Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1-2 pages of five supply chain lessons learned from the Boeing case. Each lesson can be in a short paragraph. Managing New Product Development and





1-2 pages of five supply chain lessons learned from the Boeing case. Each lesson can be in a short paragraph.
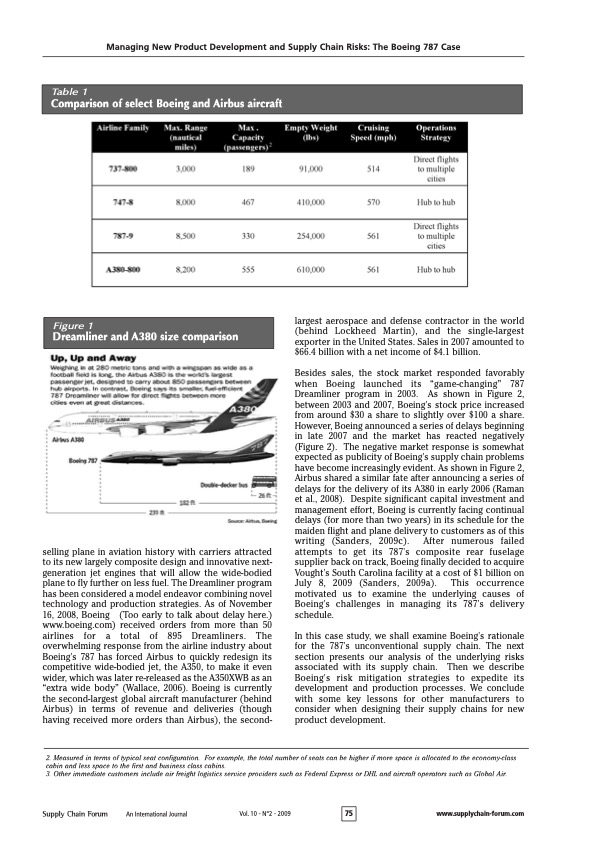
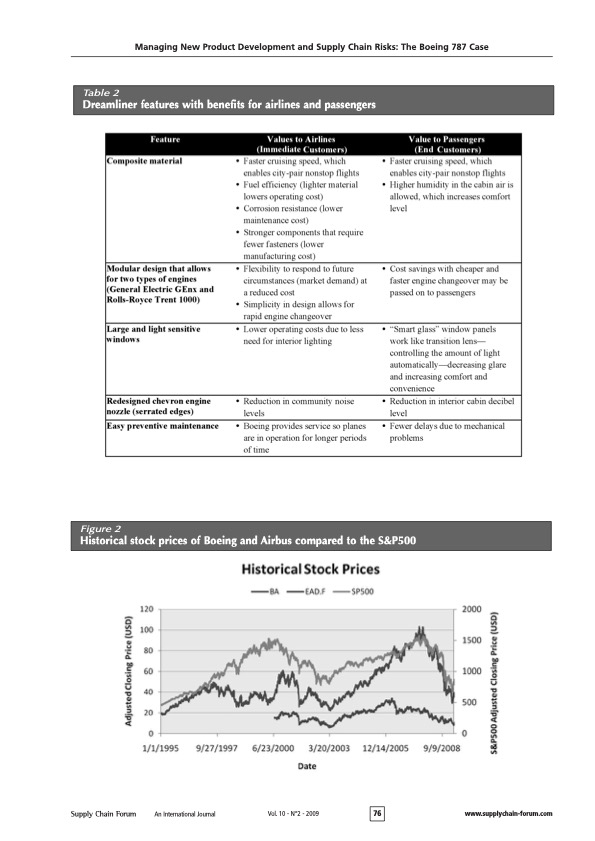
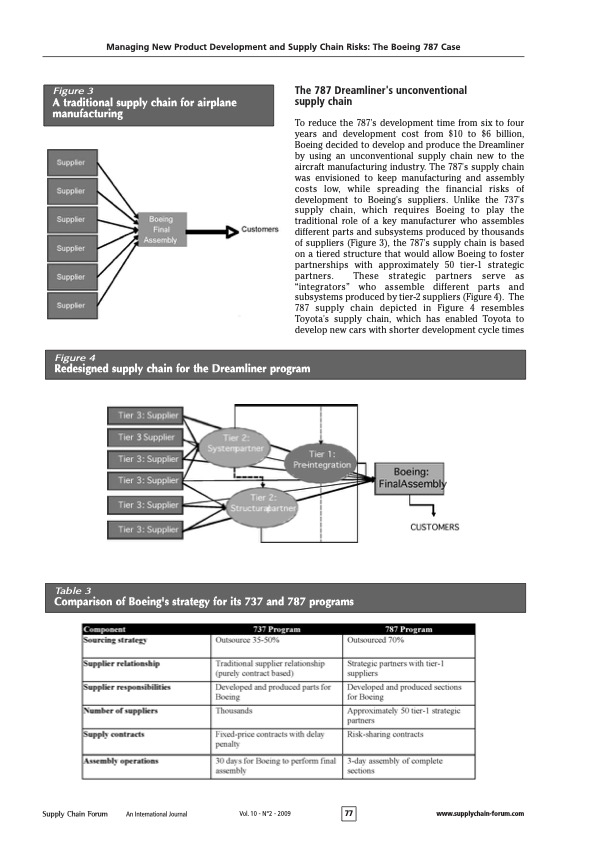
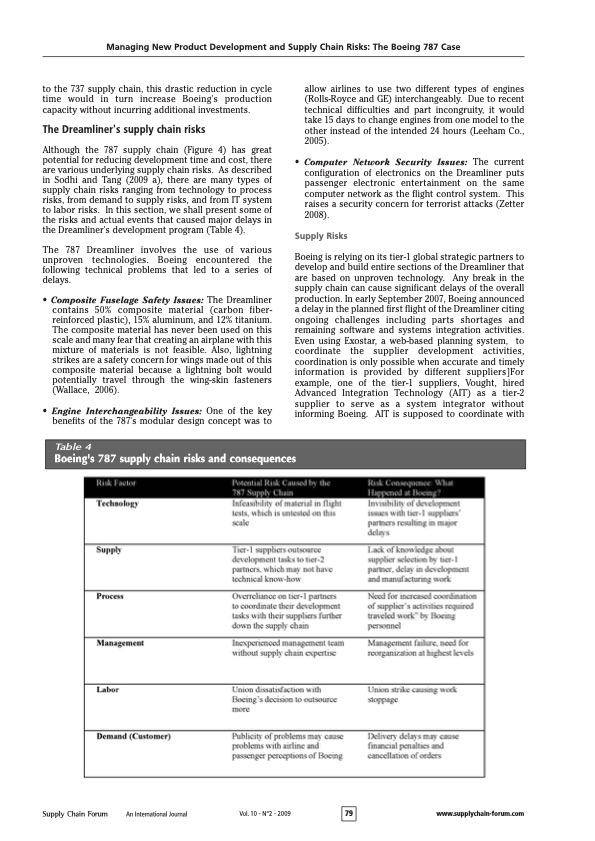
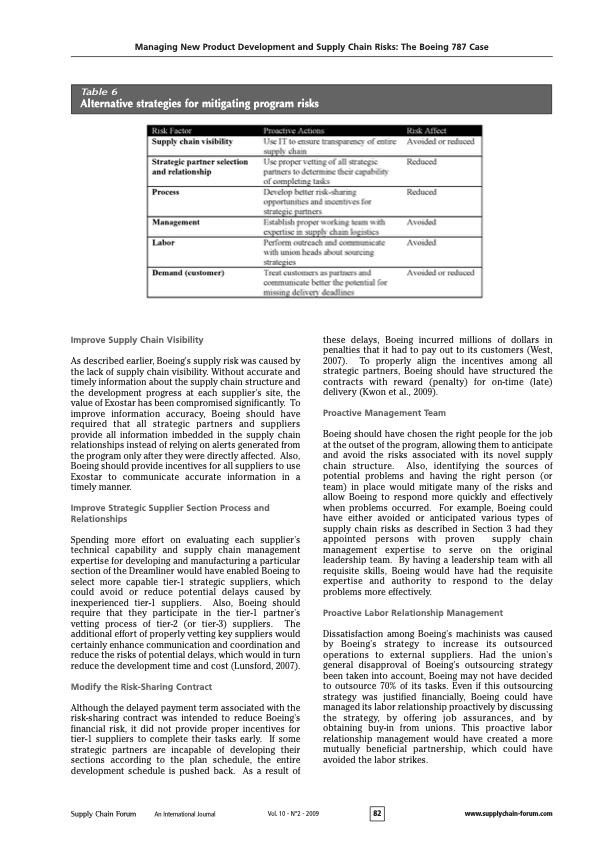
Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case The 787 Dreamliner's unconventional supply chain To reduce the 787's development time from six to four years and development cost from $10 to $6 billion, Boeing decided to develop and produce the Dreamliner by using an unconventional supply chain new to the aircraft manufacturing industry. The 787s supply chain was envisioned to keep manufacturing and assembly costs low, while spreading the financial risks of development to Boeing's suppliers. Unlike the 737s supply chain, which requires Boeing to play the traditional role of a key manufacturer who assembles different parts and subsystems produced by thousands of suppliers (Figure 3 ), the 787's supply chain is based on a tiered structure that would allow Boeing to foster partnerships with approximately 50 tier-1 strategic partners. These strategic partners serve as "integrators" who assemble different parts and subsystems produced by tier-2 suppliers (Figure 4). The 787 supply chain depicted in Figure 4 resembles Toyota's supply chain, which has enabled Toyota to develop new cars with shorter development cycle times Figure 4 Redesigned supply chain for the Dreamliner program Table 3 Comparison of Boeing's strategy for its 737 and 787 programs Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case Christopher S. Tang and Joshua D. Zimmerman UCLA Anderson Schood ctangearnderson.uda.edu joshua zimmerman.20096anderson.uda.edu Commented by James I. Nelson M.S. MBCP, CORP Business Continuity Services To stimulate revenue growth and market response, Boeing decided to develop the 787 Dreamliner. The 787 Dreamliner is not only a revolutionary aircraft, but it also utilizes an unconventional supply chain intended to drastically reduce development cost and time. However, despite significant management efforts and capital investment, Boeing is currently facing a series of delays in its schedule for the maiden flight and plane delivery to customers. This paper analyzes Boeing's rationale for the 787's unconventional supply chain, describes Boeing's challenges for managing this supply chain, and highlights some key lessons for other manufacturers to consider when designing their supply chains for new product development. Acknowiedyments: We uould like to thank Wiliam Schmidt of the Hartard Business School and ane anonymous reviewer for their constructive comments an an earlier version of this paper. Introduction Since the U.S. government deregulated air travel in 1977 , more airlines have entered the market causing fierce price competition. As airfares continued to decline, the total number of U.S. passengers per year has risen from approximately 240 million to 640 million from 1977 to 1999. At the same time, U.S. commercial aircraft manufacturers have faced major competition from European companies. After losing market share to Airbus (owned by EADS) in the late 1990s, Boeing was under pressure to decide between two basic competitive strategies: reduce the costs (and the selling prices) of existing types of aircraft or develop a new aircraft to raise revenues through value creation. In 2003, Boeing decided to focus on creating additional value for its customers (airlines) and their passengers by developing an innovative aircraft: the 787 Dreamliner. (Throughout this paper, we shall use the term "787 Dreamliner," "787," and "Dreamliner" interchangeably.) First, Boeing's value-creation strategy for the passengers was to improve their travel experience through redesigning the aircraft and offering significant improvements in comfort. For instance, relative to other aircrafts, over 50% of the primary structure of the 787 aircraft (including the fuselage and wing) would be made of composite materials (Hawk, 2005). As compared to the traditional material (aluminum) used in airplane manufacturing, the composite material allows for increased humidity and pressure to be maintained in the passenger cabin, offering substantial improvement to the flying experience. Also, the lightweight composite materials enable the Dreamliner to take long-haul fights. Consequently, the Dreamliner allows airlines to offer directonstop flights between any pair of cities without layovers, which is preferred by most international travelers (Hucko, 2007). Table 1 and Figure 1 (p. 75) compare the 787 aircraft with other popular aircrafts. Second, Boeing's value-creation strategy for its key immediate customers (the airlines) and its end customers (the passengers) was to improve flight operational efficiency by providing big-jet ranges to midsize airplanes while flying at approximately the same speed (Mach 0.85).' This efficiency would allow airlines to offer economical nonstop flights to and from more and smaller cities. In addition, with a capacity between 210 and 330 passengers and a range of up to 8,500 nautical miles, the 787 Dreamliner is designed to use 20% less fuel for comparable missions than today's similarly sized airplanes. The cost-per-seat mile is expected to be 10% lower than for any other aircraft. Also, unlike the traditional aluminum fuselages that tend to rust and fatigue, the 787's fuselages are based on composite materials, which reduce airlines' maintenance and replacement costs (Murray, 2007). Table 2 provides a summary of the Dreamliner's benefits for both the airlines and their passengers. Due to the unique value that the 787 provides to the airlines and their passengers, the number of orders exceeded expectations. The Dreamliner is the fastest- other tier-2 and tier-3 suppliers for Vought (Tang, 2007). Additionally, due to cultural differences, some tier- 2 or tier-3 suppliers do not often enter accurate and timely information into the Exostar system. As a result,various tier-1 suppliers and Boeing were not aware of the delay problems in a timely fashion, which makes it difficult for Boeing to respond to these problems quickly. Process Risks The underlying design of the 787 supply chain is likely to cause major delays because its efficiency depends on the synchronized just-in-time deliveries of all major sections from Boeing's tier-1 strategic partners. If the delivery of a section is delayed, the delivery schedule of the whole aircraft is delayed. Unless Boeing keeps some safety stocks of different complete sections, it is likely that Boeing will face late delivery. Also, under the risksharing contract, none of the strategic partners will get paid until the first completed plane is certified for flight. As strategic partners recognize the potential of being penalized unfairly if they complete their tasks before other suppliers, the risk-sharing contract payment may actually entice these strategic partners to work slower, which undermines the original intent of the risk-sharing contract (Kwon et al., 2009). Management Risks As Boeing used an unconventional supply chain structure to develop and build its Dreamliner, it is essential for Boeing to assemble a leadership team that includes some members who have a proven supply chain management record with expertise to prevent and anticipate certain risks as well as to develop contingency plans to mitigate the impact of different types of risks. However, Boeing's original leadership team for the 787 program did not include members with expertise on supply chain risk management. Without the requisite skills to manage an unconventional supply chain, Boeing was undertaking a huge managerial risk in uncharted waters. Labor Risks As