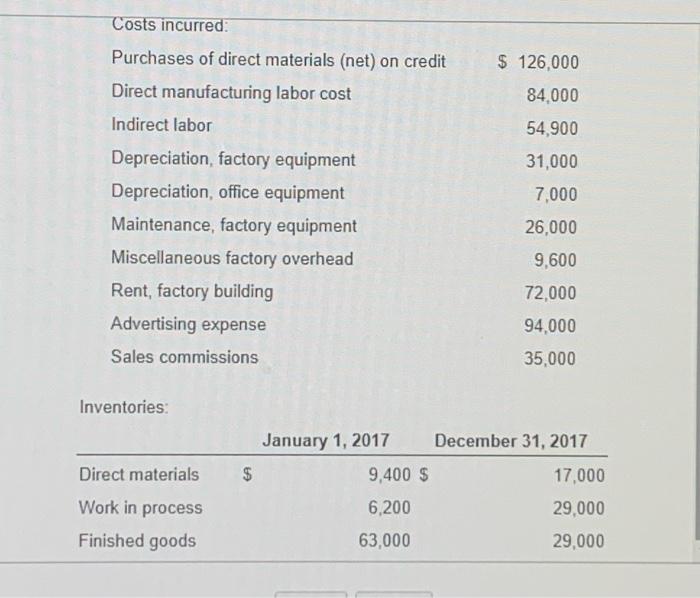
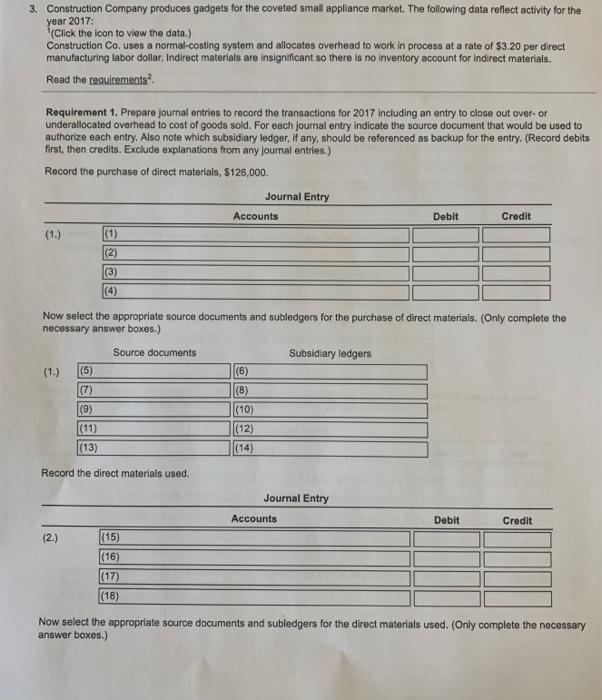
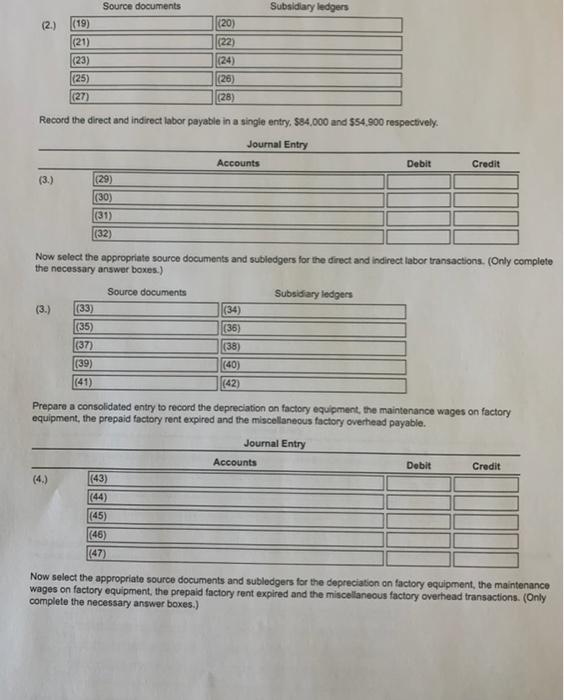
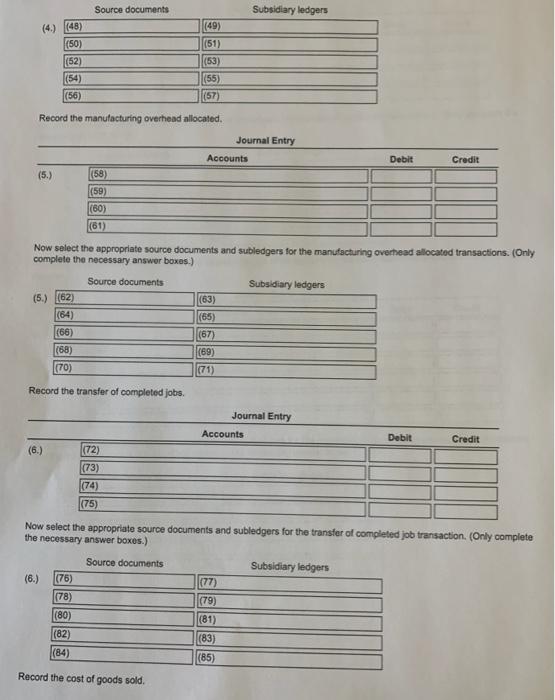
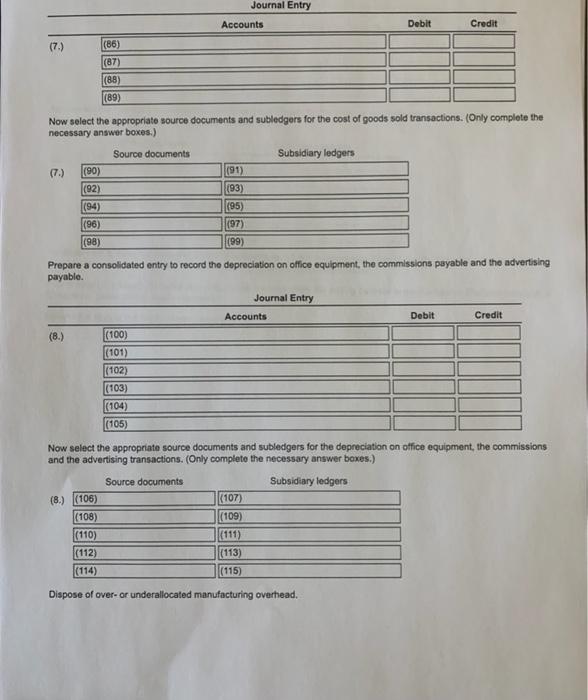
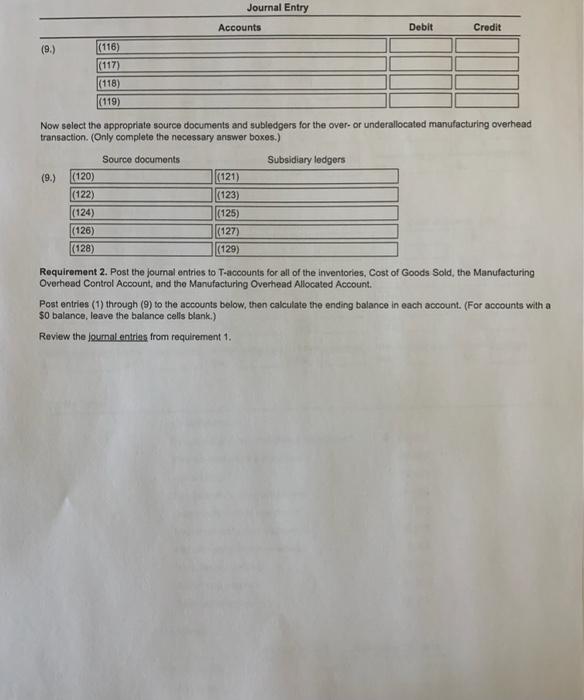
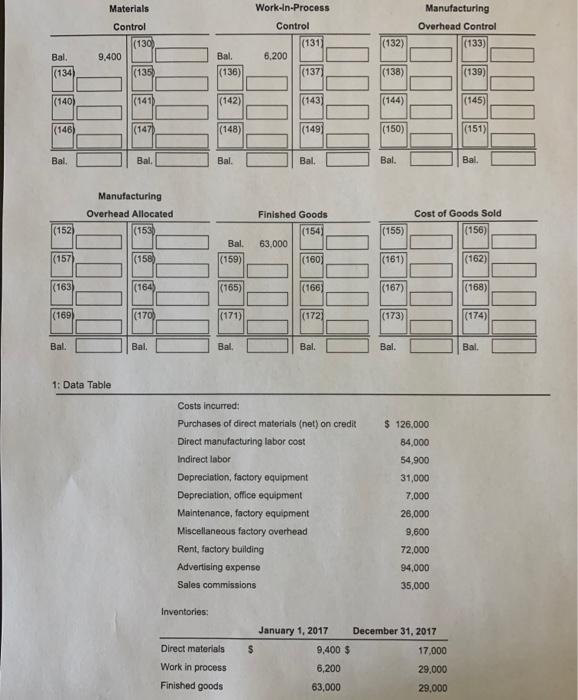


$ 126,000 84.000 54,900 31,000 Costs incurred: Purchases of direct materials (net) on credit Direct manufacturing labor cost Indirect labor Depreciation factory equipment Depreciation, office equipment Maintenance, factory equipment Miscellaneous factory overhead Rent, factory building Advertising expense Sales commissions 7,000 26,000 9,600 72,000 94,000 35,000 Inventories Direct materials EA January 1, 2017 December 31, 2017 9,400 $ 17,000 6,200 29,000 63,000 29,000 Work in process Finished goods 3. Construction Company produces gadgets for the coveted small appliance market. The following data reflect activity for the year 2017: (Click the icon to view the data.) Construction Co. uses a normal-costing system and allocates overhead to work in process at a rate of $3.20 per direct manufacturing labor dollar. Indirect materials are insignificant so there is no inventory account for indirect materials. Read the requirements? Requirement 1. Prepare journal entries to record the transactions for 2017 Including an entry to close out over-or underallocated overhead to cost of goods sold. For each journal entry indicate the source document that would be used to authorize each entry. Also note which subsidiary ledger , if any, should be referenced as backup for the entry. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from any journal entries.) Record the purchase of direct materials, S126,000 Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (1.) (1) (2) (3) (4) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the purchase of direct materials. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (1.) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13) (14) Record the direct materials used. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (2.) (15) (16) (17) (18) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the direct materials used. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (4) (48) (49) (50) (52) (54) (56) (51) (53) (55) (57) Record the manufacturing overhead allocated. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (5.) (58) (59) (60) (61) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the manufacturing overhead allocated transactions. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (5.) (62) (63) (64) (65) (68) (67) (68) (69) (70) (71) Record the transfer of completed jobs. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (6.) (72) (73) (74) (75) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the transfer of completed job transaction. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (6.) (76) (77) (78) (79) (80) (81) (82) (83) (84) (85) Record the cost of goods sold. