12.
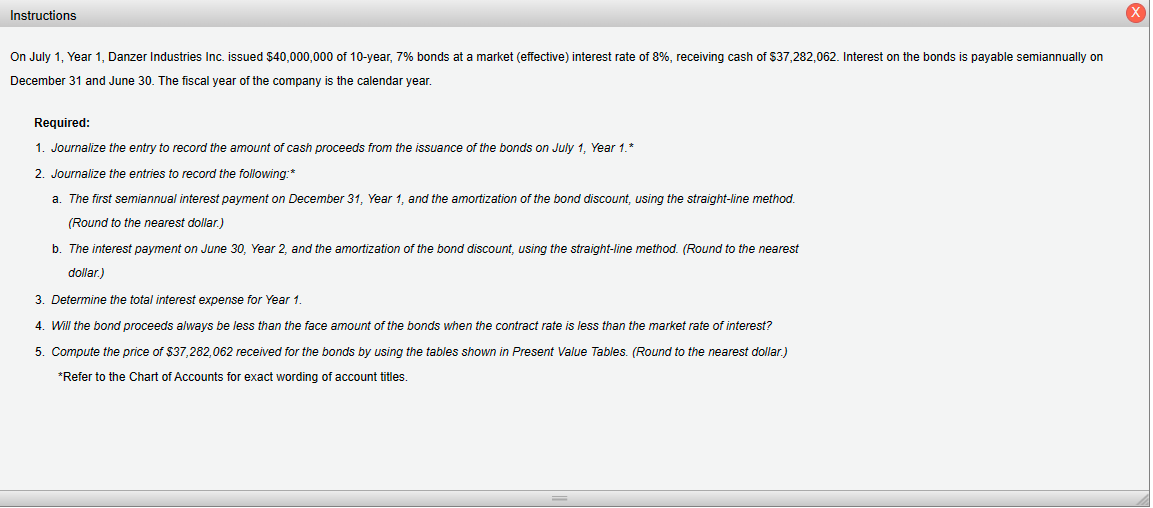
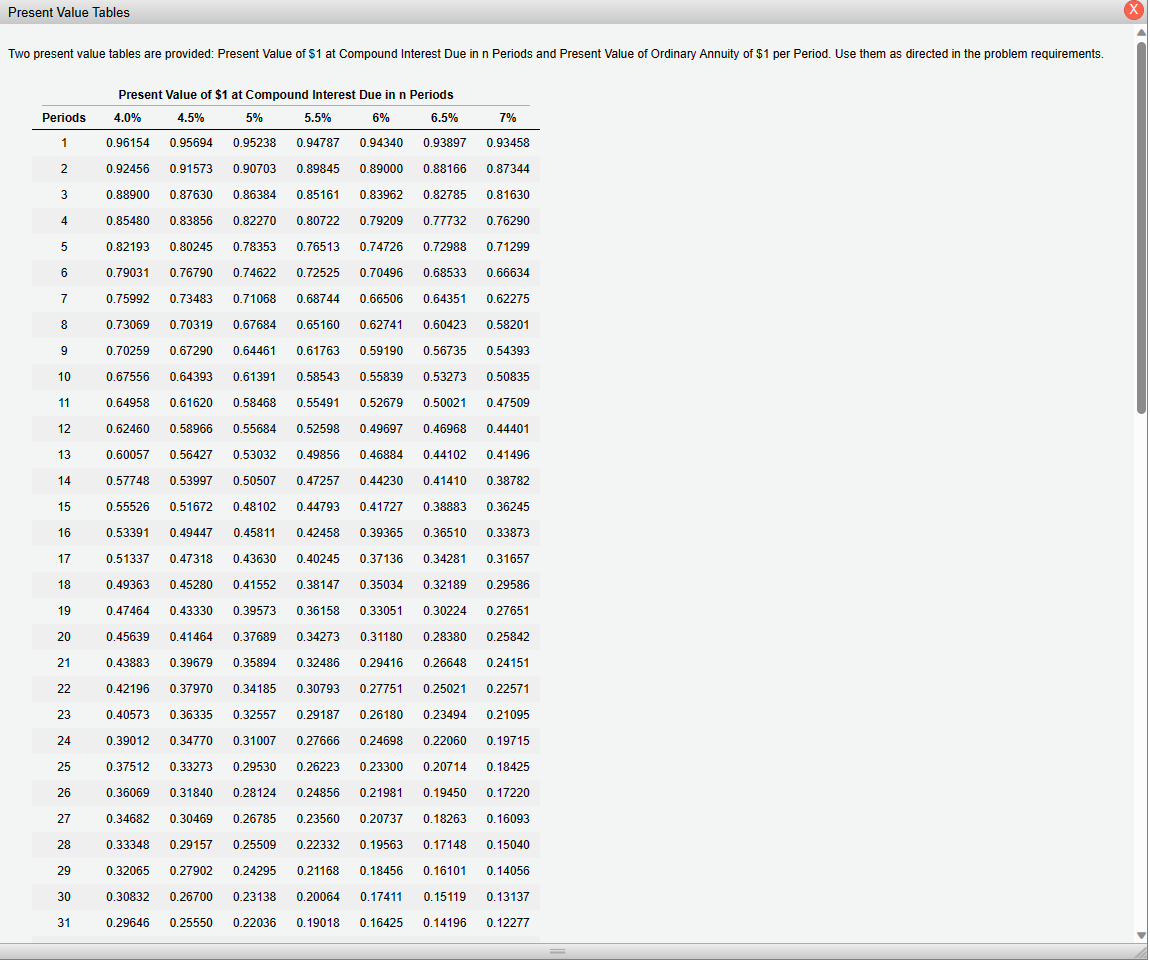
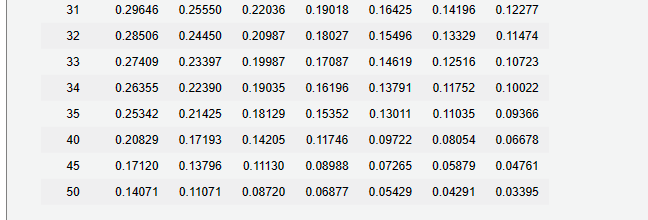
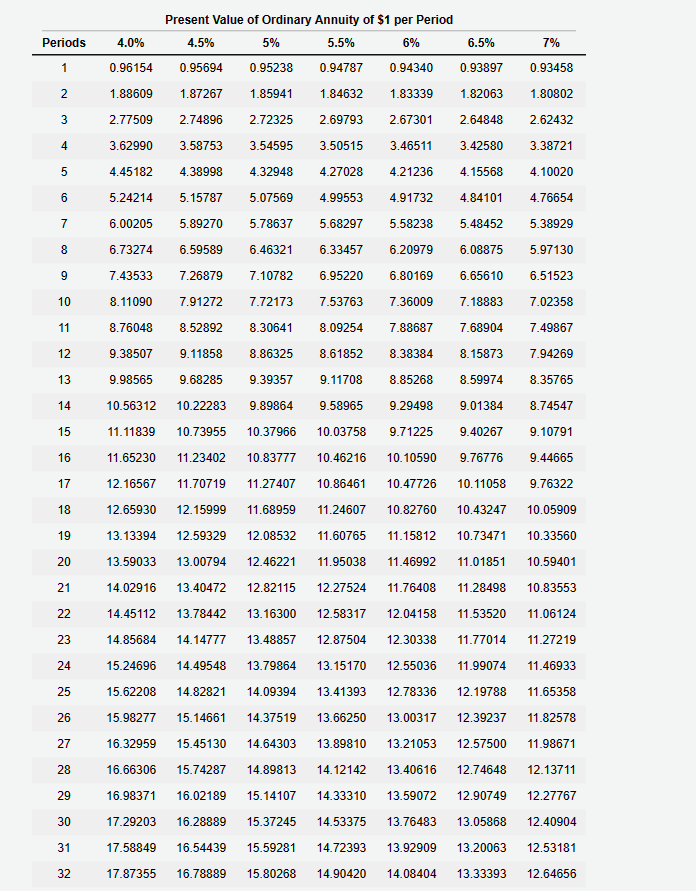
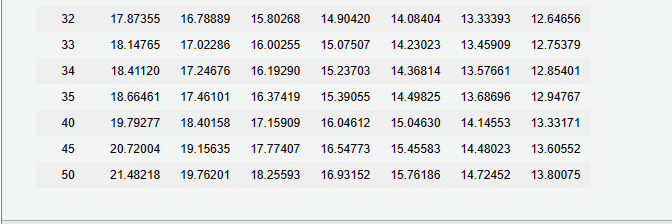
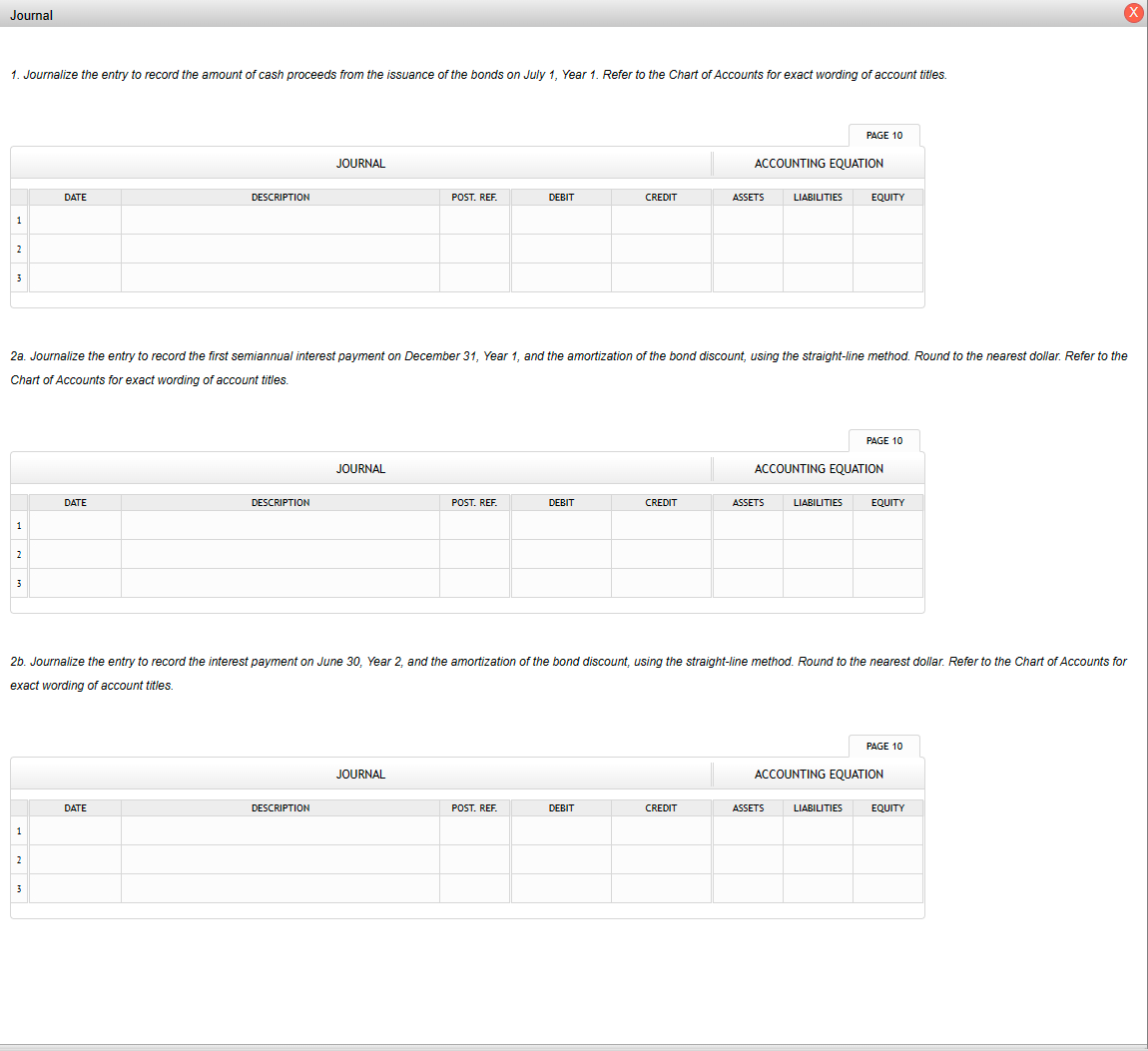
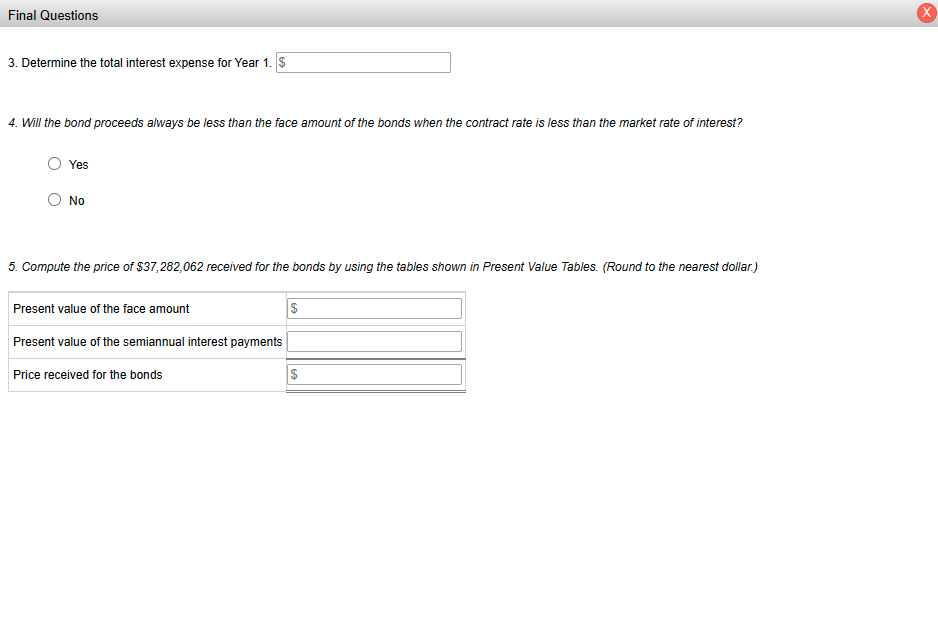
31323334354045500.296460.285060.274090.263550.253420.208290.171200.140710.255500.244500.233970.223900.214250.171930.137960.110710.220360.209870.199870.190350.181290.142050.111300.087200.190180.180270.170870.161960.153520.117460.089880.068770.164250.154960.146190.137910.130110.097220.072650.054290.141960.133290.125160.117520.110350.080540.058790.042910.122770.114740.107230.100220.093660.066780.047610.03395 3. Determine the total interest expense for Year 1. 4. Will the bond proceeds always be less than the face amount of the bonds when the contract rate is less than the market rate of interest? Yes No Two present value tables are provided: Present Value of $1 at Compound Interest Due in n Periods and Present Value of Ordinary Annuity of $1 per Period. Use them as directed in the problem requirements. 