Boeing increased its outsourcing effort, Boeing workers became concerned about their job security. Their concerns resulted in a strike by more than 25,000 Boeing employees starting in September 2008. The effects of the worker strike were also felt by Boeing's strategic partners. For example, anticipating that the strike at Boeing would trigger order cancellations and delivery delay of certain Boeing aircrafts, Spirit Aerosystems, a key supplier of Boeing, reduced its work week for employees who develop and manufacture various Boeing aircrafts. This reduced work schedule could potentially delay the delivery schedule of certain fuselage parts for the 787 (Rigby \& Hepher, 2008). Demand Risks As Boeing announced a series of delays, some customers lost their confidence in Boeing's aircraft development capability. In addition, there is a growing concern about the fact that the first 787s are overweight by about 8%, or 2.2 metric tons, which can lead to a 15% reduction in range (Norris, 2009). In response to Boeing's production and delivery delays and the doubt about 787's long range capability, some customers have begun canceling orders for the Dreamliner or migrating towards leasing contracts instead of purchasing the airplane outright. As of July 2009, the orders for the Dreamliner have been reduced from 895 (reported in November 2008) to 850 (reported in July 2009) (see Sanders, 2009b, for details). Table 5 Boeing's reactive risk mitigation strategies Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case Table 1 Comparison of select Boeing and Airbus aircraft selling plane in aviation history with carriers attracted to its new largely composite design and innovative nextgeneration jet engines that will allow the wide-bodied plane to fly further on less fuel. The Dreamliner program has been considered a model endeavor combining novel technology and production strategies. As of November 16, 2008, Boeing (Too early to talk about delay here.) www.boeing.com) received orders from more than 50 airlines for a total of 895 Dreamliners. The overwhelming response from the airline industry about Boeing's 787 has forced Airbus to quickly redesign its competitive wide-bodied jet, the A350, to make it even wider, which was later re-released as the A350XWB as an "extra wide body" (Wallace, 2006). Boeing is currently the second-largest global aircraft manufacturer (behind Airbus) in terms of revenue and deliveries (though having received more orders than Airbus), the second- largest aerospace and defense contractor in the world (behind Lockheed Martin), and the single-largest exporter in the United States. Sales in 2007 amounted to $66.4 billion with a net income of $4.1 billion. Besides sales, the stock market responded favorably when Boeing launched its "game-changing" 787 Dreamliner program in 2003. As shown in Figure 2, between 2003 and 2007, Boeing's stock price increased from around $30 a share to slightly over $100 a share. However, Boeing announced a series of delays beginning in late 2007 and the market has reacted negatively (Figure 2). The negative market response is somewhat expected as publicity of Boeing's supply chain problems have become increasingly evident. As shown in Figure 2, Airbus shared a similar fate after announcing a series of delays for the delivery of its A380 in early 2006 (Raman et al, 2008). Despite significant capital investment and management effort, Boeing is currently facing continual delays (for more than two years) in its schedule for the maiden flight and plane delivery to customers as of this writing (Sanders, 2009c). After numerous failed attempts to get its 787 's composite rear fuselage supplier back on track, Boeing finally decided to acquire Vought's South Carolina facility at a cost of $1 billion on July 8, 2009 (Sanders, 2009a). This occurrence motivated us to examine the underlying causes of Boeing's challenges in managing its 787's delivery schedule. In this case study, we shall examine Boeing's rationale for the 787's unconventional supply chain. The next section presents our analysis of the underlying risks associated with its supply chain. Then we describe Boeing's risk mitigation strategies to expedite its development and production processes. We conclude with some key lessons for other manufacturers to consider when designing their supply chains for new product development. Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case Table 2 Dreamliner features with benefits for airlines and passengers Figure 2 Historical stock prices of Boeing and Airbus compared to the S\&P500 to the 737 supply chain, this drastic reduction in cycle time would in turn increase Boeing's production capacity without incurring additional investments. The Dreamliner's supply chain risks Although the 787 supply chain (Figure 4) has great potential for reducing development time and cost, there are various underlying supply chain risks. As described in Sodhi and Tang (2009 a), there are many types of supply chain risks ranging from technology to process risks, from demand to supply risks, and from IT system to labor risks. In this section, we shall present some of the risks and actual events that caused major delays in the Dreamliner's development program (Table 4). The 787 Dreamliner involves the use of various unproven technologies. Boeing encountered the following technical problems that led to a series of delays. - Composite Fuselage Safety Issues: The Dreamliner contains 50% composite material (carbon fiberreinforced plastic), 15% aluminum, and 12% titanium. The composite material has never been used on this scale and many fear that creating an airplane with this mixture of materials is not feasible. Also, lightning strikes are a safety concern for wings made out of this composite material because a lightning bolt would potentially travel through the wing-skin fasteners (Wallace, 2006). - Engine Interchangeability Issues: One of the key benefits of the 787 's modular design concept was to allow airlines to use two different types of engines (Rolls-Royce and GE) interchangeably. Due to recent technical difficulties and part incongruity, it would take 15 days to change engines from one model to the other instead of the intended 24 hours (Leeham Co., 2005). - Computer Network Security Issues: The current configuration of electronics on the Dreamliner puts passenger electronic entertainment on the same computer network as the flight control system. This raises a security concern for terrorist attacks (Zetter 2008). Supply Risks Boeing is relying on its tier-1 global strategic partners to develop and build entire sections of the Dreamliner that are based on unproven technology. Any break in the supply chain can cause significant delays of the overall production. In early September 2007, Boeing announced a delay in the planned first flight of the Dreamliner citing ongoing challenges including parts shortages and remaining software and systems integration activities. Even using Exostar, a web-based planning system, to coordinate the supplier development activities, coordination is only possible when accurate and timely information is provided by different suppliers]For example, one of the tier-1 suppliers, Vought, hired Advanced Integration Technology (AIT) as a tier-2 supplier to serve as a system integrator without informing Boeing. AIT is supposed to coordinate with Table 4 Boeing's 787 supply chain risks and consequences Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case Table 6 Alternative strategies for mitigating program risks Improve Supply Chain Visibility As described earlier, Boeing's supply risk was caused by the lack of supply chain visibility. Without accurate and timely information about the supply chain structure and the development progress at each supplier's site, the value of Exostar has been compromised significantly. To improve information accuracy, Boeing should have required that all strategic partners and suppliers provide all information