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (7.) (86) (87) (88) (89) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the cost of goods sold transactions. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (7.) (90) (91) (92) (94) (93) (95) (96) (97) (99) (98) Prepare a consolidated entry to record the depreciation on office equipment, the commissions payable and the advertising payable. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (8.) (100) (101) (102) (103) (104) (105) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the depreciation on office equipment, the commissions and the advertising transactions. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (8.) (106) (108) (110) (112) (114) (107) (109) (111) (113) (115) Dispose of over- or underallocated manufacturing overhead. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (9.) (116) (117) (118) (119) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the over- or underallocated manufacturing overhead transaction. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (9.) (120) (121) (122) (123) (124) (125) |(126) (127) |(128) (129) Requirement 2. Post the journal entries to T-accounts for all of the inventories, Cost of Goods Sold, the Manufacturing Overhead Control Account, and the Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Account Post entries (1) through (9) to the accounts below, then calculate the ending balance in each account. (For accounts with a $0 balance, leave the balance cells blank.) Review the journal entries from requirement 1. Materials Control (130) 9.400 (135) Work-In-Process Control (131) 6,200 |(137) Manufacturing Overhead Control (133) (132) Bal. (134) Bal. (136) (138) (139) (140) (141) (142) (1431 (144) (145) (146) (147) (148) (149) (150) |(151) Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal Manufacturing Overhead Allocated (153) Cost of Goods Sold (156) (152) 55) Finished Goods (1541 63.000 (160) Bal. |(157) (158) (159) |(161) |(162) (163) (164) (165) |(166) (167) (168) (169) (170) (171) |(1721 (173) (174) Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal 1: Data Table $ 126,000 84,000 54,900 Costs incurred: Purchases of direct materials (net) on credit Direct manufacturing labor cost Indirect labor Depreciation, factory equipment Depreciation, office equipment Maintenance, factory equipment Miscellaneous factory overhead Rent, factory building Advertising expense Sales commissions 31,000 7.000 26,000 9.600 72,000 94,000 35,000 Inventories: $ Direct materials Work in process Finished goods January 1, 2017 December 31, 2017 9,400 $ 17.000 6,200 29,000 63,000 29,000 2: Requirements 1. Prepare journal entries to record the transactions for 2017 including an entry to close out over- or underallocated overhead to cost of goods sold. For each journal entry indicate the source document that would be used to authorize each entry. Also note which subsidiary ledger, if any, should be referenced as backup for the entry. 