1,917 1,955 1,995 2,055 Total Liabilities $66,012 $67,068 $69,054 $71,106 $73,222 $75,398 $77,660 SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY Common stock + Additional paid in capital 19,361 19,461 19,848 20,247 20,654 21,069 21,701 Retained earnings 66,555 67,274 68,014 68,776 69,561 70,370 72,482 Accum. other comprehensive income > (14,601) (14,601) (14,601) (14,601) (14,601) (14,601) (14,601) and other equity adjustments (52,016) (53,439) (54,808) (56,224) (57,695) (59,225) (61,440) Total Common Shareholders' Equity $19,299 $18,696 $18,452 $18,198 $17,920 $17,613 $18,142 Noncontrolling interests 1,985 1,985 1,985 1,985 1,985 1,985 2,045 Total Equity $21,284 $20,681 $20,437 $20,183 $19,905 $19,598 $20,186 Total Liabilities and Equities $87,296 $87,749 $89,491 $91,290 $93,127 $94,997 $97,846 Source for Actuals: The Coca-Cola Company, Form 10-K for the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2020. Forecasts: $ Millions Net Income Add back depreciation expense (net) Decrease in receivables - net Decrease in inventories Year +1 $ 7,250 Year +2 Year +3 Year +4 Year +5 Year +6 $ 7,458 $ 7,682 $ 7,912 $ 8,150 $ 8,394 1,396 1,467 1,540 1,615 1,692 499 (303) (103) (107) (110) (113) (116) (88) (101) (104) (107) (110) (113) Decrease in prepaid expenses Increase in accounts payable - trade Increase in current accrued liabilities Increase in income taxes payable Net change in deferred tax assets and liabilities (57) (59) (61) (63) (65) (67) 234 115 116 119 123 127 229 236 243 250 258 265 (349) 9 9 9 9 14 10 37 38 39 39 (14) Increase in long-term accrued liabilities 284 292 301 310 319 329 Net Cash Flows from Operations $ 8,604 $ 9,350 $9,657 $ 9,975 $10,302 $ 9,318 Decrease in property, plant, & equip. at cost Decrease in marketable securities (1,020) (1,051) (1,082) (1,115) (1,148) (753) (124) (127) (131) (135) (139) (143) Decrease in investment securities (578) (596) (613) (632) (651) (670) Decrease in amortizable intangible assets (net) 163 74 43 31 25 (9) Decrease in goodwill and nonamort. intangibles Decrease in other noncurrent assets (837) (862) (888) (915) (942) (970) (210) (216) (223) (229) (236) (243) Net Cash Flows from Investing Activities $(2,606) $(2,778) $(2,894) $(2,995) $(3,091) $(2,790) Increase in short-term debt 41 81 84 87 89 91 Increase in long-term debt 609 1,216 1,263 1,302 1,339 1,376 Increase in common stock + paid in capital 100 386 399 407 415 632 Increase in AOCI 0 0 0 0 0 0 Increase in treasury stock (1,423) (1,369) (1,416) (1,471) (1,530) (2,215) Dividends (6,471) (6,659) (6,860) (7,067) (7,281) (6,222) Increase in noncontrolling interests (60) (60) (60) (60) (60) Net Cash Flows from Financing Activities $(7,203) $(6,405) $(6,590) $(6,803) $(7,028) (2) $(6,339) Net Change in Cash $(1,205) $ 168 $ 173 $ 178 $ 183 $ 189
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