imbedded in the supply chain relationships instead of relying on alerts generated from the program only after they were directly affected. Also, Boeing should provide incentives for all suppliers to use Exostar to communicate accurate information in a timely manner. Improve Strategic Supplier Section Process and Relationships Spending more effort on evaluating each supplier's technical capability and supply chain management expertise for developing and manufacturing a particular section of the Dreamliner would have enabled Boeing to select more capable tier-1 strategic suppliers, which could avoid or reduce potential delays caused by inexperienced tier-1 suppliers. Also, Boeing should require that they participate in the tier-1 partner's vetting process of tier-2 (or tier-3) suppliers. The additional effort of properly vetting key suppliers would certainly enhance communication and coordination and reduce the risks of potential delays, which would in turn reduce the development time and cost (Lunsford, 2007). Modify the Risk-Sharing Contract Although the delayed payment term associated with the risk-sharing contract was intended to reduce Boeing's financial risk, it did not provide proper incentives for tier-1 suppliers to complete their tasks early. If some strategic partners are incapable of developing their sections according to the plan schedule, the entire development schedule is pushed back. As a result of these delays, Boeing incurred millions of dollars in penalties that it had to pay out to its customers (West, 2007). To properly align the incentives among all strategic partners, Boeing should have structured the contracts with reward (penalty) for on-time (late) delivery (Kwon et al., 2009). Proactive Management Team Boeing should have chosen the right people for the job at the outset of the program, allowing them to anticipate and avoid the risks associated with its novel supply chain structure. Also, identifying the sources of potential problems and having the right person (or team) in place would mitigate many of the risks and allow Boeing to respond more quickly and effectively when problems occurred. For example, Boeing could have either avoided or anticipated various types of supply chain risks as described in Section 3 had they appointed persons with proven supply chain management expertise to serve on the original leadership team. By having a leadership team with all requisite skills, Boeing would have had the requisite expertise and authority to respond to the delay problems more effectively. Proactive Labor Relationship Management Dissatisfaction among Boeing's machinists was caused by Boeing's strategy to increase its outsourced operations to external suppliers. Had the union's general disapproval of Boeing's outsourcing strategy been taken into account, Boeing may not have decided to outsource 70% of its tasks. Even if this outsourcing strategy was justified financially, Boeing could have managed its labor relationship proactively by discussing the strategy, by offering job assurances, and by obtaining buy-in from unions. This proactive labor relationship management would have created a more mutually beneficial partnership, which could have avoided the labor strikes. Boeing's reactive risk mitigation strategy To manage various disruptions as presented earlier, we now present Boeing's reactive response for reducing the negative impact of the current problems and for avoiding further complications resulting in additional delays (Table 5). To improve the safety of its composite fuselage, Boeing is redesigning its fuselage by using additional material to strengthen the wing structure; however, this additional material will increase the aircraft's overall weight. Boeing management has continued to assure its customers that it will work diligently to reduce the weight of the final version of the plane. Boeing is redesigning its installation process with the hope of reducing its changeover time from one engine model to the other. Finally, to ensure that the computer network is secure, a proper design is being required that allows for the separation of the navigation computer systems from the passenger electronic entertainment system. Mitigating Supply Risks After realizing that some tier-l strategic partners did not have the know-how to develop different sections of the aircraft or experience in managing their tier-2 suppliers to develop the requisite components for the sections, Boeing recognized the need to regain control of the development process of the 787. For instance, knowing that Vought Aircraft Industries was the weakest link in the Boeing's 787 supply chain, Boeing acquired one unit of Wought in 2008 and then another unit in 2009 (Ray, 2008; Sanders, 2009a). These two acquisitions provide Boeing direct control of these two units of Vought and their tier-2 suppliers for the fuselage development. Further, as a result of continued production delays, some of Boeing's suppliers were in jeopardy of facing massive profit losses, which put completion of the entire Dreamliner program at risk. For example, in response to threats of work stoppage, Boeing paid its tier-l strategic partner Spirit Aerosystems approximately $125 million in 2008 to ensure that this partner continued its vital operations, Ray 2008). Mitigating Process Risks As a response to suppliers' inability to meet production deadlines, Boeing decided that it must send key personnel to sites across the globe to fill suppliers' management vacuum and address production issues in person. This proved to be an expensive endeavor as personnel was pulled from responsibilities on-site at Boeing to address supply and manufacturing issues at the sites of their outsourced partners. The strategy of relying on suppliers for subassembly proved to be too risky for Boeing in certain circumstances and resulted in Boeing having to perform the work themselves. For instance, Boeing sent hundreds of its engineers to the sites of various tier-1, tier-2, or tier-3 suppliers worldwide to solve various technical problems that appeared to be the root cause of the delay in the 787s development. Ultimately, Boeing had to redesign the entire aircraft subassembly process (Gunsalus, 2007). While this hands-on approach would certainly help the process, it is very costly and time consuming, which defeats the underlying intents of the 787s redesigned supply chain as described earlier. Mitigating Management Risks To restore customers' confidence about Boeing's aircraft development capability and to reduce any further delays, Boeing recognized the need to bring in someone with a proven record of supply chain management expertise. In response, the original 787 program director, Mike Bair (with proven marketing expertise), was replaced by Patrick Shanahan, who had proven expertise in supply chain management. Shanahan is now responsible for coordination of all activities for Boeing's major plane families, which includes the Dreamliner. Moreover, Boeing has changed it top leadership by replacing its interim CEO, James Bell, with Jim McNerney in 2005. Mitigating Labor Risks To bring about an end to the strike after two months of shutdown, Boeing made concessions that would give workers a 15% wage boost over four years. On the key issue of job security, which had been the major impediment to reaching an agreement, Boeing agreed to limit the amount of work that outside vendors could perform. Therefore, Boeing's concept of outsourcing a significant amount of work to global partners could be endangered and production costs could eventually rise. In response to the wage increases and limits in outsourcing promised by Boeing, the machinists union conceded to withdraw charges filed with the Department of Labor regarding allegations of unfair bargaining practices at Boeing (Gates, 2008). Mitigating Demand (Customer) Risks As customers had begun to cancel their 787 orders and as the company's capability of developing the 787 was put into