2. Post the journal entries to T-accounts for all of the inventories, Cost of Goods Sold, the Manufacturing Overhead Control Account, and the Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Account (1) O Cash Control Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Accounts Payable Control O Commission Expense Manufacturing Overhead Control Accumulated Depreciation Control Cost of Goods Sold Materials Control Advertising Expense O Finished Goods Control Office Depreciation Expense O Rent Payable Control Work-in-Process Control Revenues O Salary Expense O Wages Payable Control (2) O Cash Control O Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Accounts Payable Control Commission Expense O Manufacturing Overhead Control O Accumulated Depreciation Control Cost of Goods Sold Materials Control Advertising Expense Finished Goods Control Office Depreciation Expense Rent Payable Control Work-in-Process Control O Revenues O Salary Expense O Wages Payable Control (3) O Cash Control Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Accounts Payable Control O Commission Expense O Manufacturing Overhead Control Accumulated Depreciation Control O Cost of Goods Sold Materials Control Advertising Expense O Finished Goods Control Office Depreciation Expense O Rent Payable Control Work-in-Process Control Revenues O Salary Expense O Wages Payable Control Cash Control O Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Accounts Payable Control Commission Expense Manufacturing Overhead Control O Accumulated Depreciation Control Cost of Goods Sold Materials Control O Advertising Expense O Finished Goods Control Office Depreciation Expense O Rent Payable Control Work-in-Process Control O Revenues Salary Expense Wages Payable Control (5) O O materials requisition records payroll request O purchase invoice O receiving report rent schedule sales involces O sales proposal accounts receivable accounts payable cash O direct material records O employee labor records O material requisition records work-in-process inventory records by job (7) O receiving report materials requisition records Orent schedule O payroll request O sales invoices O purchase invoice Osales proposal (8) O direct material records accounts receivable employee labor records accounts payable material requisition records cash work-in-process inventory records by job (9) 0 000 O receiving report materials requisition records Orent schedule O payroll request sales invoices purchase invoice sales proposal 0 000 (10) O direct material records accounts receivable employee labor records accounts payable O material requisition records cash work-in-process inventory records by job (11) O O receiving report O materials requisition records Orent schedule O payroll request O sales invoices O purchase invoice Osales proposal (12) O direct material records accounts receivable employee labor records accounts payable O material requisition records cash work-in-process inventory records by job OOOO (13) O O receiving report O materials requisition records rent schedule payroll request Osales invoices O purchase invoice sales proposal O direct material records accounts