3233343540455017.8735518.1476518.4112018.6646119.7927720.7200421.4821816.7888917.0228617.2467617.4610118.4015819.1563519.7620115.8026816.0025516.1929016.3741917.1590917.7740718.2559314.9042015.0750715.2370315.3905516.0461216.5477316.9315214.0840414.2302314.3681414.4982515.0463015.4558315.7618613.3339313.4590913.5766113.6869614.1455314.4802314.7245212.6465612.7537912.8540112.9476713.3317113.6055213.80075 December 31 and June 30 . The fiscal year of the company is the calendar year. Required: 1. Journalize the entry to record the amount of cash proceeds from the issuance of the bonds on July 1, Year 1. * 2. Journalize the entries to record the following: * a. The first semiannual interest payment on December 31, Year 1, and the amortization of the bond discount, using the straight-line method. (Round to the nearest dollar.) b. The interest payment on June 30, Year 2, and the amortization of the bond discount, using the straight-line method. (Round to the nearest dollar.) 3. Determine the total interest expense for Year 1. 4. Will the bond proceeds always be less than the face amount of the bonds when the contract rate is less than the market rate of interest? 5. Compute the price of $37,282,062 received for the bonds by using the tables shown in Present Value Tables. (Round to the nearest dollar.) *Refer to the Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles. 1. Journalize the entry to record the amount of cash proceeds from the issuance of the bonds on July 1, Year 1. Refer to the Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles 2a. Journalize the entry to record the first semiannual interest payment on December 31, Year 1, and the amortization of the bond discount, using the straight-line method. Rour Chart of Accounts for exact wording of account titles. 2b. Journalize the entry to record the interest payment on June 30 , Year 2 , and the amortization of the bond discount, using the straight-line method. Round to the nearest dollar exact wording of account titles. Chart of Accounts 110 Cash 111 Petty Cash 121 Accounts Receivable 122 Allowance for Doubtful Accounts 126 Interest Receivable 127 Notes Receivable 131 Merchandise Inventory 141 Office Supplies 142 Store Supplies 151 Prepaid Insurance 191 Land 192 Store Equipment 193 Accumulated Depreciation-Store Equipment 