question, Boeing developed the following mitigation strategies. First, as a way to compensate its customers' potential loss due to the late deliveries of their orders, Boeing is supplying replacement aircrafts (new 737 or 747 ) to various concerned airlines such as Virgin Atlantic (Lunsford October 11, 2007; Crown, 2008). Second, to restore Boeing's public image, Boeing has improved its communication by sharing its progress updates on its website. In addition, Boeing is conducting a publicity campaign to promote the superior technology of the 787 and the overall value that the airplane will offer to airlines and passengers (Crown, 2008). Boeing's potential proactive risk mitigation strategies As Boeing makes its best effort to restore confidence in its capability of developing innovative aircrafts such as the Dreamliner, there are certain risk mitigation strategies that Boeing could have embarked on at the outset of the program to better manage potential risks proactively (Table 6). Proactive Customer Relationship Management Recognizing the risks associated with innovative product development, proactive customer relationship management is critical to help customers set proper expectations when placing their orders. Better communication with customers throughout the development process can enable a company to manage customers' perceptions throughout the entire product development process. Setting proper expectations about the delivery schedules of its 787 Dreamliner may have encouraged the airlines to manage their aircraft replacement schedule differently, say order more 737s and 747s and fewer 787s. Without setting an aggressive delivery schedule to its customers, it was plausible for Boeing to reduce the penalty caused by the delayed delivery schedule. Through continuous engagement and open communication about the challenges and Boeing's contingency plans, it would have been plausible for Boeing to manage its customers' perception and its reputation better. Afterthoughts By examining the inherent risks associated with Boeing's supply chain and by analyzing Boeing's reactive mitigation strategies presented earlier, we have developed the following insights that other manufacturers may consider when managing their supply chains for efficient new product development. Assembling a Leadership Team with Requisite Expertise On the surface, it appears that Boeing's fundamental problem was caused by its attempts to simultaneously take on too many drastic changes. These changes include unproven technology, unconventional supply chains, unproven supplier's capability to take on new roles and responsibilities, and unproven IT coordination systems. However, one plausible reason for Boeing to take on so many drastic changes may be because the 787 leadership team underestimated the risks associated with all these changes. Had Boeing constructed a multi-disciplinary team with expertise to identify and evaluate various supply chain risks, it might have been possible for Boeing to anticipate and avoid potential risks, and to develop proactive mitigation strategies and contingency plans to reduce the impact of various supply chain disruptions. Obtaining Internal Support Proactively Partnerships between management and labor are essential for smooth operations for companies to implement any new initiatives including new product development programs. Although their interests are often misaligned, better communication of business strategies with union workers is a proactive step towards avoiding costly worker strikes. Also, aligning the incentives for both parties proactively is more likely to reduce potential internal disruptions down the road. Improving Supply Chain Visibility to Facilitate Coordination and Collaboration Besides the need to perform due diligence in key supplier selection to ensure that the selected supplier has the requisite capability and the commitment for success, a company should consider cultivating stronger commitment in exchange for accurate information in a timely manner. Overly relying on IT communication is highly risky when managing a new project. To mitigate the risks caused by partners further upstream or downstream, companies should strive to gain complete visibility of the entire supply chain. Having clear supply chain visibility would enhance the capability for a company to take corrective action more quickly, which is more likely to reduce the negative impact of a disruption along the supply chain. See Sodhi and Tang (2009b) for a discussion of the importance of timely response to mitigate the negative effects of supply chain disruptions. Proactive Management of Customer Expectation and Perception Due to the inherent risks associated with new product development, it is critical for a company to help its customers set proper expectations proactively, especially regarding the potential delay caused by various types of risks as highlighted in Table 3 . Setting proper expectations at the outset would reduce potential customer dissatisfaction down the road. During the development phase, it is advisable for the company to maintain open and honest communication with its customers regarding the actual progress, technical challenges, and corrective measures. Such efforts would possibly gain customer trust, which would improve their loyalty in the long run. Conclusion Boeing's Dreamliner program involves dramatic shifts in supply chain strategy from traditional methods used in the aerospace industry. In addition, Boeing boasted about its novel manufacturing techniques and its technological marvels. Such dramatic shifts from convention involve significant potential for encountering risks throughout the process. Boeing's ongoing issues with meeting delivery deadlines are a direct result of its decision to make drastic changes in the design, the development process, and the supply chain associated with the Dreamliner program simultaneously without having the proper management team in place. Further, this team did not proactively assess the risks that were later realized and did not develop coherent strategies for effectively mitigating them. Although it may be impossible to identify all potential risks and create contingency plans for all eventualities before a project begins, Boeing could have done many things differently. It is instructive for managers in any industry to view the issues that Boeing faced and analyze how these issues were handled so that they can learn from mistakes that were made before engaging in similar supply chain restructuring. Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case and lower development costs (Tang, 1999). Table 3 highlights the key differences between the 737's supply chain and the unconventional 787 supply chain. For instance, under the 787's supply chain structure, these tier-1 strategic partners are responsible for delivering complete sections of the aircraft to Boeing, which would allow Boeing to assemble these complete sections within three days at its plant in Everett, Washington (Figure 5). We now explain the relationale behind the 787's supply chain as highlighted is table 3 . Outsource more By outsourcing 70% of the development and production activities under the 787 program, Boeing can shorten the development time by leveraging suppliers' ability to develop different parts at the same time. Also, Boeing may be able to reduce the development cost of the 787 by exploiting suppliers' expertise. As Boeing outsourced more, communication and coordination between Boeing and its suppliers became critical for managing the progress of the 787 development program. To facilitate the coordination and collaboration among suppliers and Boeing, Boeing implemented a web-based tool called Exostar that is intended to gain supply chain visibility, improve control and integration of critical business processes, and reduce development time and cost Manufacturing Business Technology, 2007). Reduce direct supply base, delegate more, and focus