receivable employee labor records O accounts payable O material requisition records cash work-in-process inventory records by job $ 126,000 84.000 54,900 31,000 Costs incurred: Purchases of direct materials (net) on credit Direct manufacturing labor cost Indirect labor Depreciation factory equipment Depreciation, office equipment Maintenance, factory equipment Miscellaneous factory overhead Rent, factory building Advertising expense Sales commissions 7,000 26,000 9,600 72,000 94,000 35,000 Inventories Direct materials EA January 1, 2017 December 31, 2017 9,400 $ 17,000 6,200 29,000 63,000 29,000 Work in process Finished goods 3. Construction Company produces gadgets for the coveted small appliance market. The following data reflect activity for the year 2017: (Click the icon to view the data.) Construction Co. uses a normal-costing system and allocates overhead to work in process at a rate of $3.20 per direct manufacturing labor dollar. Indirect materials are insignificant so there is no inventory account for indirect materials. Read the requirements? Requirement 1. Prepare journal entries to record the transactions for 2017 Including an entry to close out over-or underallocated overhead to cost of goods sold. For each journal entry indicate the source document that would be used to authorize each entry. Also note which subsidiary ledger , if any, should be referenced as backup for the entry. (Record debits first, then credits. Exclude explanations from any journal entries.) Record the purchase of direct materials, S126,000 Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (1.) (1) (2) (3) (4) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the purchase of direct materials. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (1.) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13) (14) Record the direct materials used. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (2.) (15) (16) (17) (18) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the direct materials used. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (4) (48) (49) (50) (52) (54) (56) (51) (53) (55) (57) Record the manufacturing overhead allocated. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (5.) (58) (59) (60) (61) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the manufacturing overhead allocated transactions. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (5.) (62) (63) (64) (65) (68) (67) (68) (69) (70) (71) Record the transfer of completed jobs. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (6.) (72) (73) (74) (75) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the transfer of completed job transaction. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (6.) (76) (77) (78) (79) (80) (81) (82) (83) (84) (85) Record the cost of goods sold. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (7.) (86) (87) (88) (89) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the cost of goods sold transactions. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (7.) (90) (91) (92) (94) (93) (95) (96) (97) (99) (98) Prepare a consolidated entry to record the depreciation on office equipment, the commissions payable and the advertising payable. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (8.) (100) (101) (102) (103) (104) (105) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the depreciation on office equipment, the commissions and the advertising transactions. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (8.) (106) (108) (110) (112) (114) (107) (109) (111) (113) (115) Dispose of over- or underallocated manufacturing overhead. Journal Entry Accounts Debit Credit (9.) (116) (117) (118) (119) Now select the appropriate source documents and subledgers for the over- or underallocated manufacturing overhead transaction. (Only complete the necessary answer boxes.) Source documents Subsidiary ledgers (9.) (120) (121) (122) (123) (124) (125) |(126) (127) |(128) (129) Requirement 2. Post the journal entries to T-accounts for all of the inventories, Cost of Goods Sold, the Manufacturing Overhead Control Account, and the Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Account Post entries (1) through (9) to the accounts below, then calculate the ending balance in each account. (For accounts with a $0 balance, leave the balance cells blank.) Review the journal entries from requirement 1. Materials Control (130) 9.400 (135) Work-In-Process Control (131) 6,200 |(137) Manufacturing Overhead Control (133) (132) Bal. (134) Bal. (136) (138) (139) (140) (141) (142) (1431 (144) (145) (146) (147) (148) (149) (150) |(151) Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal Manufacturing Overhead Allocated (153) Cost of Goods Sold (156) (152) 55) Finished Goods (1541 63.000 (160) Bal. |(157) (158) (159) |(161) |(162) (163) (164) (165) |(166) (167) (168) (169) (170) (171) |(1721 (173) (174) Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal. Bal 1: Data Table $ 126,000 84,000 54,900 Costs incurred: Purchases of direct materials (net) on credit Direct manufacturing labor cost Indirect labor Depreciation, factory equipment Depreciation, office equipment Maintenance, factory equipment Miscellaneous factory overhead Rent, factory building Advertising expense Sales commissions 31,000 7.000 26,000 9.600 72,000 94,000 35,000 Inventories: $ Direct materials Work in process Finished goods January 1, 2017 December 31, 2017 9,400 $ 17.000 6,200 29,000 63,000 29,000 2: Requirements 1. Prepare journal entries to record the transactions for 2017 including an entry to close out over- or underallocated overhead to cost of goods sold. For each journal entry indicate the source document that would be used to authorize each entry. Also note which subsidiary ledger, if any, should be referenced as backup for the entry. 