194 Office Equipment 195 Accumulated Depreciation-Office Equipment LIABILITIES 210 Accounts Payable 221 Salaries Payable 231 Sales Tax Payable 232 Interest Payable 241 Notes Payable 251 Bonds Payable 252 Discount on Bonds Payable 253 Premium on Bonds Payable EQUITY 311 Common Stock 312 Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par-Common Stock 315 Treasury Stock 321 Preferred Stock 322 Paid-In Capital in Excess of Par-Preferred Stock 331 Paid-In Capital from Sale of Treasury Stock 340 Retained Earnings 351 Cash Dividends 352 Stock Dividends 410 Sales 610 Interest Revenue 611 Gain on Redemption of Bonds EXPENSES 510 Cost of Merchandise Sold 515 Credit Card Expense 516 Cash Short and Over 521 Sales Salaries Expense 522 Office Salaries Expense 531 Advertising Expense 532 Delivery Expense 533 Repairs Expense 534 Selling Expenses 535 Rent Expense 536 Insurance Expense 537 Office Supplies Expense 538 Store Supplies Expense 541 Bad Debt Expense 561 Depreciation Expense-Store Equipment 562 Depreciation Expense-Office Equipment 590 Miscellaneous Expense 710 Interest Expense 711 Loss on Redemption of Bonds