more To reduce development time and cost for the Dreamliner, Boeing fostered strategic partnerships with approximately 50 tier-1 suppliers who will design and build entire sections of the plane and ship them to Boeing. By reducing its direct supply base, Boeing could focus more of its attention and resources on working with tier-l suppliers (pre-integration stages) rather than with raw material procurement and early component subassembly. However, unless the supplier relationship is managed correctly, reducing the supply base can increase supply risks because of the reduced bargaining power of the manufacturer (Tang, 1999). The rationale behind this shift is to empower its strategic suppliers to develop and produce different sections in parallel so as to reduce the development time. Also, by shifting more assembly operations to its strategic partners located in different countries, there is a potential savings in development cost as well (Figure b). Reduce financial risks Under the 787 program, Boeing instituted a new risksharing contract under which no strategic suppliers will receive payment for the development cost until Boeing delivers its first 787 to its customers (slated to be ANA airlines). This contract payment term was intended to provide incentives for strategic partners to collaborate and coordinate their development efforts. Although this contract imposes certain financial risks for Boeing's strategic suppliers if delivery deadlines are missed, they are incentivized by being allowed to own their intellectual property, which can then be licensed to other companies in the future. Another incentive for the strategic partners to accept this payment term is that it allows them to increase their revenues (and potential profits) by taking up the development and production of the entire section of the plane instead of a small part of the plane. Increase production capacity without incurring additional costs Decentralizing the manufacturing process would allow Boeing to outsource noncritical processes. The intention is to reduce the capital investment for the 787 development program. Also, under the 787 supply chain, Boeing needs only three days to assemble complete sections of the Dreamliner at its plant. Relative Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case The 787 Dreamliner's unconventional supply chain To reduce the 787's development time from six to four years and development cost from $10 to $6 billion, Boeing decided to develop and produce the Dreamliner by using an unconventional supply chain new to the aircraft manufacturing industry. The 787s supply chain was envisioned to keep manufacturing and assembly costs low, while spreading the financial risks of development to Boeing's suppliers. Unlike the 737s supply chain, which requires Boeing to play the traditional role of a key manufacturer who assembles different parts and subsystems produced by thousands of suppliers (Figure 3 ), the 787's supply chain is based on a tiered structure that would allow Boeing to foster partnerships with approximately 50 tier-1 strategic partners. These strategic partners serve as "integrators" who assemble different parts and subsystems produced by tier-2 suppliers (Figure 4). The 787 supply chain depicted in Figure 4 resembles Toyota's supply chain, which has enabled Toyota to develop new cars with shorter development cycle times Figure 4 Redesigned supply chain for the Dreamliner program Table 3 Comparison of Boeing's strategy for its 737 and 787 programs Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case Christopher S. Tang and Joshua D. Zimmerman UCLA Anderson Schood ctangearnderson.uda.edu joshua zimmerman.20096anderson.uda.edu Commented by James I. Nelson M.S. MBCP, CORP Business Continuity Services To stimulate revenue growth and market response, Boeing decided to develop the 787 Dreamliner. The 787 Dreamliner is not only a revolutionary aircraft, but it also utilizes an unconventional supply chain intended to drastically reduce development cost and time. However, despite significant management efforts and capital investment, Boeing is currently facing a series of delays in its schedule for the maiden flight and plane delivery to customers. This paper analyzes Boeing's rationale for the 787's unconventional supply chain, describes Boeing's challenges for managing this supply chain, and highlights some key lessons for other manufacturers to consider when designing their supply chains for new product development. Acknowiedyments: We uould like to thank Wiliam Schmidt of the Hartard Business School and ane anonymous reviewer for their constructive comments an an earlier version of this paper. Introduction Since the U.S. government deregulated air travel in 1977 , more airlines have entered the market causing fierce price competition. As airfares continued to decline, the total number of U.S. passengers per year has risen from approximately 240 million to 640 million from 1977 to 1999. At the same time, U.S. commercial aircraft manufacturers have faced major competition from European companies. After losing market share to Airbus (owned by EADS) in the late 1990s, Boeing was under pressure to decide between two basic competitive strategies: reduce the costs (and the selling prices) of existing types of aircraft or develop a new aircraft to raise revenues through value creation. In 2003, Boeing decided to focus on creating additional value for its customers (airlines) and their passengers by developing an innovative aircraft: the 787 Dreamliner. (Throughout this paper, we shall use the term "787 Dreamliner," "787," and "Dreamliner" interchangeably.) First, Boeing's value-creation strategy for the passengers was to improve their travel experience through redesigning the aircraft and offering significant improvements in comfort. For instance, relative to other aircrafts, over 50% of the primary structure of the 787 aircraft (including the fuselage and wing) would be made of composite materials (Hawk, 2005). As compared to the traditional material (aluminum) used in airplane manufacturing, the composite material allows for increased humidity and pressure to be maintained in the passenger cabin, offering substantial improvement to the flying experience. Also, the lightweight composite materials enable the Dreamliner to take long-haul fights. Consequently, the Dreamliner allows airlines to offer directonstop flights between any pair of cities without layovers, which is preferred by most international travelers (Hucko, 2007). Table 1 and Figure 1 (p. 75) compare the 787 aircraft with other popular aircrafts. Second, Boeing's value-creation strategy for its key immediate customers (the airlines) and its end customers (the passengers) was to improve flight operational efficiency by providing big-jet ranges to midsize airplanes while flying at approximately the same speed (Mach 0.85).' This efficiency would allow airlines to offer economical nonstop flights to and from more and smaller cities. In addition, with a capacity between 210 and 330 passengers and a range of up to 8,500 nautical miles, the 787 Dreamliner is designed to use 20% less fuel for comparable missions than today's similarly sized airplanes. The cost-per-seat mile is expected to be 10% lower than for any other aircraft. Also, unlike the traditional aluminum fuselages that tend to rust and fatigue, the 787's fuselages are based on composite materials, which reduce airlines' maintenance and replacement costs (Murray, 2007). Table 2 provides a summary of the Dreamliner's benefits for both the airlines and their passengers. Due to the unique value that the 787 provides to the airlines and their passengers, the number of orders exceeded expectations. The Dreamliner is the fastest- other tier-2 and tier-3 suppliers for Vought (Tang, 2007). Additionally, due to cultural differences, some tier- 2 or tier-3 suppliers do not often enter accurate and timely information into the Exostar system. As a result,various