2. Post the journal entries to T-accounts for all of the inventories, Cost of Goods Sold, the Manufacturing Overhead Control Account, and the Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Account (1) O Cash Control Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Accounts Payable Control O Commission Expense Manufacturing Overhead Control Accumulated Depreciation Control Cost of Goods Sold Materials Control Advertising Expense O Finished Goods Control Office Depreciation Expense O Rent Payable Control Work-in-Process Control Revenues O Salary Expense O Wages Payable Control (2) O Cash Control O Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Accounts Payable Control Commission Expense O Manufacturing Overhead Control O Accumulated Depreciation Control Cost of Goods Sold Materials Control Advertising Expense Finished Goods Control Office Depreciation Expense Rent Payable Control Work-in-Process Control O Revenues O Salary Expense O Wages Payable Control (3) O Cash Control Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Accounts Payable Control O Commission Expense O Manufacturing Overhead Control Accumulated Depreciation Control O Cost of Goods Sold Materials Control Advertising Expense O Finished Goods Control Office Depreciation Expense O Rent Payable Control Work-in-Process Control Revenues O Salary Expense O Wages Payable Control Cash Control O Manufacturing Overhead Allocated Accounts Payable Control Commission Expense Manufacturing Overhead Control O Accumulated Depreciation Control Cost of Goods Sold Materials Control O Advertising Expense O Finished Goods Control Office Depreciation Expense O Rent Payable Control Work-in-Process Control O Revenues Salary Expense Wages Payable Control (5) O O materials requisition records payroll request O purchase invoice O receiving report rent schedule sales involces O sales proposal accounts receivable accounts payable cash O direct material records O employee labor records O material requisition records work-in-process inventory records by job (7) O receiving report materials requisition records Orent schedule O payroll request O sales invoices O purchase invoice Osales proposal (8) O direct material records accounts receivable employee labor records accounts payable material requisition records cash work-in-process inventory records by job (9) 0 000 O receiving report materials requisition records Orent schedule O payroll request sales invoices purchase invoice sales proposal 0 000 (10) O direct material records accounts receivable employee labor records accounts payable O material requisition records cash work-in-process inventory records by job (11) O O receiving report O materials requisition records Orent schedule O payroll request O sales invoices O purchase invoice Osales proposal (12) O direct material records accounts receivable employee labor records accounts payable O material requisition records cash work-in-process inventory records by job OOOO (13) O O receiving report O materials requisition records rent schedule payroll request Osales invoices O purchase invoice sales proposal O direct material records accounts receivable employee labor records O accounts payable O material requisition records cash work-in-process inventory records by job