tier-1 suppliers and Boeing were not aware of the delay problems in a timely fashion, which makes it difficult for Boeing to respond to these problems quickly. Process Risks The underlying design of the 787 supply chain is likely to cause major delays because its efficiency depends on the synchronized just-in-time deliveries of all major sections from Boeing's tier-1 strategic partners. If the delivery of a section is delayed, the delivery schedule of the whole aircraft is delayed. Unless Boeing keeps some safety stocks of different complete sections, it is likely that Boeing will face late delivery. Also, under the risksharing contract, none of the strategic partners will get paid until the first completed plane is certified for flight. As strategic partners recognize the potential of being penalized unfairly if they complete their tasks before other suppliers, the risk-sharing contract payment may actually entice these strategic partners to work slower, which undermines the original intent of the risk-sharing contract (Kwon et al., 2009). Management Risks As Boeing used an unconventional supply chain structure to develop and build its Dreamliner, it is essential for Boeing to assemble a leadership team that includes some members who have a proven supply chain management record with expertise to prevent and anticipate certain risks as well as to develop contingency plans to mitigate the impact of different types of risks. However, Boeing's original leadership team for the 787 program did not include members with expertise on supply chain risk management. Without the requisite skills to manage an unconventional supply chain, Boeing was undertaking a huge managerial risk in uncharted waters. Labor Risks As Boeing increased its outsourcing effort, Boeing workers became concerned about their job security. Their concerns resulted in a strike by more than 25,000 Boeing employees starting in September 2008. The effects of the worker strike were also felt by Boeing's strategic partners. For example, anticipating that the strike at Boeing would trigger order cancellations and delivery delay of certain Boeing aircrafts, Spirit Aerosystems, a key supplier of Boeing, reduced its work week for employees who develop and manufacture various Boeing aircrafts. This reduced work schedule could potentially delay the delivery schedule of certain fuselage parts for the 787 (Rigby \& Hepher, 2008). Demand Risks As Boeing announced a series of delays, some customers lost their confidence in Boeing's aircraft development capability. In addition, there is a growing concern about the fact that the first 787s are overweight by about 8%, or 2.2 metric tons, which can lead to a 15% reduction in range (Norris, 2009). In response to Boeing's production and delivery delays and the doubt about 787's long range capability, some customers have begun canceling orders for the Dreamliner or migrating towards leasing contracts instead of purchasing the airplane outright. As of July 2009, the orders for the Dreamliner have been reduced from 895 (reported in November 2008) to 850 (reported in July 2009) (see Sanders, 2009b, for details). Table 5 Boeing's reactive risk mitigation strategies Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case Table 1 Comparison of select Boeing and Airbus aircraft selling plane in aviation history with carriers attracted to its new largely composite design and innovative nextgeneration jet engines that will allow the wide-bodied plane to fly further on less fuel. The Dreamliner program has been considered a model endeavor combining novel technology and production strategies. As of November 16, 2008, Boeing (Too early to talk about delay here.) www.boeing.com) received orders from more than 50 airlines for a total of 895 Dreamliners. The overwhelming response from the airline industry about Boeing's 787 has forced Airbus to quickly redesign its competitive wide-bodied jet, the A350, to make it even wider, which was later re-released as the A350XWB as an "extra wide body" (Wallace, 2006). Boeing is currently the second-largest global aircraft manufacturer (behind Airbus) in terms of revenue and deliveries (though having received more orders than Airbus), the second- largest aerospace and defense contractor in the world (behind Lockheed Martin), and the single-largest exporter in the United States. Sales in 2007 amounted to $66.4 billion with a net income of $4.1 billion. Besides sales, the stock market responded favorably when Boeing launched its "game-changing" 787 Dreamliner program in 2003. As shown in Figure 2, between 2003 and 2007, Boeing's stock price increased from around $30 a share to slightly over $100 a share. However, Boeing announced a series of delays beginning in late 2007 and the market has reacted negatively (Figure 2). The negative market response is somewhat expected as publicity of Boeing's supply chain problems have become increasingly evident. As shown in Figure 2, Airbus shared a similar fate after announcing a series of delays for the delivery of its A380 in early 2006 (Raman et al, 2008). Despite significant capital investment and management effort, Boeing is currently facing continual delays (for more than two years) in its schedule for the maiden flight and plane delivery to customers as of this writing (Sanders, 2009c). After numerous failed attempts to get its 787 's composite rear fuselage supplier back on track, Boeing finally decided to acquire Vought's South Carolina facility at a cost of $1 billion on July 8, 2009 (Sanders, 2009a). This occurrence motivated us to examine the underlying causes of Boeing's challenges in managing its 787's delivery schedule. In this case study, we shall examine Boeing's rationale for the 787's unconventional supply chain. The next section presents our analysis of the underlying risks associated with its supply chain. Then we describe Boeing's risk mitigation strategies to expedite its development and production processes. We conclude with some key lessons for other manufacturers to consider when designing their supply chains for new product development. Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case Table 2 Dreamliner features with benefits for airlines and passengers Figure 2 Historical stock prices of Boeing and Airbus compared to the S\&P500 to the 737 supply chain, this drastic reduction in cycle time would in turn increase Boeing's production capacity without incurring additional investments. The Dreamliner's supply chain risks Although the 787 supply chain (Figure 4) has great potential for reducing development time and cost, there are various underlying supply chain risks. As described in Sodhi and Tang (2009 a), there are many types of supply chain risks ranging from technology to process risks, from demand to supply risks, and from IT system to labor risks. In this section, we shall present some of the risks and actual events that caused major delays in the Dreamliner's development program (Table 4). The 787 Dreamliner involves the use of various unproven technologies. Boeing encountered the following technical problems that led to a series of delays. - Composite Fuselage Safety Issues: The Dreamliner contains 50% composite material (carbon fiberreinforced plastic), 15% aluminum, and 12% titanium. The composite material has never been used on this scale and many fear that creating an airplane with this mixture of materials is not feasible. Also, lightning strikes are a safety concern for wings made out of this composite material because a lightning bolt would potentially travel through the wing-skin fasteners (Wallace, 2006). - Engine Interchangeability Issues: One of the key benefits of the 787 's modular design concept was to allow airlines to use two different types of engines (Rolls-Royce and GE) interchangeably. Due to recent technical difficulties and part incongruity, it would take 15 days to change engines from one model to the other instead of the intended 24 hours (Leeham Co., 2005). - Computer Network Security Issues: The current configuration of electronics on the Dreamliner puts passenger electronic entertainment on the same computer network as the flight control system. This raises a security concern for terrorist attacks (Zetter 2008). Supply Risks Boeing is relying on its tier-1 global strategic partners to develop and build entire sections of the Dreamliner that are based on unproven technology. Any break in the supply chain can cause significant delays of the overall production. In early September 2007, Boeing announced a delay in the planned first flight of the Dreamliner citing ongoing challenges including parts shortages and remaining software and systems integration activities. Even using Exostar, a web-based planning system, to coordinate the supplier development activities, coordination is only possible when accurate and timely information is provided by different suppliers]For example, one of the tier-1 suppliers, Vought, hired Advanced Integration Technology (AIT) as a tier-2 supplier to serve as a system integrator without informing Boeing. AIT is supposed to coordinate with Table 4 Boeing's 787 supply chain risks and consequences Managing New Product Development and Supply Chain Risks: The Boeing 787 Case Table 6 Alternative strategies for mitigating program risks Improve Supply Chain Visibility As described earlier, Boeing's supply risk was caused by the lack of supply chain visibility. Without accurate and timely information about the supply chain structure and the development progress at each supplier's site, the value of Exostar has been compromised significantly. To improve information accuracy, Boeing should have required that all strategic partners and suppliers provide all information imbedded in the supply chain relationships instead of relying on alerts generated from the program only after they were directly affected. Also, Boeing should provide incentives for all suppliers to use Exostar to communicate accurate information in a timely manner. Improve Strategic Supplier Section Process and Relationships Spending more effort on evaluating each supplier's technical capability and supply chain management expertise for developing and manufacturing a particular section of the Dreamliner would have enabled Boeing to select more capable tier-1 strategic suppliers, which could avoid or reduce potential delays caused by inexperienced tier-1 suppliers. Also, Boeing should require that they participate in the tier-1 partner's vetting process of tier-2 (or tier-3) suppliers. The additional effort of properly vetting key suppliers would certainly enhance communication and coordination and reduce the risks of potential delays, which would in turn reduce the development time and cost (Lunsford, 2007). Modify the Risk-Sharing Contract Although the delayed payment term associated with the risk-sharing contract was intended to reduce Boeing's financial risk, it did not provide proper incentives for tier-1 suppliers to complete their tasks early. If some strategic partners are incapable of developing their sections according to the plan schedule, the entire development schedule is pushed back. As a result of these delays, Boeing incurred millions of dollars in penalties that it had to pay out to its customers (West, 2007). To properly align the incentives among all strategic partners, Boeing should have structured the contracts with reward (penalty) for on-time (late) delivery (Kwon et al., 2009). Proactive Management Team Boeing should have chosen the right people for the job at the outset of the program, allowing them to anticipate and avoid the risks associated with its novel supply chain structure. Also, identifying the sources of potential problems and having the right person (or team) in place would mitigate many of the risks and allow Boeing to respond more quickly and effectively when problems occurred. For example, Boeing could have either avoided or anticipated various types of supply chain risks as described in Section 3 had they appointed persons with proven supply chain management expertise to serve on the original leadership team. By having a leadership team with all requisite skills, Boeing would have had the requisite expertise and authority to respond to the delay problems more effectively. Proactive Labor Relationship Management Dissatisfaction among Boeing's machinists was caused by Boeing's strategy to increase its outsourced operations to external suppliers. Had the union's general disapproval of Boeing's outsourcing strategy been taken into account, Boeing may not have decided to outsource 70% of its tasks. Even if this outsourcing strategy was justified financially, Boeing could have managed its labor relationship proactively by discussing the strategy, by offering job assurances, and by obtaining buy-in from unions. This proactive labor relationship management would have created a more mutually beneficial partnership, which could have avoided the labor strikes. Boeing's reactive risk mitigation strategy To manage various disruptions as presented earlier, we now present Boeing's reactive response for reducing the negative impact of the current problems and for avoiding further complications resulting in additional delays (Table 5). To improve the safety of its composite fuselage, Boeing is redesigning its fuselage by using additional material to strengthen the wing structure; however, this additional material will increase the aircraft's overall weight. Boeing management has continued to assure its customers that it will work diligently to reduce the weight of the final version of the plane. Boeing is redesigning its installation process with the hope of reducing its changeover time from one engine model to the other. Finally, to ensure that the computer network is secure, a proper design is being required that allows for the separation of the navigation computer systems from the passenger electronic entertainment system. Mitigating Supply Risks After realizing that some tier-l strategic partners did not have the know-how to develop different sections of the aircraft or experience in managing their tier-2 suppliers to develop the requisite components for the sections, Boeing recognized the need to regain control of the development process of the 787. For instance, knowing that Vought Aircraft Industries was the weakest link in the Boeing's 787 supply chain, Boeing acquired one unit of Wought in 2008 and then another unit in 2009 (Ray, 2008; Sanders, 2009a). These two acquisitions provide Boeing direct control of these two units of Vought and their tier-2 suppliers for the fuselage development. Further, as a result of continued production delays, some of Boeing's suppliers were in jeopardy of facing massive profit losses, which put completion of the entire Dreamliner program at risk. For example, in response to threats of work stoppage, Boeing paid its tier-l strategic partner Spirit Aerosystems approximately $125 million in 2008 to ensure that this partner continued its vital operations, Ray 2008). Mitigating Process Risks As a response to suppliers' inability to meet production deadlines, Boeing decided that it must send key personnel to sites across the globe to fill suppliers' management vacuum and address production issues in person. This proved to be an expensive endeavor as personnel was pulled from responsibilities on-site at Boeing to address supply and manufacturing issues at the sites of their outsourced partners. The strategy of relying on suppliers for subassembly proved to be too risky for Boeing in certain circumstances and resulted in Boeing having to perform the work themselves. For instance, Boeing sent hundreds of its engineers to the sites of various tier-1, tier-2, or tier-3 suppliers worldwide to solve various technical problems that appeared to be the root cause of the delay in the 787s development. Ultimately, Boeing had to redesign the entire aircraft subassembly process (Gunsalus, 2007). While this hands-on approach would certainly help the process, it is very costly and time consuming, which defeats the underlying intents of the 787s redesigned supply chain as described earlier. Mitigating Management Risks To restore customers' confidence about Boeing's aircraft development capability and to reduce any further delays, Boeing recognized the need to bring in someone with a proven record of supply chain management expertise. In response, the original 787 program director, Mike Bair (with proven marketing expertise), was replaced by Patrick Shanahan, who had proven expertise in supply chain management. Shanahan is now responsible for coordination of all activities for Boeing's major plane families, which includes the Dreamliner. Moreover, Boeing has changed it top leadership by replacing its interim CEO, James Bell, with Jim McNerney in 2005. Mitigating Labor Risks To bring about an end to the strike after two months of shutdown, Boeing made concessions that would give workers a 15% wage boost over four years. On the key issue of job security, which had been the major impediment to reaching an agreement, Boeing agreed to limit the amount of work that outside vendors could perform. Therefore, Boeing's concept of outsourcing a significant amount of work to global partners could be endangered and production costs could eventually rise. In response to the wage increases and limits in outsourcing promised by Boeing, the machinists union conceded to withdraw charges filed with the Department of Labor regarding allegations of unfair bargaining practices at Boeing (Gates, 2008). Mitigating Demand (Customer) Risks As customers had begun to cancel their 787 orders and as the company's capability of developing the 787 was put into question, Boeing developed the following mitigation strategies. First, as a way to compensate its customers' potential loss due to the late deliveries of their orders, Boeing is supplying replacement aircrafts (new 737 or 747 ) to various concerned airlines such as Virgin Atlantic (Lunsford October 11, 2007; Crown, 2008). Second, to restore Boeing's public image, Boeing has improved its communication by sharing its progress updates on its website. In addition, Boeing is conducting a publicity campaign to promote the superior technology of the 787 and the overall value that the airplane will offer to airlines and passengers (Crown, 2008). Boeing's potential proactive risk mitigation strategies As Boeing makes its best effort to restore confidence in its capability of developing innovative aircrafts such as the Dreamliner, there are certain risk mitigation strategies that Boeing could have embarked on at the outset of the program to better manage potential risks proactively (Table 6). Proactive Customer Relationship Management Recognizing the risks associated with innovative product development, proactive customer relationship management is critical to help customers set proper expectations when placing their orders. Better communication with customers throughout the development process can enable a company to manage customers' perceptions throughout the entire product development process. Setting proper expectations about the delivery schedules of its 787 Dreamliner may have encouraged the airlines to manage their aircraft replacement schedule differently, say order more 737s and 747s and fewer 787s. Without setting an aggressive delivery schedule to its customers, it was plausible for Boeing to reduce the penalty caused by the delayed delivery schedule. Through continuous engagement and open communication about the challenges and Boeing's contingency plans, it would have been plausible for Boeing to manage its customers' perception and its reputation better. Afterthoughts By examining the inherent risks associated with Boeing's supply chain and by analyzing Boeing's reactive mitigation strategies presented earlier, we have developed the following insights that other manufacturers may consider when managing their supply chains for efficient new product development. Assembling a Leadership Team with Requisite Expertise On the surface, it appears that Boeing's fundamental problem was caused by its attempts to simultaneously take on too many drastic changes. These changes include unproven technology, unconventional supply chains, unproven supplier's capability to take on new roles and responsibilities, and unproven IT coordination systems. However, one plausible reason for Boeing to take on so many drastic changes may be because the 787 leadership team underestimated the risks associated with all these changes. Had Boeing constructed a multi-disciplinary team with expertise to identify and evaluate various supply chain risks, it might have been possible for Boeing to anticipate and avoid potential risks, and to develop proactive mitigation strategies and contingency plans to reduce the impact of various supply chain disruptions. Obtaining Internal Support Proactively Partnerships between management and labor are essential for smooth operations for companies to implement any new initiatives including new product development programs. Although their interests are often misaligned, better communication of business strategies with union workers is a proactive step towards avoiding costly worker strikes. Also, aligning the incentives for both parties proactively is more likely to reduce potential internal disruptions down the road. Improving Supply Chain Visibility to Facilitate Coordination and Collaboration Besides the need to perform due diligence in key supplier selection to ensure that the selected supplier has the requisite capability and the commitment for success, a company should consider cultivating stronger commitment in exchange for accurate information in a timely manner. Overly relying on IT communication is highly risky when managing a new project. To mitigate the risks caused by partners further upstream or downstream, companies should strive to gain complete visibility of the entire supply chain. Having clear supply chain visibility would enhance the capability for a company to take corrective action more quickly, which is more likely to reduce the negative impact of a disruption along the supply chain. See Sodhi and Tang (2009b) for a discussion of the importance of timely response to mitigate the negative effects of supply chain disruptions. Proactive Management of Customer Expectation and Perception Due to the inherent risks associated with new product development, it is critical for a company to help its customers set proper expectations proactively, especially regarding the potential delay caused by various types of risks as highlighted in Table 3 . Setting proper expectations at the outset would reduce potential customer dissatisfaction down the road. During the development phase, it is advisable for the company to maintain open and honest communication with its customers regarding the actual progress, technical challenges, and corrective measures. Such efforts would possibly gain customer trust, which would improve their loyalty in the long run. Conclusion Boeing's Dreamliner program involves dramatic shifts in supply chain strategy from traditional methods used in the aerospace industry. In addition, Boeing boasted about its novel manufacturing techniques and its technological marvels. Such dramatic shifts from convention involve significant potential for encountering risks throughout the process. Boeing's ongoing issues with meeting delivery deadlines are a direct result of its decision to make drastic changes in the design, the development process, and the supply chain associated with the Dreamliner program simultaneously without having the proper management team in place. Further, this team did not proactively assess the risks that were later realized and did not develop coherent strategies for effectively mitigating them. Although it may be impossible to identify all potentialStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


